Key Takeaways
- Arithmetic errors in smart contracts have caused over $2 billion in losses through exploits like BatchOverflow, affecting protocols across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets.
- Integer overflow occurs when calculations exceed maximum values, wrapping to zero, while underflow happens when subtracting below zero creates massive unexpected numbers.
- Solidity version 0.8.0 introduced native overflow and underflow protection, automatically reverting transactions when arithmetic errors would occur during execution.
- Division errors and precision loss in fixed-point calculations can silently drain funds through rounding vulnerabilities that accumulate over multiple transactions.
- SafeMath libraries provide explicit checked arithmetic operations essential for contracts using Solidity versions below 0.8.0 to prevent mathematical exploits.
- Professional security audits focusing on arithmetic errors should examine all mathematical operations, boundary conditions, and edge cases before mainnet deployment.
- Gas optimization techniques that use unchecked blocks can reintroduce arithmetic error vulnerabilities, requiring careful balance between efficiency and security.
- Formal verification methods mathematically prove absence of arithmetic errors, providing highest assurance for high-value DeFi protocols handling significant assets.
Introduction to Arithmetic Errors in Smart Contracts
Arithmetic errors represent one of the most devastating vulnerability classes in smart contract security, responsible for billions in losses across the blockchain ecosystem. With over eight years of experience auditing and securing smart contracts across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets, our agency has witnessed firsthand how seemingly simple mathematical mistakes can lead to catastrophic exploits. These vulnerabilities occur when calculations produce unexpected results due to the inherent limitations of computer arithmetic, particularly integer overflow, underflow, and precision loss. Understanding arithmetic errors is fundamental for anyone building or investing in blockchain applications, as even a single unchecked operation can compromise entire protocols.
Why Arithmetic Precision Matters in Blockchain Logic
Smart contracts execute financial logic handling millions or billions in value, making arithmetic precision absolutely critical. Unlike traditional applications where bugs can be patched, deployed smart contracts are immutable, meaning arithmetic errors become permanent vulnerabilities. The Ethereum Virtual Machine operates exclusively with integers, lacking native floating-point support, which creates unique challenges for representing fractional values. When calculations involve token decimals, exchange rates, or interest computations, even minor precision errors can compound into significant financial discrepancies that attackers exploit systematically.
