Key Takeaways
- BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem emerged from the 2018 Bitcoin Cash hard fork, positioning itself as the closest implementation to Satoshi’s original vision.
- Bitcoin SV removes block size limits entirely, enabling theoretically unlimited transaction throughput for enterprise-scale applications and data storage.
- Transaction fees on BSV in Bitcoin remain extremely low, often below one cent, making micropayments and high-volume applications economically viable.
- The restored Bitcoin Script opcodes enable smart contract functionality, token issuance, and complex conditional transactions on the BSV network.
- Enterprise adoption represents a core focus for BSV in Bitcoin, targeting businesses requiring regulatory compliance, stable protocols, and scalable infrastructure.
- Mining economics on BSV in Bitcoin depend heavily on transaction fees rather than block subsidies as the network scales to handle massive transaction volumes.
- BSV in Bitcoin faces significant challenges including limited exchange listings, controversial leadership associations, and smaller community compared to Bitcoin.
- Data storage applications on BSV in Bitcoin include supply chain tracking, digital identity systems, and immutable record keeping for enterprise clients.
- Protocol stability is a defining characteristic of BSV in Bitcoin, with the aim of providing businesses predictable infrastructure without frequent changes.
- The future of BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem depends on enterprise adoption success, regulatory clarity, and ability to demonstrate real-world utility.
Understanding Bitcoin SV Within the Broader Bitcoin Landscape
Bitcoin SV represents one of several implementations claiming connection to the original Bitcoin protocol, each offering distinct approaches to scaling, governance, and utility. Understanding BSV in Bitcoin context requires examining how different factions within the cryptocurrency community interpreted Satoshi Nakamoto’s vision and made divergent technical decisions. The resulting landscape includes Bitcoin (BTC), Bitcoin Cash (BCH), and Bitcoin SV (BSV), each serving different use cases and communities across global markets including USA, UK, UAE, and Canada.
Our agency has spent over eight years analyzing blockchain ecosystems and helping clients navigate the complex relationships between Bitcoin variants. This experience informs our understanding of how BSV fits within the broader cryptocurrency landscape and its potential applications for enterprise clients. The network’s integration with Decentralized Exchange platforms and other blockchain infrastructure demonstrates its technical compatibility despite community divisions.
BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem occupies a unique position emphasizing massive scalability, regulatory compliance, and enterprise utility rather than the store-of-value narrative dominant in Bitcoin communities. This positioning creates both opportunities and challenges for adoption across different market segments.
How Bitcoin SV Interprets the Original Bitcoin Whitepaper
BSV in Bitcoin variants claims the closest alignment with Satoshi Nakamoto’s original vision as expressed in the 2008 whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” This interpretation emphasizes the “electronic cash” description, arguing that Bitcoin was intended for everyday transactions at global scale rather than primarily as digital gold or store of value. BSV proponents point to early forum posts and communications attributed to Satoshi discussing massive scaling.
The whitepaper interpretation extends to technical decisions including the removal of artificial limits on block sizes that BSV considers later additions not part of the original design. Critics argue this interpretation is selective and ignores practical limitations Satoshi implemented. The debate highlights how different readings of foundational documents can produce divergent technical and philosophical approaches within cryptocurrency communities.
Enterprise clients across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada evaluating BSV in Bitcoin options must consider these philosophical foundations and their practical implications for long-term protocol stability and ecosystem support.
BSV’s Approach to On-Chain Scaling and Large Block Sizes
On-chain scaling represents the most distinctive technical characteristic of BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem. While Bitcoin maintains a 1MB base block size with SegWit extensions and Bitcoin Cash uses 32MB blocks, BSV has removed all protocol-level block size limits. This approach enables theoretically unlimited transaction throughput, with the network having processed blocks exceeding 4GB in testing environments.
