Key Takeaways
- Central Bank Digital Currencies represent the digital evolution of fiat money, offering government-backed stability while enabling instant, traceable transactions that will fundamentally reshape how crypto exchanges operate.
- Digital currency exchanges are positioned to become critical infrastructure bridging traditional finance and cryptocurrency markets, facilitating seamless conversions between CBDCs and decentralized digital assets.
- The future of digital payments will be characterized by instant cross-border settlements, reduced transaction costs, and 24/7 availability as CBDCs integrate with existing crypto exchange infrastructure.
- Institutional crypto adoption is accelerating as CBDCs provide regulatory clarity and stable digital assets that complement volatile cryptocurrency investments in diversified portfolios.
- Global crypto regulations are converging around enhanced KYC/AML standards, transparent reporting mechanisms, and compliance frameworks that will apply equally to CBDC and cryptocurrency transactions.
- Crypto exchanges must proactively develop technical infrastructure, establish central bank partnerships, and implement flexible compliance systems to remain competitive in the CBDC-integrated financial ecosystem.
- Cross-border digital payments will transform from multi-day processes costing 5-7% in fees to near-instant settlements with minimal costs as CBDC networks interconnect through crypto exchange platforms.
- The regulatory landscape for crypto exchanges will evolve from fragmented national approaches to internationally coordinated standards as CBDCs create pressure for harmonized digital asset governance.
The convergence of cryptocurrency exchanges and Central Bank Digital Currencies marks a pivotal transformation in global finance. As an agency with over 8 years of experience developing blockchain infrastructure and cryptocurrency exchange platforms, we have witnessed the evolution from purely decentralized crypto markets to an emerging hybrid ecosystem where government-backed digital currencies coexist with permissionless cryptocurrencies. This comprehensive analysis explores how crypto exchanges are adapting to the CBDC era and what this means for the future of digital payments.
Central Bank Digital Currencies represent more than technological upgrades to existing payment systems. They signal a fundamental reimagining of money itself, combining the efficiency and programmability of cryptocurrencies with the stability and regulatory oversight of traditional fiat currencies. For cryptocurrency exchanges, CBDCs present both unprecedented opportunities and complex challenges that will define the next decade of digital asset markets. Understanding how these parallel systems will interact is essential for exchange operators, investors, and regulators navigating this transformative period.
Understanding Crypto Exchanges and Central Bank Digital Currencies
What Are Crypto Exchanges?
Cryptocurrency exchange platforms serve as digital marketplaces where users buy, sell, and trade digital assets. These platforms have evolved from simple peer-to-peer trading venues into sophisticated financial infrastructure supporting millions of daily transactions across hundreds of cryptocurrencies. Modern exchanges provide order matching, custody services, liquidity provision, and increasingly, advanced financial products like derivatives and lending.
The cryptocurrency exchange ecosystem divides into two primary categories: centralized and decentralized platforms. Centralized exchanges operate under corporate management, maintaining custody of user funds and providing streamlined user experiences similar to traditional brokerage platforms. Examples include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken, which collectively process billions in daily trading volume. These platforms offer high liquidity, fiat currency on-ramps, and regulatory compliance infrastructure that appeals to mainstream users and institutional investors.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operate through smart contracts on blockchain networks, enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. Users maintain custody of their assets throughout the trading process, interacting directly with liquidity pools rather than centralized order books. Platforms like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap exemplify this model, prioritizing user autonomy and censorship resistance. While DEXs offer greater privacy and control, they typically feature lower liquidity and more complex user experiences compared to centralized alternatives. For businesses exploring these opportunities, partnering with experienced cryptocurrency exchange development experts ensures robust and compliant platform architecture.
Introduction to Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Digital fiat currencies, commonly known as CBDCs, represent government-issued digital money that exists exclusively in electronic form. Unlike cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are centralized, meaning central banks maintain complete control over issuance, distribution, and monetary policy. Each CBDC unit maintains a fixed one-to-one relationship with the corresponding physical currency, ensuring price stability and eliminating the volatility characteristic of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
CBDCs leverage distributed ledger technology to enable instant settlements, enhanced traceability, and programmable money features while preserving central bank authority over monetary policy. The technology enables central banks to implement negative interest rates, distribute stimulus payments instantly, and monitor money flows in real-time for economic planning purposes. This represents a fundamental shift from anonymous cash transactions to fully traceable digital payments, raising important privacy considerations that different jurisdictions address through varying architectural choices.