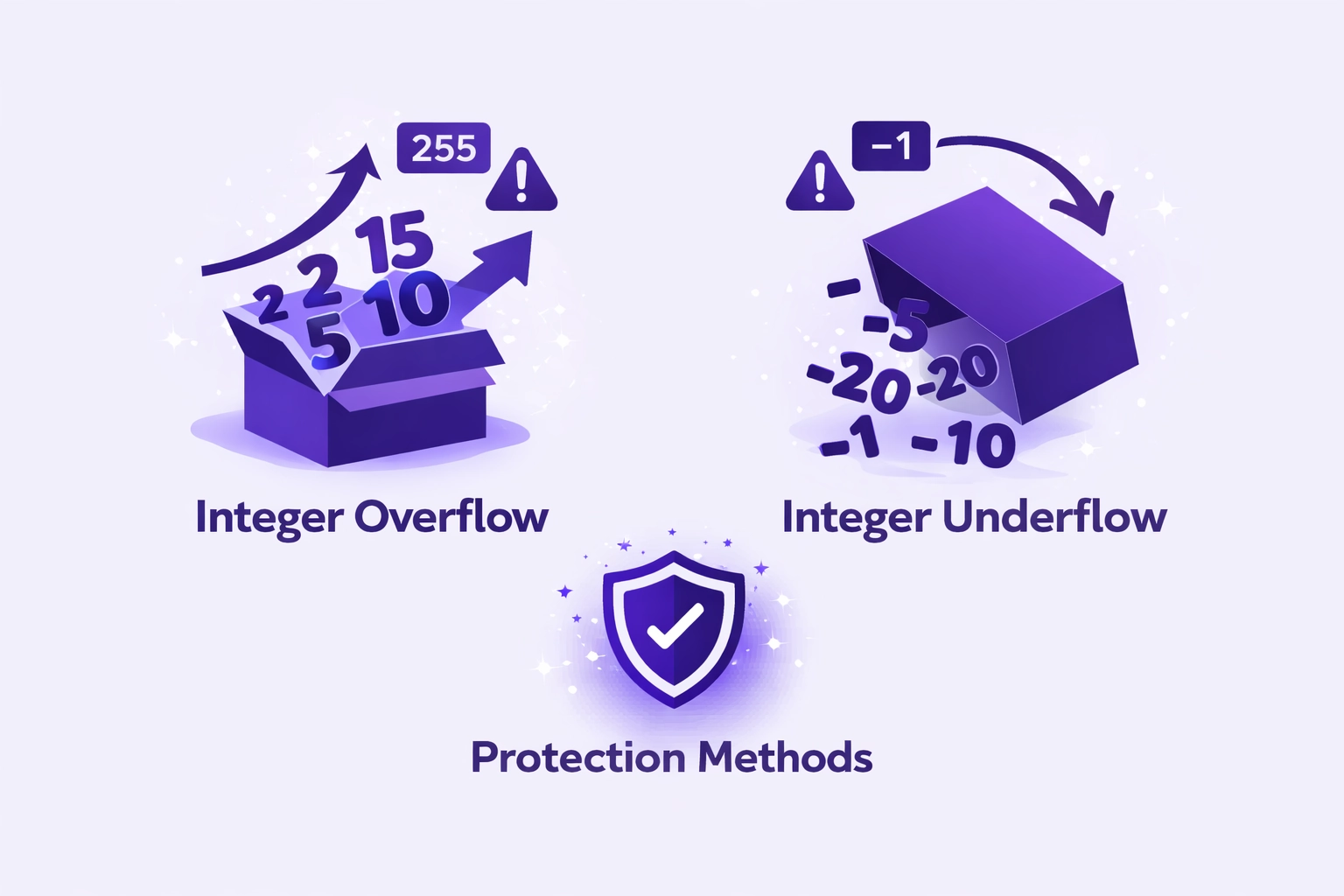
Integer Overflow and Underflow Explained
Integer Overflow
- Exceeds max uint256 value
- Wraps around to zero
- Creates tokens from nothing
- Bypasses balance checks
Integer Underflow
- Subtracts below zero
- Wraps to max value
- Inflates attacker balance
- Drains protocol funds
Protection Methods
- SafeMath libraries
- Solidity 0.8+ defaults
- Input validation checks
- Boundary testing
Division Errors and Rounding Vulnerabilities
| Error Type | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Division by Zero | Dividing when denominator equals zero | Transaction revert, DoS potential |
| Truncation | Integer division drops remainders | Silent value loss over time |
| Round Down Exploit | Manipulating small amounts | Free tokens through dust attacks |
| Order Dependency | Multiply before divide errors | Precision loss in calculations |
| Accumulation | Rounding errors compound | Significant fund discrepancies |
Precision Loss in Fixed-Point and Floating-Point Calculations
The EVM lacks native floating-point support, forcing smart contracts to simulate decimal arithmetic using fixed-point representations. This introduces arithmetic errors when converting between different precision scales or performing calculations that exceed available precision. DeFi protocols across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets commonly use 18 decimal places to match ETH precision, but operations between tokens with different decimals create conversion vulnerabilities that attackers systematically exploit.
Risk Warning: Precision loss in interest calculations can silently drain millions from lending protocols over extended periods.
How Arithmetic Errors Lead to Smart Contract Exploits
| Exploit Vector | Arithmetic Error Used | Attack Method |
|---|---|---|
| Token Minting | Integer overflow in supply | Create unlimited tokens |
| Balance Manipulation | Underflow in transfer | Inflate attacker balance |
| Price Oracle Attack | Precision loss in price | Manipulate exchange rates |
| Reward Drain | Rounding in rewards | Extract extra rewards |
| Loan Manipulation | Interest calculation errors | Borrow without repayment |
Real-World Smart Contract Attacks Caused by Arithmetic Bugs
The BatchOverflow attack in April 2018 exploited arithmetic errors in multiple ERC-20 tokens, allowing attackers to generate unlimited tokens by triggering integer overflow in batch transfer functions. The Beauty Chain (BEC) token lost $900 million in market value within hours. These incidents across global exchanges including those serving USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian users demonstrated how arithmetic errors could devastate entire token ecosystems.