| Network | Block Size | TPS Capacity | Scaling Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | 1-4 MB | 7-10 TPS | Layer 2 Solutions |
| Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | 32 MB | 100+ TPS | Moderate On-Chain |
| Bitcoin SV (BSV) | Unlimited | 50,000+ TPS | Full On-Chain |
| Visa Network | N/A | 24,000 TPS | Centralized |
Transaction Throughput and Network Performance on Bitcoin SV
BSV in Bitcoin network has demonstrated significant transaction throughput capabilities during stress tests and actual network usage periods. The network has processed over 50,000 transactions per second in testing scenarios, far exceeding the capacity of Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash. This throughput enables use cases impossible on more constrained networks, including high-frequency micropayments and real-time data logging applications.[1]
However, actual daily transaction volumes on BSV remain modest compared to theoretical capacity, reflecting limited adoption rather than technical constraints. The network typically processes tens of thousands of transactions daily, with periodic spikes during specific application launches or testing events. This gap between capacity and usage represents both a challenge and opportunity for the ecosystem.
Network performance depends on miner infrastructure capabilities to process and propagate large blocks. BSV has invested in specialized infrastructure including the Teranode project designed to handle enterprise-scale transaction volumes while maintaining decentralization among professional mining operations.
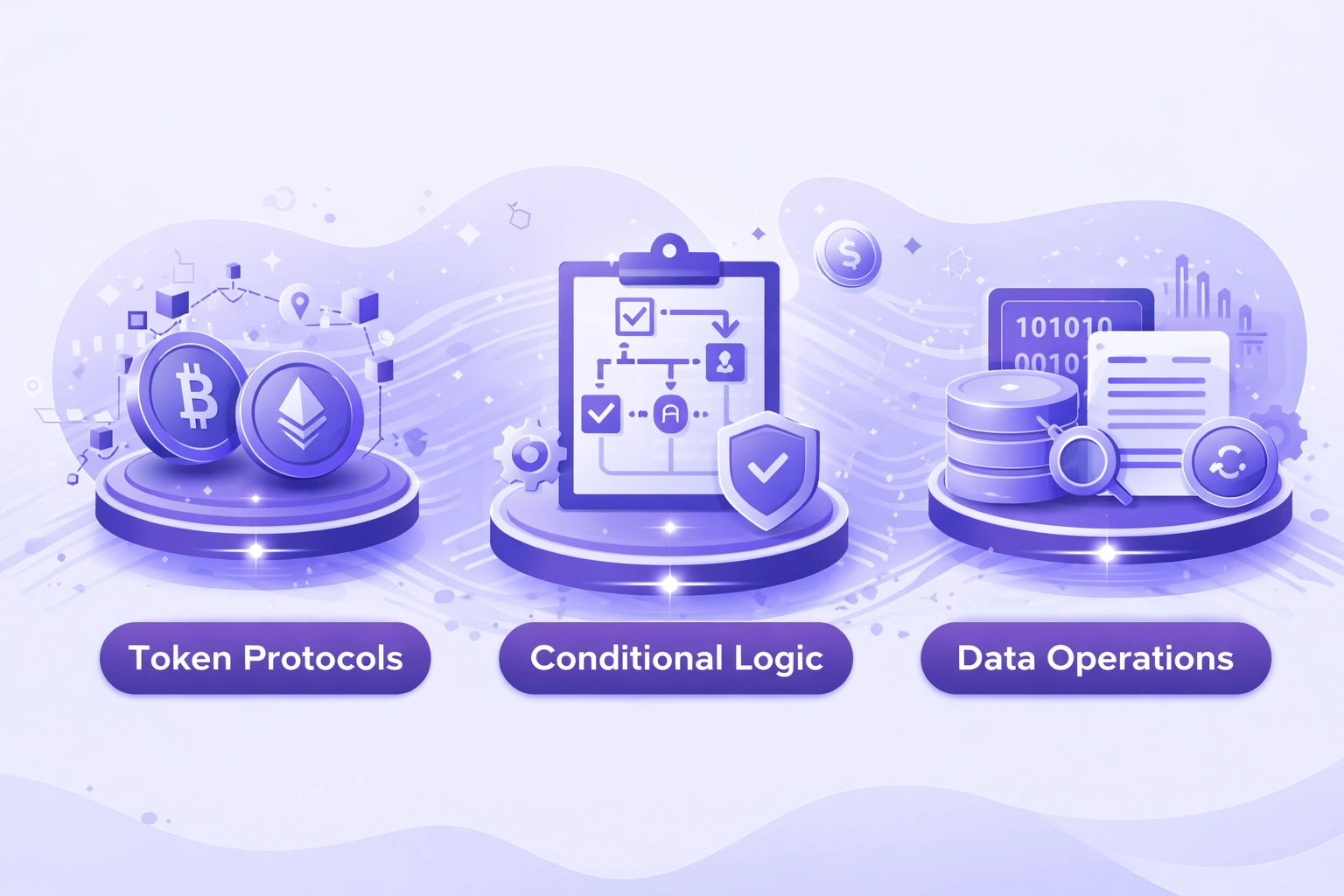 Smart Contract Capabilities Enabled by Bitcoin Script on BSV
Smart Contract Capabilities Enabled by Bitcoin Script on BSV
BSV restores original Bitcoin Script opcodes enabling sophisticated programmable transactions.