Key global examples demonstrate diverse approaches to CBDC implementation. China’s digital yuan (e-CNY) leads in scale, with pilots across major cities serving millions of users in retail and wholesale applications. The Bahamas’ Sand Dollar became the world’s first fully deployed CBDC in 2020, focusing on financial inclusion across the island nation’s dispersed geography. Sweden’s e-krona project addresses declining cash usage in one of the world’s most cashless societies. The European Central Bank’s digital euro development aims to preserve monetary sovereignty as private stablecoins and foreign CBDCs gain traction. India, Nigeria, and numerous other nations have launched or announced CBDC initiatives, creating a global race toward digital currency adoption.
How Crypto Exchanges Interact with CBDCs
The integration of CBDCs into cryptocurrency exchanges creates multiple touchpoints between government-issued digital currencies and decentralized assets. Exchanges can function as CBDC distribution channels, allowing users to acquire digital fiat directly from their trading accounts without traditional banking intermediaries. This streamlines the fiat on-ramp process, reducing friction for new cryptocurrency investors and potentially expanding the addressable market for digital assets.
CBDC integration enables instant settlement for cryptocurrency purchases, eliminating the multi-day clearing periods currently required for bank transfers. Users could deposit CBDCs into exchange wallets and immediately begin trading, with withdrawals settling back to CBDC wallets in seconds rather than hours or days. This velocity improvement enhances capital efficiency and makes cryptocurrency markets more accessible to traders who cannot afford to have funds locked in transit.
The fundamental differences between CBDCs and cryptocurrencies create complementary use cases within exchange ecosystems. CBDCs offer price stability, government backing, and regulatory clarity, making them ideal for storing value between trades, facilitating payments, and serving as quote currencies for trading pairs. Cryptocurrencies provide decentralization, censorship resistance, and investment opportunities through price appreciation. Exchanges that successfully integrate both enable users to optimize between stability and growth potential, holding CBDCs for predictable value storage while speculating on cryptocurrencies for potential returns.
The Role of Digital Currency Exchanges in Modern Finance
Growth and Popularity of Digital Currency Exchanges
Digital currency exchanges have experienced explosive growth over the past decade, evolving from niche platforms serving early cryptocurrency enthusiasts to mainstream financial infrastructure attracting retail and institutional participants. Global trading volumes on cryptocurrency exchanges exceeded $60 trillion in 2023, surpassing many traditional asset classes and demonstrating the sector’s maturation. User bases have expanded from millions to hundreds of millions, with major exchanges reporting 50 million or more registered accounts.
Retail investor adoption has surged as cryptocurrency awareness has penetrated mainstream consciousness. Simplified user interfaces, mobile applications, and educational resources have lowered barriers to entry, enabling non-technical users to participate in digital asset markets. The 2020-2021 bull market accelerated retail adoption, bringing cryptocurrency discussions into everyday conversations and financial planning considerations. Social media influence, celebrity endorsements, and FOMO-driven participation expanded the retail investor base dramatically.
Institutional crypto adoption represents perhaps the most significant trend reshaping digital currency exchanges. Hedge funds, asset managers, family offices, and even publicly traded corporations have allocated portions of their portfolios to cryptocurrencies. This institutional participation demands sophisticated trading infrastructure, regulatory compliance, custody solutions, and market depth that only well-capitalized exchanges can provide. The institutional influx has professionalized cryptocurrency markets, reducing volatility and establishing cryptocurrencies as a legitimate asset class within diversified investment portfolios.
Benefits of Using Digital Currency Exchanges
Liquidity stands as the primary benefit digital currency exchanges provide to market participants. High-volume exchanges offer tight bid-ask spreads, enabling traders to execute large orders with minimal price impact. This liquidity attracts more participants in a virtuous cycle, as traders gravitate toward platforms where they can enter and exit positions efficiently. Market depth allows institutional investors to deploy significant capital without moving markets, a crucial consideration for large-scale cryptocurrency adoption.
