Key Takeaways
- AI Platforms are comprehensive software ecosystems that enable organizations to build, train, deploy, and manage machine learning models and intelligent applications at scale across various business functions.
- Data quality issues represent one of the most significant challenges in AI Application projects, with poor data leading to inaccurate predictions, biased outcomes, and ultimately failed implementations.
- Model drift occurs when AI models gradually lose accuracy over time due to changes in real world data patterns, requiring continuous monitoring and periodic retraining to maintain performance.
- Security vulnerabilities in AI systems can expose sensitive data, enable adversarial attacks, and compromise model integrity, making robust security frameworks essential for enterprise deployments.
- Integration complexity with existing legacy systems remains a major obstacle, often requiring significant technical expertise and custom middleware solutions to achieve seamless connectivity.
- Cloud based AI Platforms offer scalability and reduced infrastructure costs, while on premise solutions provide greater control over data privacy and regulatory compliance requirements.
- The shortage of skilled AI professionals creates implementation bottlenecks, making platform selection based on ease of use and available support resources increasingly important.
- Ethical considerations including algorithmic bias, transparency, and accountability require careful attention throughout the AI lifecycle from data collection to model deployment.
- Total cost of ownership extends beyond licensing fees to include infrastructure, training, maintenance, and ongoing optimization expenses that organizations must budget appropriately.
- Future trends point toward AutoML capabilities, edge computing integration, and explainable AI features becoming standard components of next generation AI Platforms.
Introduction to AI Platforms
The digital transformation journey has placed AI Platforms at the center of enterprise technology strategies. These sophisticated environments provide the infrastructure, tools, and frameworks necessary to harness the power of artificial intelligence across organizational operations. Understanding what AI platforms offer and where they can fail is essential knowledge for technology leaders, data scientists, and business stakeholders alike.
Modern AI platforms have evolved from simple machine learning toolkits to comprehensive ecosystems that support the entire AI lifecycle. They encompass everything from data preparation and feature engineering to model training, validation, deployment, and ongoing monitoring. This evolution reflects the growing maturity of AI as a discipline and the increasing demands organizations place on their intelligent systems.

What Are AI Platforms?
An AI Platform is a unified software environment that provides the necessary tools, infrastructure, and services to build, train, deploy, and manage artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions. These platforms abstract away much of the complexity involved in AI projects, allowing organizations to focus on solving business problems rather than managing technical infrastructure.
At their core, AI platforms serve as intermediaries between raw data and actionable intelligence. They provide standardized workflows for data ingestion, preprocessing, model creation, and deployment while offering collaborative features that enable teams to work together effectively on complex AI initiatives.
Expert Statement:
“The true value of an AI Platform lies not just in its technical capabilities, but in how effectively it bridges the gap between data science expertise and business outcomes. Organizations that choose platforms aligned with their specific use cases and skill levels consistently achieve faster time to value and higher return on investment.”
Evolution of Artificial Intelligence Platforms
The journey of AI platforms spans several decades, marked by significant technological breakthroughs and shifting paradigms. Understanding this evolution helps contextualize current capabilities and anticipate future directions.
The Early Era (1950s to 1990s)
Initial AI efforts focused on rule-based systems and expert systems that required manual knowledge encoding. These early platforms were limited in scope, expensive to maintain, and struggled with scalability. The AI winter periods during this era reflected the gap between expectations and technological reality.
The Machine Learning Revolution (2000s to 2010s)
Advances in computational power and algorithm sophistication enabled statistical machine learning approaches to flourish. Platforms began offering automated model training capabilities, though significant expertise remained necessary for successful implementations.
The Deep Learning Era (2010s to Present)
Neural network architectures, particularly deep learning, transformed AI capabilities dramatically. Modern platforms now support complex architectures including convolutional neural networks, transformers, and generative models, democratizing access to powerful AI capabilities.