Token Protocols
- STAS token standard for fungible assets
- RUN protocol for NFTs and collectibles
- Tokenized securities issuance
- Loyalty point systems
Conditional Logic
- Multi-signature transactions
- Time-locked releases
- Hash-locked contracts
- Escrow arrangements
Data Operations
- On-chain data storage
- Document timestamping
- Proof of existence
- Supply chain tracking
Data Storage and Enterprise Use Cases on the BSV Blockchain
BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem uniquely enables substantial on-chain data storage due to its unlimited block sizes and low transaction fees. Unlike Bitcoin where data storage is expensive and limited, BSV allows enterprises to write significant data directly to the blockchain at minimal cost. This capability has attracted interest from businesses requiring immutable, timestamped records for compliance, audit trails, and data integrity verification across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada markets.
Enterprise use cases include supply chain provenance tracking where each product movement is recorded on-chain, creating tamper-proof audit trails. Healthcare applications store hashed patient records for integrity verification while maintaining privacy. Legal and financial services use timestamping for contract execution proof. Media companies explore content authentication and rights management.
The data utility focus differentiates BSV from other Bitcoin variants that primarily emphasize monetary functions. This positioning creates natural enterprise adoption pathways but also raises questions about blockchain bloat and long-term storage requirements for node operators.
Mining Economics and Incentive Structure in Bitcoin SV
1. Block Reward Foundation
Miners receive block subsidies following Bitcoin’s halving schedule, currently 3.125 BSV per block after the 2024 halving.
2. Transaction Fee Collection
Each transaction pays fees to miners, with BSV’s low per-transaction fees offset by high volume potential.
3. Volume-Based Revenue
BSV model depends on massive transaction volumes generating cumulative fee revenue as subsidies decrease.
4. Infrastructure Investment
Miners must invest in high-capacity infrastructure to process large blocks and capture transaction fees.
5. Competitive Hash Power
BSV competes for SHA-256 mining power with Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash, affecting security and profitability.
6. Difficulty Adjustment
Network difficulty adjusts to maintain consistent block times regardless of hash power fluctuations.
7. Miner Specialization
BSV encourages professional mining operations with enterprise-grade infrastructure for optimal performance.
8. Long-term Sustainability
Economic viability depends on achieving transaction volumes that generate sufficient fee revenue post-subsidy.
Comparing Bitcoin SV With Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
Understanding BSV in Bitcoin family requires examining how it compares with its parent chains across key dimensions. Each network has made distinct technical and philosophical choices that determine their suitability for different use cases and user preferences.
| Feature | Bitcoin (BTC) | Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | Bitcoin SV (BSV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Block Size | 1-4 MB | 32 MB | Unlimited |
| Transaction Fees | $1-50+ | $0.01-0.10 | $0.001-0.01 |
| Primary Use Case | Store of Value | Digital Cash | Enterprise Data |
| Market Cap Rank | #1 | Top 20 | Top 100 |
| Exchange Support | Universal | Widespread | Limited |
Security Model and Consensus Mechanism of Bitcoin SV
BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem uses the same Nakamoto Consensus mechanism as Bitcoin, relying on proof-of-work mining with the SHA-256 algorithm. This means BSV shares the foundational security model that has protected Bitcoin for over fifteen years. However, BSV’s significantly lower hash rate compared to Bitcoin creates different security characteristics that enterprises and users must understand.