Accessibility represents another critical advantage, with digital currency exchanges operating 24/7/365 without the market hours restrictions of traditional stock exchanges. Users can trade from anywhere with internet access, democratizing financial market participation globally. This constant availability aligns with cryptocurrency’s borderless nature and supports users across all time zones. Mobile applications extend accessibility further, enabling trading from smartphones and tablets.
Transaction speed on digital currency exchanges vastly exceeds traditional banking systems. Cryptocurrency deposits and withdrawals settle in minutes rather than the days required for international wire transfers. Trades execute in milliseconds, allowing rapid response to market movements. When CBDCs integrate, settlement speeds will approach instantaneous for all transactions, eliminating counterparty risk and improving capital efficiency. Compared to traditional banking systems that operate on batch processing and multi-day clearing cycles, digital currency exchanges represent the future of real-time finance.
Challenges for Digital Currency Exchanges
Security concerns remain paramount for digital currency exchanges, which manage billions in customer assets and face constant threats from sophisticated attackers. Exchange hacks have resulted in hundreds of millions in losses, eroding user trust and attracting regulatory scrutiny. Cold storage solutions, multi-signature wallets, insurance funds, and security audits have improved protection, but the risk persists. As exchanges integrate CBDCs, security standards must meet or exceed traditional banking requirements given the government-backing of these digital assets.
Regulatory hurdles create ongoing challenges as global crypto regulations evolve across different jurisdictions. Exchanges must navigate conflicting requirements for licensing, customer verification, reporting, and operational practices. Some jurisdictions embrace cryptocurrency innovation with clear regulatory frameworks, while others impose restrictive policies or outright bans. This fragmentation forces exchanges to either limit geographic availability or maintain complex compliance programs spanning multiple regulatory regimes. CBDC integration may accelerate regulatory harmonization as governments recognize the need for internationally coordinated digital currency standards.
Future of Digital Payments in the Era of CBDCs
How Central Bank Digital Currencies Will Shape Payments
The future of digital payments will be defined by the speed, efficiency, and programmability that CBDCs enable. Cross-border digital payments currently suffer from high costs, slow settlement times, and complex intermediary chains involving multiple banks and clearing systems. CBDCs can eliminate these inefficiencies by enabling direct central bank-to-central bank transfers or through interoperable CBDC networks that settle transactions in seconds rather than days.
Transaction costs for international payments average 5-7% for remittances and 1-3% for commercial transfers when accounting for foreign exchange spreads and intermediary fees. CBDC networks could reduce these costs to fractions of a percent by removing intermediaries and enabling real-time foreign exchange settlement. This cost reduction would particularly benefit developing nations where remittances constitute significant portions of GDP, directly improving living standards for millions of families.
Reduced reliance on physical cash represents another transformative impact of CBDCs on payment systems. Cash handling, storage, and transportation cost economies billions annually while creating security risks and facilitating illicit activities. Digital fiat currencies eliminate these inefficiencies while preserving the accessibility and government backing that make cash attractive to users who distrust or cannot access traditional banking. CBDCs can provide financial inclusion to unbanked populations through mobile-based digital wallets, extending formal financial services to previously excluded communities.