1950s to 1990s
Rule Based Expert Systems
2000s to 2010s
Statistical ML Emergence
2010s to 2020s
Deep Learning Revolution
2020s Onward
Generative AI and AutoML
Key Components of an AI Platform
Understanding the core components of AI platforms helps organizations evaluate options and identify potential failure points. Each component plays a critical role in the overall functionality and reliability of the system.
| Component | Function | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Data Management Layer | Handles data ingestion, storage, preprocessing, and feature engineering | Data quality issues, scalability bottlenecks, format incompatibilities |
| Model Training Engine | Provides algorithms, frameworks, and computational resources for training | Resource constraints, overfitting, long training times |
| Model Registry | Version control and management of trained models | Version confusion, storage limitations, metadata loss |
| Deployment Infrastructure | Serves models in production environments via APIs or embedded systems | Latency issues, scaling failures, deployment errors |
| Monitoring Dashboard | Tracks model performance, data drift, and system health | Alert fatigue, incomplete metrics, delayed notifications |
| Collaboration Tools | Enables team coordination, experiment tracking, and knowledge sharing | Access control issues, workflow conflicts, documentation gaps |
Types of AI Platforms
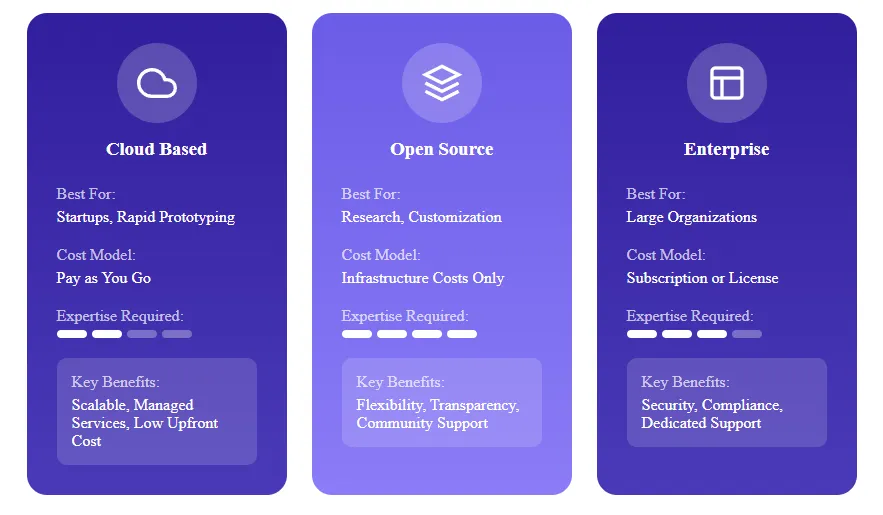
The AI platform landscape offers diverse options catering to different organizational needs, technical capabilities, and deployment preferences. Selecting the right type significantly impacts implementation success and ongoing operational efficiency.
Cloud Based AI Platforms
These platforms operate entirely in the cloud, offering scalable infrastructure and managed services. Major providers include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure. They excel in scenarios requiring rapid scaling, distributed computing, and minimal infrastructure management overhead.
Open Source AI Platforms
Community driven platforms like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Apache Spark provide flexibility and transparency. Organizations can customize these platforms extensively but must manage infrastructure and support internally. They suit teams with strong technical capabilities and specific customization requirements.
Enterprise AI Platforms
Comprehensive commercial solutions designed for large organizations offer end to end capabilities with enterprise grade security, compliance features, and dedicated support. Examples include IBM Watson, Salesforce Einstein, and DataRobot.
Hybrid AI Platforms
Combining cloud and on premise capabilities, hybrid platforms address data sovereignty requirements while leveraging cloud scalability for certain workloads. This approach suits regulated industries and organizations with distributed data sources.
| Platform Type | Best For | Cost Model | Technical Expertise Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Based | Startups, rapid prototyping | Pay as you go | Low to Medium |
| Open Source | Research, customization | Infrastructure costs | High |
| Enterprise | Large organizations | Subscription or license | Medium |
| Hybrid | Regulated industries | Mixed model | Medium to High |
How AI Platforms Work
Understanding the operational mechanics of AI platforms reveals where problems can emerge and how to address them proactively. The workflow typically follows a structured lifecycle with multiple interconnected stages.
→
→
→
→
→
Continuous feedback loop enables iterative improvement and model optimization
The data collection phase gathers information from various sources including databases, APIs, IoT devices, and user interactions. Preprocessing transforms raw data into formats suitable for model training through cleaning, normalization, and feature extraction. Model training applies algorithms to learn patterns from prepared data, while validation ensures the model generalizes well to unseen examples.
Deployment moves validated models into production environments where they serve predictions to applications and users. Continuous monitoring tracks performance metrics, detects drift, and triggers retraining when necessary. This cyclical process ensures AI systems remain accurate and relevant over time.