The lower hash rate means BSV is theoretically more vulnerable to 51% attacks where a malicious actor controls majority mining power. The network has experienced reorganization events that raised security concerns. BSV proponents argue that the focus on professional mining operations and regulatory compliance provides different security guarantees than pure hash rate measurements.
Transaction finality considerations differ across Bitcoin variants. While Bitcoin users often wait for six confirmations (approximately one hour), BSV’s larger blocks and different usage patterns may require adjusted confirmation requirements depending on transaction value and risk tolerance.
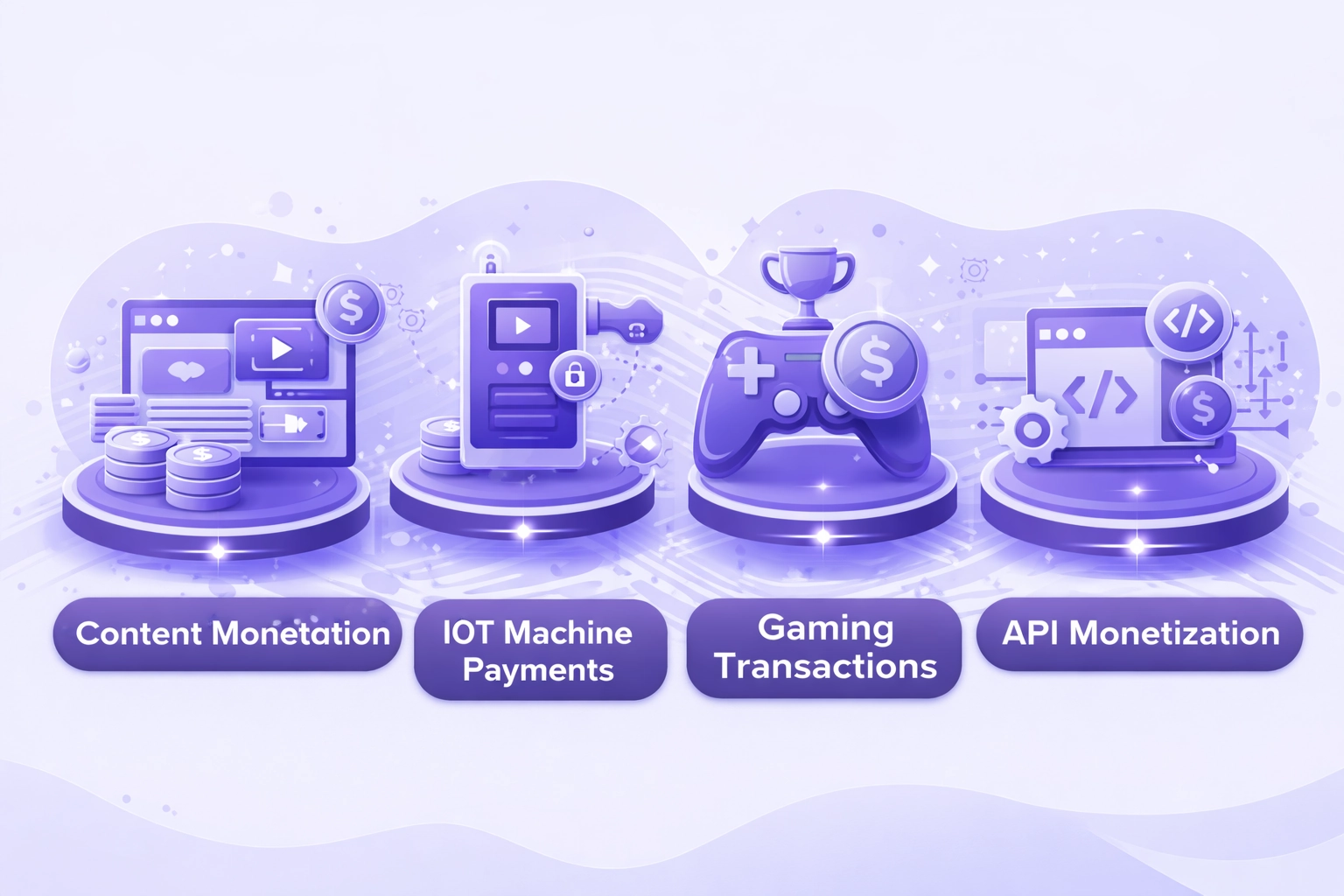 Role of Bitcoin SV in Microtransactions and Payments
Role of Bitcoin SV in Microtransactions and Payments
BSV’s low fees enable payment use cases impractical on higher-fee networks.