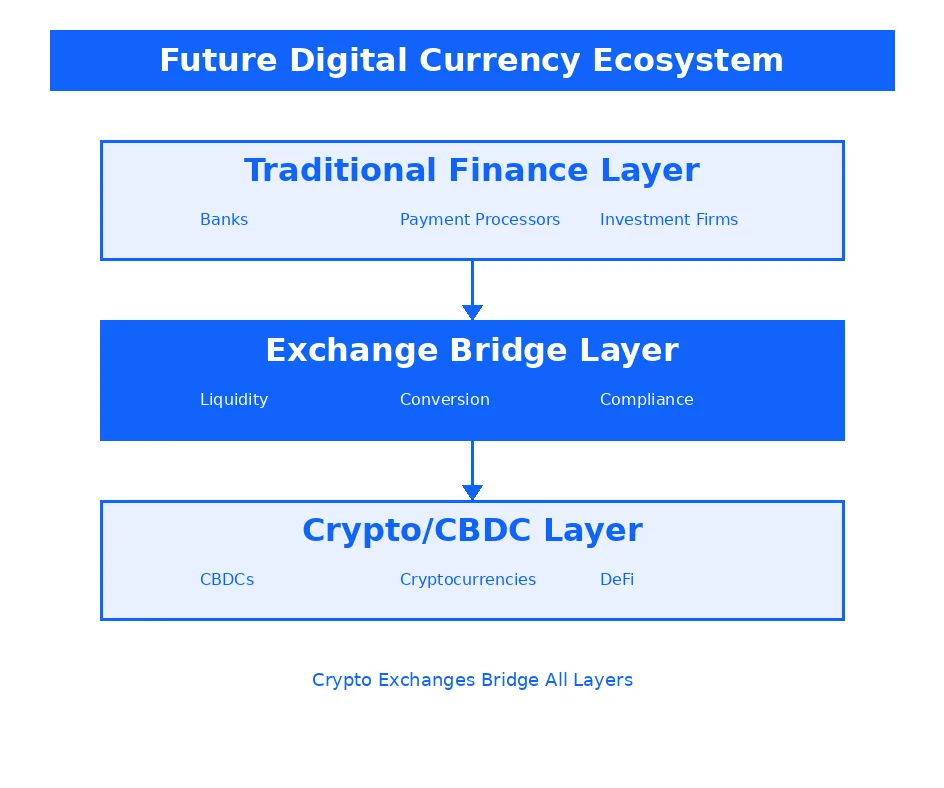
Role of Crypto Exchanges in Facilitating Future Payments
Crypto exchanges are uniquely positioned to bridge the gap between crypto and fiat CBDCs, serving as conversion points where users can seamlessly move value between government-issued digital currencies and decentralized cryptocurrencies. This intermediary role transforms exchanges from pure trading platforms into comprehensive digital financial hubs offering payments, remittances, savings, and investment services. The technical infrastructure exchanges have developed for handling cryptocurrency transactions translates directly to CBDC processing, providing operational advantages over traditional financial institutions.
Institutional crypto adoption trends accelerate as CBDCs provide regulatory clarity and stable digital assets that institutions can confidently integrate into treasury management and payment workflows. Corporations can hold CBDC reserves for operational liquidity while maintaining cryptocurrency positions for investment diversification. Crypto exchanges facilitate this institutional participation through custody services, OTC trading desks, and advanced order types that meet institutional requirements. The legitimacy CBDCs confer on digital asset markets generally may reduce institutional hesitation around cryptocurrency investment.
Case Study: Countries Pioneering CBDC Adoption
China’s digital yuan (e-CNY) provides the most comprehensive example of CBDC deployment at scale. Launched in pilot form in 2020, the e-CNY has expanded to over 260 million wallets processing hundreds of billions of yuan in transactions. The system integrates with existing payment platforms like WeChat Pay and Alipay while offering offline transaction capabilities through NFC technology. For crypto exchanges, China’s approach demonstrates how CBDCs can coexist with private payment systems, suggesting integration models that preserve exchange functionality while incorporating government digital currencies.
Sweden’s e-krona project addresses the unique challenge of declining cash usage in an increasingly cashless society. With cash transactions representing less than 10% of retail payments, Sweden faces a future where private payment providers could dominate the payment infrastructure. The e-krona aims to preserve public access to central bank money in digital form, ensuring monetary sovereignty and payment system resilience. This case illustrates how CBDCs serve strategic purposes beyond technological modernization, protecting national interests in digital payment ecosystems.
The Bahamas’ Sand Dollar demonstrates CBDC potential for financial inclusion in geographically dispersed populations. With 30 inhabited islands spread across 100,000 square miles of ocean, traditional banking infrastructure proves costly and inefficient. The Sand Dollar enables all residents to access digital payments via mobile phones, reducing reliance on physical cash and improving economic participation for remote communities. For crypto exchanges, this highlights how CBDCs can expand addressable markets by bringing unbanked populations into digital finance ecosystems where they can access both government currencies and cryptocurrencies.