Core Features of Modern AI Platforms
Contemporary AI Platforms offer sophisticated capabilities that streamline the entire machine learning workflow. These features determine how effectively organizations can implement and scale their AI initiatives.
AutoML Capabilities
Automated machine learning features that handle algorithm selection, hyperparameter tuning, and feature engineering, enabling faster model creation with reduced expertise requirements.
MLOps Integration
Machine learning operations tools that facilitate continuous integration, deployment, and monitoring of models in production environments with version control and reproducibility.
Explainable AI
Tools that provide transparency into model decisions, helping stakeholders understand why specific predictions were made and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Distributed Computing
Infrastructure that enables training on massive datasets by distributing workloads across multiple machines, significantly reducing time to model completion.
Benefits of Using AI Platforms for Businesses
Organizations implementing AI Application solutions through dedicated platforms realize numerous advantages that justify the investment and complexity involved in adoption.
Accelerated Time to Value: Pre built components, templates, and automated workflows significantly reduce the time required to move from concept to production. What previously took months can now be accomplished in weeks with the right platform.
Reduced Technical Barriers: Visual interfaces, no code tools, and guided workflows enable business users to participate in AI projects without deep technical expertise, democratizing access to intelligent capabilities across the organization.
Scalable Infrastructure: Cloud based platforms automatically scale computational resources based on demand, eliminating the need for upfront hardware investments and enabling organizations to grow their AI capabilities organically.
Improved Collaboration: Centralized environments with shared notebooks, experiment tracking, and model registries enable data science teams to collaborate effectively, reducing duplication and accelerating knowledge transfer.
AI Platforms for Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning and deep learning workloads require specialized infrastructure that can handle intensive computational demands while providing the flexibility needed for experimentation and iteration.
Modern platforms support diverse algorithmic approaches ranging from classical machine learning techniques like random forests and gradient boosting to sophisticated deep learning architectures including transformers, convolutional networks, and recurrent neural networks. GPU acceleration has become standard, enabling training of complex models that would be impractical on traditional CPU infrastructure.
Transfer learning capabilities allow organizations to leverage pre trained models as starting points, dramatically reducing the data and computational resources required for specific applications. This approach proves particularly valuable for natural language processing and computer vision tasks where foundational models capture general knowledge applicable across domains.

AI Platforms for Data Science and Analytics
Data science focused platforms emphasize exploratory analysis, visualization, and collaborative workflows that support the iterative nature of analytical work. These environments integrate statistical tools, programming languages, and business intelligence capabilities into cohesive experiences.
Jupyter notebooks and similar interactive environments remain central to data science workflows, enabling analysts to combine code, visualizations, and documentation in shareable formats. Platforms enhance these tools with version control, scheduled execution, and parameterized runs that bridge the gap between exploration and production.
AI Platforms for Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing capabilities have advanced dramatically with the emergence of large language models and transformer architectures. AI Platforms now offer pre built NLP services alongside tools for custom model creation.
Common NLP applications include sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, text classification, machine translation, and conversational AI. Platforms provide APIs for these capabilities while also supporting fine tuning of foundational models for domain specific requirements.
Sentiment Analysis
Customer feedback interpretation
Text Classification
Document categorization
Named Entity Recognition
Information extraction
Conversational AI
Chatbots and assistants
AI Platforms for Computer Vision Applications
Computer vision represents one of the most successful application areas for deep learning, with platforms offering comprehensive tools for image and video analysis tasks including object detection, facial recognition, optical character recognition, and autonomous navigation.
Pre trained vision models enable rapid prototyping of applications, while annotation tools facilitate creation of labeled datasets for custom model training. Edge deployment options allow computer vision models to run on devices with limited connectivity, supporting use cases in manufacturing, retail, and mobile applications.
AI Platforms for Automation and Intelligent Workflows
Intelligent automation combines AI capabilities with robotic process automation to create workflows that can handle complex, judgment intensive tasks previously requiring human intervention. AI Application ecosystems increasingly integrate with business process management tools.
Document processing automation extracts information from invoices, contracts, and forms using optical character recognition and natural language understanding. Decision automation applies predictive models to route cases, approve requests, and escalate exceptions based on learned patterns and business rules.
