Blockchain has changed how we store, transfer, and verify data. Whether you send cryptocurrency, interact with a smart contract, or mint an NFT, every action becomes a transaction on the blockchain. But how does the system check that your transaction is valid? How does it prevent double spending? And how do thousands of nodes agree on the same version of truth?
This article explains how transactions are verified in blockchain, step by step, using simple language. You will learn how miners or validators approve transactions, how consensus mechanisms work, and why blockchain is considered secure. Several external resources are also included as anchor text for further exploration.
1. Understanding What a Blockchain Transaction Really Is
A blockchain transaction is a digital record showing the transfer of data, assets, or information on a decentralized network. For example:
- Sending Bitcoin from one wallet to another
- Logging supply chain information
- Executing a smart contract
- Voting in a blockchain-based governance system
Each transaction contains three basic elements:
- Sender address
- Receiver address
- Amount or action taken
Before a transaction is added to the blockchain, it must be checked, validated, and added to a block. This is handled by thousands of computers (nodes) across the world.
Learn more in Bitcoin’s official documentation.
2. Step-by-Step Process of How a Blockchain Transaction Is Verified
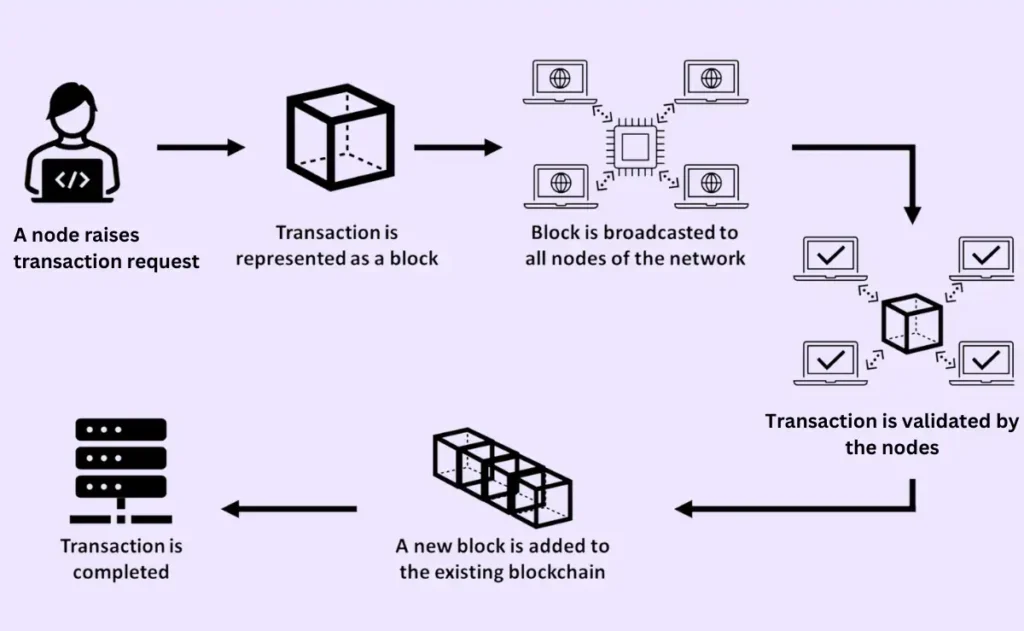
This is the core verification flow used in almost every blockchain network:
Step 1: The User Creates a Transaction
The process starts when a user submits a transaction through:
- A crypto wallet
- A decentralized application
- A smart contract
- An exchange
The wallet cryptographically signs the transaction using something called a private key, proving the sender’s identity.
To understand cryptographic signatures, refer to NIST’s Digital Signature Standard Guide.
Step 2: Nodes Receive and Validate Basic Rules
After the user submits the transaction:
- It is broadcast to the network.
- Nodes receive the transaction.
- They check for basic rules:
- Is the digital signature valid?
- Is the sender’s balance sufficient?
- Is the transaction formatted correctly?
If it passes these rules, it enters the mempool (a temporary waiting area).
Step 3: Miners or Validators Select Transactions
Blockchain networks must decide who gets to verify a transaction. This depends on the consensus mechanism used:
- Proof of Work (PoW) → miners (Bitcoin)
- Proof of Stake (PoS) → validators (Ethereum)
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) → elected validators (EOS, Tron)
- Proof of Authority (PoA) → approved validators (private blockchains)
Validators pick legitimate transactions from the mempool to include in the next block.
To explore consensus mechanisms, check Ethereum’s developer resources.
Start Your Blockchain Journey Today
If you want to build blockchain solutions, integrate crypto payments, or create secure decentralized applications, Nadcab Labs can help you at every step.
Step 4: Validators Verify Transactions Thoroughly
Before adding a transaction to a block, validators perform deeper checks:
- Confirm that inputs haven’t been spent before (prevents double spending)
- Validate the sender’s signature again
- Verify timestamp
- Confirm network rules (gas limit, nonce, fees, etc.)
If everything is valid, the validator includes it in the block.