| Phase | Timeline | Key Activities | Exchange Preparation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBDC Research | 1-2 years | Central bank exploration, technology assessment, policy design | Monitor developments, engage with regulators |
| Pilot Programs | 1-3 years | Limited deployment, testing infrastructure, user trials | Develop integration prototypes, establish partnerships |
| Limited Launch | 6-12 months | Regional deployment, gradual user onboarding | Beta CBDC integration, compliance implementation |
| Full Deployment | Ongoing | National availability, international connectivity | Full CBDC support, cross-border functionality |
| Ecosystem Maturation | 2-5 years | Advanced features, international coordination | Innovation layer development, DeFi integration |
Regulatory Landscape for Crypto Exchanges and CBDCs
Global Crypto Regulations Affecting Exchanges
The regulatory landscape for crypto exchanges varies dramatically across jurisdictions, creating complex compliance challenges for platforms operating internationally. The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation establishes comprehensive standards for cryptocurrency services, requiring licensing, capital requirements, and consumer protection measures. This framework aims to provide regulatory clarity while fostering innovation, potentially serving as a model for other jurisdictions.
The United States employs a fragmented regulatory approach with oversight divided among the SEC, CFTC, FinCEN, and state regulators. This creates uncertainty as different agencies assert jurisdiction over various aspects of cryptocurrency exchange operations. Some states like Wyoming and Texas have implemented crypto-friendly regulations, while others maintain restrictive stances. Federal legislation may eventually harmonize these approaches, particularly as CBDCs create pressure for nationally consistent digital asset policies.
Asian jurisdictions demonstrate diverse regulatory philosophies. Singapore and Hong Kong have established clear frameworks encouraging exchange operations under robust oversight. Japan requires exchange licensing and maintains strict consumer protection standards following high-profile hacks. China’s approach combines CBDC promotion with cryptocurrency trading restrictions, illustrating how CBDC adoption does not necessarily correlate with broader crypto acceptance. These varying approaches require exchanges to maintain flexible compliance systems adaptable to different regulatory environments.
Crypto Exchanges Regulation and Compliance Challenges
Anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements form the foundation of crypto exchange regulation globally. Exchanges must verify user identities, monitor transactions for suspicious activity, report large or unusual transfers, and maintain detailed records for regulatory inspection. These requirements mirror traditional financial institution obligations, reflecting regulatory intent to bring cryptocurrency markets under existing financial crime prevention frameworks.
Implementation challenges arise from the pseudonymous nature of blockchain transactions and the global accessibility of cryptocurrency markets. Exchanges must balance regulatory compliance with user privacy expectations and operational efficiency. Advanced analytics tools help identify suspicious patterns while automated KYC systems streamline user onboarding. As CBDC integration progresses, exchanges may benefit from CBDCs’ built-in compliance features, which can automatically enforce transaction limits and reporting requirements at the protocol level.
Tax implications for digital currency exchanges create additional compliance complexity. Users must report cryptocurrency gains and losses for tax purposes, but calculating cost basis across multiple transactions, airdrops, and staking rewards proves challenging. Exchanges increasingly provide tax reporting tools and transaction histories formatted for tax preparation software. CBDC integration may simplify tax compliance by providing clear fiat valuation points for cryptocurrency transactions, reducing ambiguity in gain/loss calculations.
Preparing for Future Regulations
Crypto exchanges can adapt to CBDC integration and evolving regulations through proactive compliance infrastructure development. This includes implementing flexible KYC systems that can accommodate varying jurisdictional requirements, establishing real-time transaction monitoring capable of handling both cryptocurrency and CBDC flows, and developing reporting mechanisms that satisfy both crypto-specific regulations and traditional financial oversight. Early engagement with central banks and regulators positions exchanges as collaborative partners rather than regulatory targets.
Transparent reporting and audit mechanisms build trust with regulators and users alike. Regular third-party audits of reserves, published proof-of-reserves demonstrating 1:1 backing of customer deposits, and clear disclosures about fee structures and risk factors establish exchanges as responsible financial service providers. As CBDCs blur lines between traditional finance and cryptocurrency markets, exchanges that demonstrate commitment to transparency will gain competitive advantages in attracting both users and regulatory approval.