Security and Compliance in AI Platforms
Security considerations in AI platforms extend beyond traditional cybersecurity to encompass model integrity, data privacy, and adversarial robustness. Organizations must address these concerns comprehensively to protect their AI investments.
| Security Concern | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Data Privacy | Sensitive information in training data may be exposed or leaked | Encryption, access controls, differential privacy techniques |
| Model Theft | Proprietary models may be extracted or reverse engineered | Model watermarking, API rate limiting, secure deployment |
| Adversarial Attacks | Malicious inputs designed to cause incorrect predictions | Adversarial training, input validation, ensemble methods |
| Data Poisoning | Compromised training data leading to corrupted models | Data validation, provenance tracking, anomaly detection |
Compliance requirements vary by industry and geography, with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA imposing specific obligations on AI systems that process personal data. Platforms must provide audit trails, consent management, and data retention controls to support compliance efforts.
How to Choose the Right AI Platform
Selecting an appropriate AI platform requires careful evaluation of organizational needs, technical capabilities, and long term strategic goals. The following considerations guide effective decision making.
Use Case Alignment: Evaluate whether the platform excels at your specific application types. Some platforms specialize in natural language processing while others focus on computer vision or time series forecasting. Matching platform strengths to your requirements improves outcomes.
Team Expertise: Consider the technical skills available within your organization. Platforms with visual interfaces and AutoML features suit teams with limited data science expertise, while open source frameworks provide flexibility for experienced practitioners.
Scalability Requirements: Project future growth in data volumes, model complexity, and user demand. Ensure the platform can scale appropriately without requiring migration to alternative solutions.
Integration Capabilities: Assess how well the platform connects with existing data sources, enterprise applications, and deployment targets. Strong integration reduces implementation complexity and ongoing maintenance burden.
Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond licensing fees to consider infrastructure costs, training requirements, maintenance effort, and potential vendor lock in implications.
Use Case Fit
Team Skills
Scalability
Integration
Total Cost
Security
Future Trends in AI Platform Innovation
The AI platform landscape continues evolving rapidly, with several emerging trends shaping future capabilities and architectures.
Generative AI Integration: Large language models and diffusion models are being incorporated into mainstream platforms, enabling new categories of applications including content generation, code synthesis, and creative design assistance.
Edge AI Deployment: Growing demand for low latency inference drives platform support for deploying models on edge devices, IoT sensors, and mobile applications. This trend addresses bandwidth constraints and privacy requirements.
Responsible AI Frameworks: Platforms increasingly embed tools for bias detection, fairness assessment, and transparency reporting, helping organizations implement AI ethically and comply with emerging regulations.
Federated Learning: Privacy preserving techniques enable model training across distributed data sources without centralizing sensitive information, opening new possibilities for collaborative AI in healthcare, finance, and other regulated domains.
Challenges and Limitations of AI Platforms
Despite significant advances, AI Platforms face persistent challenges that organizations must navigate carefully. Understanding these limitations helps set realistic expectations and plan appropriate mitigations.
Data Quality Issues
The adage “garbage in, garbage out” remains profoundly true for AI systems. Poor data quality including missing values, inconsistent formats, labeling errors, and bias in training sets fundamentally limits model performance regardless of platform sophistication.
Model Drift and Degradation
Models trained on historical data may lose accuracy as real world conditions change. This drift occurs gradually and often goes undetected until significant performance degradation occurs, potentially causing business harm before remediation.
Skill Shortages
Despite platform improvements in accessibility, effective AI implementation still requires specialized expertise. The global shortage of qualified data scientists, ML engineers, and AI architects constrains organizational ability to leverage platform capabilities fully.
Integration Complexity
Connecting AI platforms with legacy systems, data warehouses, and enterprise applications often proves more difficult than anticipated. Technical debt, incompatible formats, and security requirements complicate integration efforts.
| Challenge | Impact Level | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality | Critical | Invest in data governance and quality monitoring |
| Model Drift | High | Implement continuous monitoring and retraining pipelines |
| Skill Gaps | High | Partner with experts or invest in training programs |
| Integration Issues | Medium | Adopt API first architecture and middleware solutions |
| Cost Overruns | Medium | Establish clear budgets and usage monitoring |
| Vendor Lock in | Medium | Use portable formats and avoid proprietary dependencies |
Ready to Build Your AI Platform Strategy?
Connect with our AI experts to navigate the complexities of platform selection, implementation, and optimization for your business needs.
Conclusion: The Growing Importance of AI Platforms
The trajectory of AI Platforms points toward increasingly sophisticated, accessible, and integrated solutions that will become fundamental components of enterprise technology stacks. Organizations that understand both the potential and pitfalls of these platforms position themselves for competitive advantage in an AI driven economy.