Total Losses from Arithmetic Errors
Tokens Affected by BatchOverflow
Beauty Chain Single Incident
Financial and Security Risks of Unchecked Calculations
Arithmetic errors pose existential threats to smart contract protocols, enabling attackers to drain entire treasuries, manipulate governance votes, or destabilize token economies. Beyond direct financial losses, these vulnerabilities damage protocol reputation, trigger regulatory scrutiny, and erode user trust. Insurance providers and institutional investors increasingly require formal verification of arithmetic safety before engaging with DeFi protocols.
Arithmetic Error Detection and Prevention Lifecycle
Code Review
Manual examination of all arithmetic operations identifying potential overflow and precision issues.
Static Analysis
Automated tools scan code for arithmetic error patterns and unchecked operations systematically.
Boundary Testing
Test with extreme values including zero, max uint256, and edge cases for all numeric inputs.
Fuzz Testing
Random input generation discovers unexpected arithmetic errors through thousands of test iterations.
Formal Verification
Mathematical proofs verify absence of arithmetic errors for critical financial calculations.
External Audit
Independent security experts review all arithmetic logic with fresh perspective and experience.
Bug Bounty
Public bug bounty programs incentivize researchers to discover arithmetic errors before attackers.
Continuous Monitoring
Post-deployment monitoring detects anomalous arithmetic behavior indicating potential exploitation.
Role of Arithmetic Errors in DeFi Protocol Failures
DeFi protocols are particularly vulnerable to arithmetic errors due to complex financial calculations involving interest rates, collateralization ratios, and token exchanges. The Compound protocol suffered governance attacks exploiting precision errors in reward calculations. Yield aggregators across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets have experienced losses when arithmetic errors in strategy contracts allowed attackers to manipulate share prices. Our agency has audited numerous DeFi protocols, consistently finding arithmetic vulnerabilities that would have enabled significant exploits.[1]
Eliminate Dangerous Arithmetic Errors Today
Our security experts identify arithmetic errors threatening your smart contracts. Get comprehensive auditing to prevent costly exploits before they happen.
Gas Optimization Side Effects on Arithmetic Safety
Unchecked Blocks
- Bypass overflow checks
- Save gas on operations
- Reintroduce vulnerabilities
- Require careful review
Assembly Usage
- Direct EVM operations
- No automatic checks
- Maximum gas efficiency
- High error risk
Safe Optimization
- Document all unchecked code
- Prove safety mathematically
- Test extensively
- Audit specifically
How Blockchain Virtual Machines Handle Arithmetic Operations
| Platform | Integer Types | Overflow Handling |
|---|---|---|
| Ethereum (Solidity 0.8+) | uint8 to uint256 | Automatic revert on overflow |
| Ethereum (Solidity < 0.8) | uint8 to uint256 | Silent wrap-around |
| Solana (Rust) | u8 to u128 | Panic in debug, wrap in release |
| Vyper | uint256 only | Built-in overflow protection |
Preventing Arithmetic Errors Using Safe Math Techniques
SafeMath libraries revolutionized smart contract security by providing checked arithmetic operations that revert on overflow or underflow. OpenZeppelin’s SafeMath became the industry standard for Solidity versions below 0.8.0. Modern contracts using Solidity 0.8+ benefit from native overflow protection, though developers must carefully evaluate when using unchecked blocks for gas optimization. Best practices include always validating inputs, using appropriate integer sizes, and ordering operations to multiply before dividing to preserve precision.