Institutional Crypto Adoption and the CBDC Impact
Why Institutions Are Embracing Crypto Exchanges
Digital asset diversification offers institutions portfolio optimization opportunities through exposure to assets with low correlation to traditional markets. Cryptocurrencies have demonstrated the potential for significant returns while behaving independently of stocks, bonds, and commodities during various market cycles. This diversification benefit attracts institutional allocators seeking to improve risk-adjusted returns.
Risk management strategies for institutional cryptocurrency exposure have matured significantly. Regulated custody solutions from established financial institutions, comprehensive insurance products, and sophisticated hedging instruments enable institutions to manage cryptocurrency risk within existing investment frameworks. Derivative markets provide tools for controlling downside exposure while maintaining upside potential. These risk management capabilities transform cryptocurrencies from speculative gambles into legitimate portfolio components.
CBDCs and Institutional Investment Opportunities
Partnerships between traditional banks and crypto exchanges create pathways for institutional capital to enter cryptocurrency markets while maintaining regulatory comfort. Banks provide fiat currency infrastructure and compliance expertise while exchanges offer cryptocurrency market access and custody services. These collaborations enable seamless movement between traditional finance and digital assets, reducing friction for institutional participants. Keeping pace with the dynamic cryptocurrency exchange market expansion requires institutions to establish these strategic partnerships.
The integration of digital fiat currencies in investment portfolios provides stable, government-backed assets that complement volatile cryptocurrency holdings. Institutions can maintain CBDC positions for liquidity management and predictable returns while allocating portions of portfolios to cryptocurrencies for growth potential. This combination optimizes risk-return profiles and enables dynamic rebalancing between stability and appreciation opportunities. CBDCs also serve as efficient collateral for cryptocurrency derivatives and lending, improving capital efficiency across institutional trading strategies.
Future Trends in Institutional Crypto Adoption
Over the next 5 to 10 years, institutional crypto adoption will likely expand from hedge funds and family offices to mainstream pension funds, endowments, and insurance companies. Regulatory clarity around CBDCs will accelerate this trend by establishing precedents for digital asset oversight and demonstrating government comfort with blockchain-based financial infrastructure. Improved custody solutions, deeper liquidity, and standardized investment vehicles like ETFs will further reduce barriers to institutional participation.
The impact on liquidity and market stability could prove transformative. Institutional participation typically reduces volatility as professional investors employ disciplined strategies rather than emotional trading. Deeper liquidity enables larger transactions with less price impact, attracting additional institutional capital in a virtuous cycle. However, institutions also bring sophisticated trading strategies that could introduce new forms of market dynamics. Overall, institutional adoption combined with CBDC integration promises to mature cryptocurrency markets toward stability levels approaching traditional asset classes.
Cross-Border Digital Payments and Global Crypto Exchanges
How CBDCs Enable Seamless International Payments
Reducing settlement times represents one of the most significant benefits CBDCs offer for international payments. Current cross-border transfers require 3 to 5 business days for settlement as funds move through correspondent banking networks with manual reconciliation at each step. CBDC networks can settle transactions in seconds through direct central bank clearing or interconnected CBDC platforms, eliminating intermediary delays entirely. This speed improvement transforms business operations by enabling just-in-time payments and reducing working capital requirements.
Transaction fee reduction follows naturally from removing intermediaries. Each bank and payment processor in the current cross-border payment chain extracts fees, resulting in total costs of 5-7% for retail remittances and 1-3% for commercial transfers. CBDC direct settlement eliminates most intermediaries, potentially reducing fees to fractions of a percent. Foreign exchange spreads also narrow as real-time CBDC markets enable competitive pricing without multi-day forward contracts. These cost savings directly benefit consumers and businesses, particularly in developing nations where remittance fees consume significant portions of family incomes.
Enhancing financial inclusion represents a broader impact of CBDC-enabled cross-border payments. Mobile-based CBDC wallets require only internet connectivity, bypassing the need for traditional bank accounts with their documentation requirements, minimum balances, and fees. This accessibility brings billions of unbanked individuals into formal financial systems where they can receive international payments, access credit, and build financial histories. Crypto exchanges can serve these newly included populations by offering cryptocurrency investment opportunities alongside CBDC payment services.