Success with AI platforms requires more than technology selection. It demands organizational readiness, data maturity, skilled teams, and clear alignment between AI initiatives and business objectives. The challenges outlined throughout this guide are real but manageable with proper planning and expert guidance.
As AI capabilities continue advancing at unprecedented rates, platforms will evolve to incorporate new techniques, address emerging challenges, and expand into previously impossible use cases. Organizations that build strong AI foundations today will be best positioned to capitalize on these future developments.
Nadcab Labs brings over 8 years of deep expertise in AI Application implementation and AI Platform advisory services. Our team of seasoned professionals has successfully guided hundreds of organizations through the complexities of AI adoption, from initial strategy formulation to production deployment and ongoing optimization. With comprehensive knowledge spanning cloud-based solutions, enterprise platforms, and custom implementations, Nadcab Labs delivers authoritative guidance that helps clients avoid common pitfalls while maximizing the value of their AI investments. Our proven methodology combines technical excellence with business acumen, ensuring that AI initiatives deliver measurable outcomes aligned with organizational goals. Trust Nadcab Labs as your partner in navigating the AI platform landscape with confidence and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
The cost of implementing an AI platform varies significantly based on complexity, features, and deployment type. Small businesses can start with cloud based solutions ranging from $500 to $5,000 monthly. Custom enterprise solutions may cost $50,000 to $500,000 or more. Many providers offer tiered pricing models, allowing businesses to scale costs according to usage and requirements without heavy upfront investment.
AI platforms are designed to augment human capabilities rather than completely replace employees. While they automate repetitive tasks and handle data processing efficiently, human oversight remains essential for strategic decisions, creative thinking, and ethical considerations. Most successful implementations combine AI automation with human expertise, creating collaborative workflows that maximize productivity while maintaining quality control and accountability.
When AI platforms generate incorrect predictions, businesses may face financial losses, reputational damage, or operational disruptions. Mitigation strategies include implementing validation layers, continuous monitoring systems, and human review processes for critical decisions. Regular model retraining, diverse training datasets, and establishing fallback mechanisms help minimize errors. Organizations should also maintain audit trails to identify and correct systematic issues promptly.
Training duration depends on model complexity, dataset size, and computational resources. Simple models may train within hours, while complex deep learning models can take days or weeks. Cloud based platforms with GPU acceleration significantly reduce training time. Transfer learning techniques allow leveraging pre trained models, cutting training periods from weeks to mere hours for many applications.
Most cloud based AI platforms require internet connectivity for processing and model updates. However, edge AI solutions and on premise deployments can function offline once deployed. Hybrid architectures allow local processing for time sensitive tasks while syncing with cloud services periodically. The choice depends on latency requirements, data privacy concerns, and operational environment constraints.
Python remains the dominant language for AI due to extensive library support. However, modern AI platforms increasingly offer no code and low code interfaces, eliminating programming requirements for basic users. R, Java, and JavaScript are also supported. Many platforms provide visual drag and drop tools, making AI accessible to business users without technical backgrounds.
Most enterprise AI platforms offer robust integration capabilities through APIs, connectors, and middleware solutions. They support common database formats, CRM systems, ERP software, and data warehouses. Integration complexity varies based on legacy system architecture. Pre built connectors accelerate deployment, while custom integrations may require additional effort and technical expertise.
AI platforms require regular maintenance including model retraining, security patches, and performance optimization. Retraining frequency depends on data drift and changing business conditions, typically ranging from monthly to quarterly. Cloud platforms handle infrastructure maintenance automatically, while on premise solutions require dedicated IT resources. Continuous monitoring helps identify when updates become necessary.
Traditional automation follows predefined rules and cannot adapt to new scenarios without reprogramming. AI platforms learn from data, recognize patterns, and improve over time through machine learning. They handle unstructured data like images and text, make predictions, and adapt to changing conditions autonomously. This intelligence enables handling complex, variable tasks impossible for rule based systems.
Startups can leverage AI platforms effectively despite limited data through several approaches. Transfer learning uses pre trained models requiring minimal additional data. Synthetic data generation creates training datasets artificially. Many platforms offer pre built models for common use cases. Starting with simpler algorithms and scaling complexity as data accumulates provides a practical pathway for data constrained organizations.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.