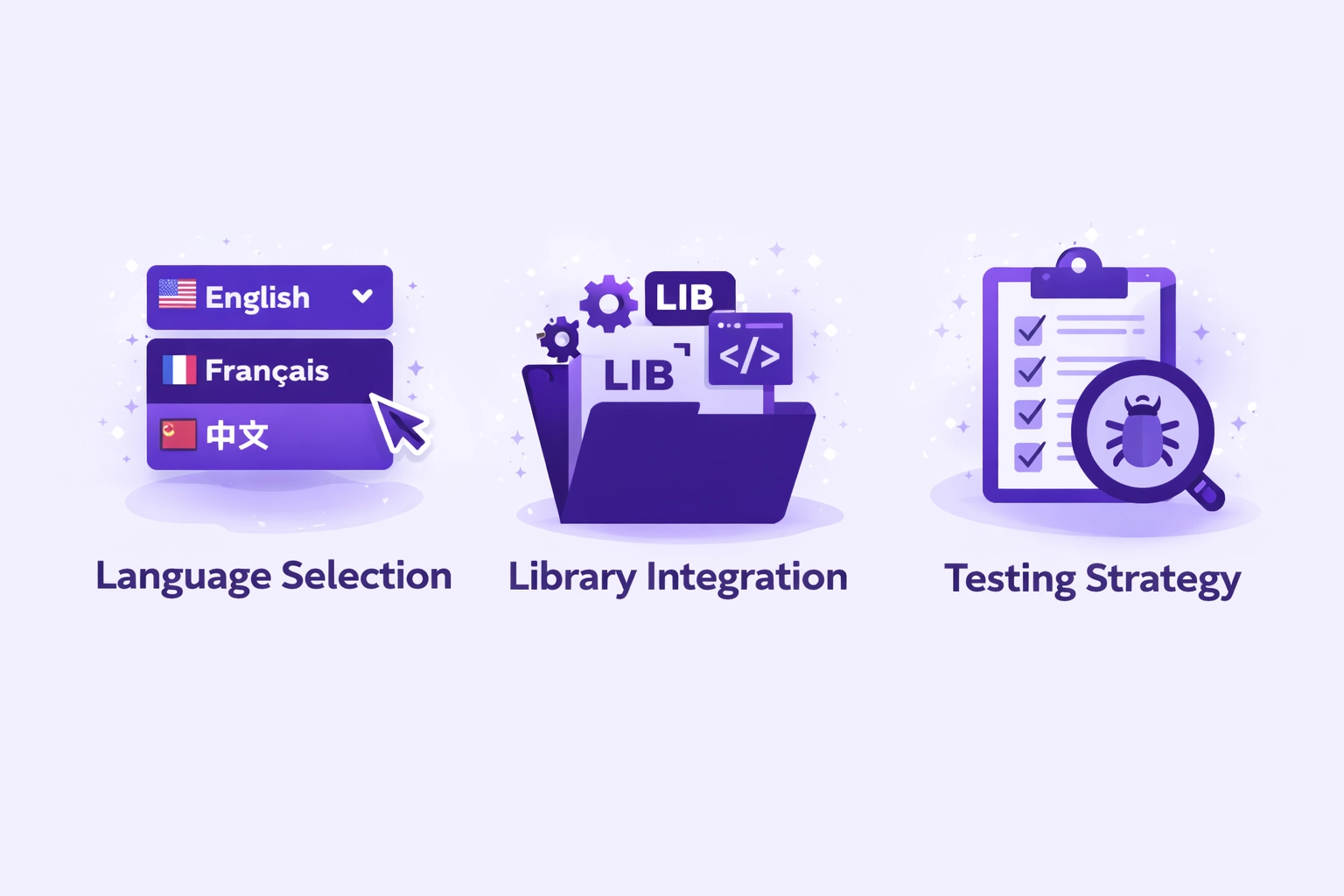
Arithmetic Safety Implementation Criteria
Language Selection
- Use Solidity 0.8+ when possible
- Consider Vyper for safety
- Evaluate Rust for Solana
- Match to platform requirements
Library Integration
- Use OpenZeppelin SafeMath
- Implement PRBMath for fixed-point
- Verify library versions
- Audit dependencies
Testing Strategy
- Boundary value analysis
- Fuzz testing with Foundry
- Formal verification for critical paths
- Invariant testing
Auditing Smart Contracts for Arithmetic Vulnerabilities
| Audit Focus | Description | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Overflow/Underflow | Check all arithmetic operations for wrap-around | Critical |
| Division Safety | Verify divisors cannot be zero | Critical |
| Precision Handling | Review decimal conversions and rounding | High |
| Unchecked Blocks | Evaluate safety of gas optimizations | High |
| Input Validation | Confirm all numeric inputs are bounded | High |
Authoritative Industry Standards for Arithmetic Safety
Standard 1: Use Solidity 0.8.0 or higher for all new contracts to benefit from native overflow protection.