The Role of Crypto Exchanges in Facilitating Cross-Border Transactions
Case examples of international crypto transactions demonstrate how exchanges already facilitate cross-border value transfer more efficiently than traditional banking. Cryptocurrency remittances to Latin America, Africa, and Asia have grown dramatically as workers send earnings home through cryptocurrency exchanges, avoiding high wire transfer fees. Recipients can either convert to local currency through local exchanges or hold cryptocurrencies as inflation hedges. Transaction times of minutes rather than days and fees of 1-2% versus 5-7% make cryptocurrency remittances increasingly attractive.
Potential collaboration with central banks could position crypto exchanges as distribution and conversion points for CBDCs in cross-border contexts. Exchanges could offer CBDC-to-cryptocurrency and CBDC-to-CBDC conversion services, enabling travelers, businesses, and investors to move seamlessly between different national digital currencies and cryptocurrencies. This intermediary role leverages exchanges’ existing infrastructure for handling multiple currencies and processing high-volume transactions. Central banks benefit from exchange market-making capabilities and established user bases, while exchanges gain legitimacy and new revenue streams.
Challenges and Risks
Regulatory discrepancies across countries create challenges for cross-border CBDC integration through crypto exchanges. Different jurisdictions will implement varying CBDC architectures, privacy protections, and access controls. Exchanges operating internationally must navigate these differences while maintaining consistent user experiences. Some nations may restrict CBDC convertibility to cryptocurrencies for capital control purposes, limiting exchange functionality. Harmonizing CBDC regulations internationally will prove essential for realizing the full potential of seamless cross-border digital payments.
Security and fraud concerns intensify as CBDCs integrate with cryptocurrency networks. Bridges between different blockchain systems create potential attack vectors where hackers could exploit vulnerabilities to steal CBDCs or cryptocurrencies. Exchanges must implement robust security measures including multi-signature wallets, real-time fraud detection, and comprehensive insurance to protect CBDC transactions. The government-backing of CBDCs raises stakes compared to purely cryptocurrency transactions, as CBDC security failures could undermine confidence in government-issued digital currencies themselves.
| Feature | Traditional Cryptocurrencies | Central Bank Digital Currencies |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Decentralized protocol/community | Central bank/government |
| Price Stability | Volatile, market-determined | Stable, pegged to fiat |
| Privacy | Pseudonymous to anonymous | Varies by design, potentially traceable |
| Regulatory Status | Evolving, varies by jurisdiction | Clear legal tender status |
| Monetary Policy | Algorithmic, predetermined | Central bank controlled |
| Primary Use Case | Investment, speculation, payments | Payments, monetary policy |
| Programmability | Smart contracts, DeFi | Limited, policy-driven features |
The Future of Crypto Exchanges in a CBDC-Driven World
Predicting the Evolution of Digital Currency Exchanges
The transformation of crypto exchanges from speculative trading platforms to comprehensive payment hubs represents a fundamental shift in their value proposition. As CBDCs enable instant settlements and reduce friction for everyday transactions, exchanges will evolve to support merchant payments, peer-to-peer transfers, and bill pay services alongside traditional trading functions. This evolution mirrors how PayPal and other payment processors expanded from simple money transfer services to full-featured financial platforms.
Integration of advanced technologies like DeFi protocols and smart contracts will unlock new capabilities for exchanges. Automated market makers could provide liquidity for CBDC-cryptocurrency pairs without traditional order books. Smart contract-based lending could offer instant loans collateralized by CBDC or cryptocurrency holdings. Yield farming opportunities might emerge where users earn returns on CBDC deposits through liquidity provision. These DeFi integrations transform exchanges into financial innovation laboratories where traditional finance and cryptocurrency converge.
Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
Balancing innovation with regulatory compliance will define successful exchanges in the CBDC era. Regulatory frameworks will tighten as CBDCs blur lines between cryptocurrency and traditional finance, requiring exchanges to implement comprehensive compliance programs. However, regulation also provides legitimacy and reduces uncertainty, potentially accelerating mainstream adoption. Exchanges that proactively engage with regulators and build robust crypto exchange compliance infrastructure will thrive, while those resisting oversight face existential risks.