Content Monetization
Pay-per-article, video tips, and social media micropayments become viable at sub-cent transaction costs.
IoT Machine Payments
Autonomous devices can exchange value for services, data, or resources in real-time without intermediaries.
Gaming Transactions
In-game purchases, rewards, and item trades can occur on-chain with negligible fees per transaction.
API Monetization
Pay-per-call API services become practical, enabling new business models for data and service providers.
BSV’s Focus on Regulatory Compliance and Enterprise Adoption
BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem distinguishes itself through explicit focus on regulatory compliance, positioning as a blockchain suitable for regulated industries across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada. Unlike privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, BSV in Bitcoin embraces transparency and works with legal frameworks rather than seeking to circumvent them. This approach appeals to enterprises requiring clear legal standing for blockchain deployments.
The compliance focus includes support for identity verification, audit trails, and cooperation with law enforcement when legally required. BSV in Bitcoin proponents argue this positions the network favorably as governments worldwide develop cryptocurrency regulations. Critics suggest this approach compromises the censorship-resistance principles central to Bitcoin’s original value proposition.
Enterprise clients evaluating BSV for deployment benefit from this regulatory positioning but must also consider the trade-offs in terms of decentralization and community values compared to other blockchain options.
Ecosystem Applications Built on Bitcoin SV
Various applications leverage BSV in Bitcoin unique capabilities for specialized use cases.
Twetch: Social media platform enabling users to earn from content through micropayments and on-chain interactions.
HandCash: User-friendly wallet with social payments, gaming integration, and simplified onboarding for new users.
TAAL: Enterprise blockchain services provider offering infrastructure, transaction processing, and business solutions.
Tokenized: Smart contract platform enabling compliant tokenization of real-world assets and securities.
CryptoFights: Blockchain gaming platform demonstrating high-volume on-chain transaction capabilities.
WeatherSV: IoT application storing weather data on-chain demonstrating data storage use cases.
RelayX: Exchange and wallet platform with superwallet features combining trading and payments.
Run Protocol: NFT and token standard enabling creation and transfer of digital assets on BSV.
Challenges and Criticisms Facing Bitcoin SV
BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem faces significant challenges that prospective users and investors must carefully consider. The most prominent criticism involves controversial associations with key figures, particularly regarding disputed claims about Bitcoin’s origins. These controversies have led to delistings from major exchanges including Binance, Kraken, and ShapeShift, significantly limiting liquidity and accessibility for users in USA, UK, UAE, and Canada markets.
Technical criticisms include concerns about centralization as large block sizes require substantial infrastructure investment that smaller operators cannot afford. The network’s lower hash rate compared to Bitcoin raises security questions. Some observers question whether the promised transaction volumes and enterprise adoption will materialize at scale necessary for long-term viability.
Community fragmentation within the broader Bitcoin ecosystem means BSV operates with limited development resources, exchange support, and network effects compared to Bitcoin and even Bitcoin Cash. These challenges create meaningful risks for businesses considering BSV for critical applications.