Standard 2: Document and justify every unchecked block with mathematical proof of safety.
Standard 3: Implement comprehensive boundary testing for all arithmetic operations before deployment.
Standard 4: Order operations to multiply before divide, preserving maximum precision in calculations.
Standard 5: Validate all numeric inputs against reasonable bounds before performing calculations.
Standard 6: Require formal verification for financial calculations in protocols managing over $10M in assets.
Future Approaches to Eliminating Arithmetic Risks in Smart Contracts
The blockchain industry continues evolving approaches to eliminate arithmetic errors through language improvements, formal verification tools, and automated auditing systems. Emerging languages like Move implement resource-oriented programming that prevents certain arithmetic vulnerabilities by design. Machine learning-powered audit tools increasingly detect arithmetic errors automatically. Formal verification is becoming more accessible, enabling mathematical proofs of arithmetic safety for critical protocols across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets.
With eight years of experience securing smart contracts, our agency has witnessed significant progress in preventing arithmetic errors. However, vigilance remains essential as new attack vectors emerge and gas optimization pressures create temptation to bypass safety mechanisms. The combination of modern language features, comprehensive testing, professional audits, and ongoing monitoring provides the strongest defense against arithmetic errors that continue threatening blockchain protocols.
Protect Your Smart Contracts from Arithmetic Errors
Partner with our experienced security team to identify and eliminate arithmetic vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
Frequently Asked Questions
Arithmetic errors in smart contracts occur when mathematical operations produce unexpected results due to overflow, underflow, or precision loss. These vulnerabilities are dangerous because they can enable attackers to manipulate token balances, drain funds, or bypass security checks in blockchain applications.
Integer overflow happens when calculations exceed maximum value limits, wrapping around to zero. Underflow occurs when subtracting below zero, resulting in massive positive numbers. Both arithmetic errors enable attackers to create tokens from nothing or bypass balance checks in vulnerable contracts.
SafeMath is a library providing explicit overflow protection through checked arithmetic operations. Since Solidity 0.8.0, native overflow checks are built-in by default. Both prevent arithmetic errors, but native checks consume less gas while SafeMath offers backward compatibility for older contracts.
The BatchOverflow attack in 2018 exploited arithmetic errors in multiple ERC-20 tokens, creating unlimited tokens. The Beauty Chain hack lost $900 million through integer overflow. These incidents demonstrate how arithmetic errors can cause catastrophic financial losses in blockchain protocols.
Auditors detect arithmetic errors through manual code review, automated static analysis tools, and formal verification methods. They examine all mathematical operations, boundary conditions, and edge cases. Testing with extreme values helps identify potential overflow, underflow, and precision vulnerabilities.
Different blockchain platforms handle arithmetic errors differently. Ethereum’s Solidity added native checks in version 0.8.0. Rust-based platforms like Solana have stricter type systems. Each virtual machine handles integer operations uniquely, requiring platform-specific security considerations for arithmetic safety.
Best practices include using checked arithmetic operations, implementing SafeMath libraries for older Solidity versions, thorough input validation, comprehensive testing with boundary values, and professional security audits. Regular code reviews and formal verification further reduce arithmetic error risks.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.