The potential for institutional adoption and mass-market use expands dramatically as CBDCs validate digital currency infrastructure. Mainstream financial institutions may partner with or acquire cryptocurrency exchanges to access CBDC distribution channels and cryptocurrency trading capabilities. Retail adoption could surge as CBDCs normalize digital currency usage, reducing psychological barriers to cryptocurrency investment. This mainstream acceptance would fulfill cryptocurrency’s original vision of democratizing finance while preserving the innovation and freedom that characterized the industry’s early days.
Build Your Future-Ready Crypto Exchange Today
Partner with experts to develop secure, scalable crypto exchanges integrated with CBDCs for instant settlements and seamless digital payments.
Conclusion
The convergence of crypto exchanges and Central Bank Digital Currencies represents a defining moment in financial history. As governments worldwide develop and deploy CBDCs, cryptocurrency exchanges are evolving from niche trading platforms into critical infrastructure bridging traditional finance, government digital currencies, and decentralized cryptocurrencies. This transformation promises to accelerate institutional crypto adoption, streamline cross-border digital payments, and fundamentally reshape the future of digital payments.
With over 8 years of experience in blockchain development and cryptocurrency exchange architecture, we have witnessed the industry’s maturation from experimental technology to mainstream financial infrastructure. The regulatory landscape for crypto exchanges will continue evolving as global crypto regulations converge around enhanced compliance standards, but this evolution creates opportunities for platforms that proactively prepare for CBDC integration and demonstrate commitment to transparency and user protection.
The future of crypto exchanges in a CBDC-driven world is not one of displacement but integration. Exchanges that successfully navigate this transition will emerge as essential components of the digital economy, facilitating seamless movement between stability and growth, government control and individual sovereignty, traditional finance and cryptocurrency innovation. For stakeholders across the ecosystem, understanding and preparing for this convergence is essential to capturing the opportunities ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
Central Bank Digital Currencies are digital forms of a country’s fiat currency issued and regulated by the central bank. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, CBDCs are centralized, government-backed, and designed to maintain the same value as physical cash. They represent the digitalization of traditional money, offering faster transactions, improved traceability, and enhanced monetary policy implementation while maintaining central bank control over the money supply.
Crypto exchanges can serve as platforms where users convert CBDCs to cryptocurrencies and vice versa, similar to how they currently handle fiat-to-crypto conversions. As CBDCs become more prevalent, exchanges will likely integrate CBDC payment rails, enabling instant settlements and reducing reliance on traditional banking infrastructure. This integration creates a bridge between government-issued digital currencies and decentralized cryptocurrencies, potentially expanding the user base for both.
CBDCs will not replace cryptocurrencies but rather coexist alongside them on digital currency exchanges. While CBDCs offer stability and government backing, cryptocurrencies provide decentralization, privacy features, and investment opportunities. Exchanges will likely offer both, allowing users to hold stable digital fiat for payments while trading cryptocurrencies for investment purposes. The two serve different functions within the broader digital asset ecosystem.
The primary regulatory challenges include navigating varying CBDC regulations across different jurisdictions, implementing enhanced KYC and AML procedures for CBDC transactions, ensuring compliance with cross-border payment regulations, managing tax reporting requirements for CBDC-crypto conversions, and adapting to evolving central bank policies. Exchanges must build flexible compliance frameworks that can accommodate both traditional crypto regulations and emerging CBDC-specific requirements.
CBDCs will significantly streamline cross-border payments by reducing settlement times from days to seconds, lowering transaction fees through direct central bank clearing, eliminating currency conversion intermediaries, and providing 24/7 availability. Crypto exchanges can leverage CBDCs to offer faster international remittances, improved liquidity for global trading pairs, and more efficient arbitrage opportunities across markets, fundamentally transforming how value moves across borders.
China leads with its digital yuan (e-CNY) already in widespread pilot use across multiple cities. The Bahamas launched the Sand Dollar as the first fully deployed CBDC. Sweden’s e-krona is in advanced testing phases. Other significant developments include the European Central Bank’s digital euro project, India’s digital rupee pilots, and Nigeria’s eNaira. These early adopters provide valuable insights for how crypto exchanges should prepare for CBDC integration.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