Community, Infrastructure, and Support for BSV
The BSV community, while smaller than Bitcoin’s, maintains active participation across technical and business domains. The Bitcoin Association coordinates ecosystem promotion, conferences, and educational initiatives. Technical teams including nChain and BSV Blockchain Association maintain node software and pursue infrastructure improvements like Teranode for enhanced scalability.
Infrastructure support includes multiple wallet options, block explorers, and services, though the ecosystem remains significantly smaller than Bitcoin’s extensive infrastructure. Exchange availability has contracted due to delistings, creating liquidity challenges that affect price stability and accessibility for new users.
Educational resources and documentation support builders entering the ecosystem. Annual conferences like CoinGeek bring together the community and showcase applications. However, recruiting talent and building mindshare against larger, more established ecosystems remains an ongoing challenge for BSV in Bitcoin growth trajectory.
Future Outlook of Bitcoin SV in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
The future of BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem depends on several critical factors that will determine whether its unique positioning translates into sustainable growth and adoption. Enterprise adoption success represents the most important variable, as BSV’s value proposition centers on business utility rather than retail speculation. Meaningful deployments from recognizable enterprises would validate the technical approach and potentially attract further investment.
Regulatory clarity in major markets including USA, UK, UAE, and Canada will influence which blockchain platforms enterprises select for compliant deployments. BSV’s explicit compliance focus may prove advantageous as regulations mature, though competing platforms also pursue regulatory acceptance. The network’s ability to resolve governance controversies and rebuild exchange relationships will significantly impact liquidity and accessibility.
Growth Factors
- Enterprise adoption milestones
- Regulatory framework clarity
- Technical scalability proof
- Exchange listing recovery
Risk Factors
- Continued exchange delistings
- Governance controversies
- Competition from alternatives
- Security concerns
Key Milestones
- Teranode deployment
- Major enterprise contracts
- Sustained transaction growth
- Community expansion
Navigate Blockchain Technology with Expert Guidance!
Our team has 8+ years helping enterprises across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada evaluate and implement blockchain solutions tailored to their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bitcoin SV (Satoshi Vision) is a cryptocurrency that emerged from a hard fork of Bitcoin Cash in November 2018. It positions itself as the implementation most faithful to the original Bitcoin whitepaper written by Satoshi Nakamoto. BSV in Bitcoin ecosystem represents a distinct approach emphasizing massive on-chain scaling, larger block sizes, and enterprise utility while maintaining the original Bitcoin protocol design principles.
Bitcoin SV differentiates itself through unlimited block sizes enabling massive transaction throughput, restored original opcodes for enhanced scripting capabilities, and focus on regulatory compliance for enterprise adoption. While Bitcoin prioritizes store of value with limited block sizes and Bitcoin Cash offers moderate scaling, BSV in Bitcoin variants pursues unbounded scaling to support global payment systems and data applications on a single blockchain.
Bitcoin SV supports smart contract functionality through Bitcoin Script, the original scripting language from Bitcoin’s creation. Unlike Ethereum’s Turing-complete approach, BSV in Bitcoin uses a more constrained but secure scripting model. The restored opcodes enable complex conditional transactions, token creation, and automated agreements while maintaining predictable execution costs suitable for enterprise applications across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada markets.
Enterprises select BSV in Bitcoin options for its extremely low transaction fees (often fractions of a cent), high throughput capacity supporting thousands of transactions per second, and on-chain data storage capabilities. The network’s focus on regulatory compliance and stable protocol design appeals to businesses requiring predictable infrastructure for supply chain tracking, digital identity, and micropayment systems.
Investment decisions require careful consideration of risk factors unique to each cryptocurrency. BSV in Bitcoin family has significantly lower market capitalization and liquidity compared to Bitcoin. While BSV in Bitcoin offers technological differentiators like larger blocks and lower fees, it faces challenges including controversial leadership, limited exchange support, and smaller community adoption. Investors should conduct thorough research before any cryptocurrency investment.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