Step 5: A Block Is Created with Verified Transactions
Once enough transactions are verified, they’re grouped into a block. The block contains:
- A block header
- List of verified transactions
- Merkle root
- Timestamp
- Previous block hash
This block is then proposed to the network for approval.
Merkle trees play a vital role here; see IBM’s Blockchain Merkle Tree Explanation.
Step 6: Consensus Mechanism Confirms the Block
Before a block is added to the chain, the entire network must agree that:
- The block is valid
- The miner or validator followed rules
- The block fits the chain
This is where the consensus algorithm comes into action.
If PoW (Proof of Work):
Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle.
First one to solve it wins and adds the block.
More details in Investopedia’s Proof of Work guide.
If PoS (Proof of Stake):
Validators with staked tokens get selected.
They approve the block based on an economic incentive.
Learn more from Ethereum’s PoS explanation.
Step 7: Block Is Added to the Blockchain & Finalized
Once consensus is achieved:
- The block is added to the chain.
- All nodes update their ledgers.
- The transaction becomes final and irreversible.
This is what gives blockchain its immutability and security.
3. Why Transaction Verification Is Necessary
Transaction verification is the foundation of trust in any blockchain network. Because blockchain does not rely on banks, government agencies, or centralized authorities, it needs a strong method to confirm that every transaction is valid. Verification ensures that every activity recorded on the blockchain follows strict rules so the system remains secure and reliable. Verification ensures that no one can:
- Double Spending
- Fake signatures
- Change transaction history
- Control the network
- Insert false data
Blockchain is decentralized; no bank or authority controls it.
This makes verification essential.
According to The World Economic Forum’s blockchain report, verification is one of the main reasons blockchain is trusted globally.
4. Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake in Transaction Verification
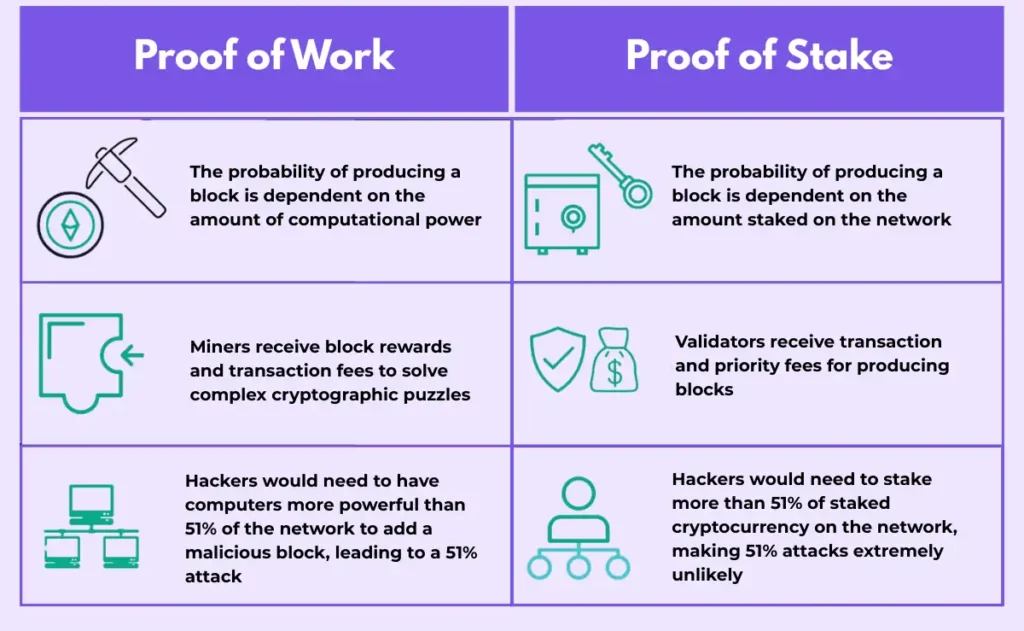
While both PoW and PoS validate transactions, they do it differently. Both mechanisms ensure the network remains secure and trustworthy, but each uses a completely different approach, resource requirement, and verification method to achieve consensus.
1. Proof of Work (PoW)
Used by: Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin
How it works:
- Miners compete using computational power.
- First miner to solve the puzzle adds the block.
- Receives block reward + transaction fees.
Pros: Highly secure
Cons: Energy-intensive
More details: Bitcoin Mining Overview – Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance
2. Proof of Stake (PoS)
Used by: Ethereum, Cardano, Solana
How it works:
- Validators stake tokens.
- Network randomly selects validators.
- They verify transactions and create blocks.
Pros: Energy efficient
Cons: Risk of centralization if big holders dominate staking
Deep dive: Cardano PoS Research Paper
5. The Role of Nodes in Blockchain Verification
Nodes are the computers that maintain the blockchain. Each node has one job:
Verify every new transaction and block.
Types of nodes:
1. Full Nodes
- Store the entire blockchain
- Validate all transactions independently
- Prevent rule violations
2. Light Nodes
- Store only essential data
- Depend on full nodes for verification
- Common in mobile wallets
3. Mining/Validator Nodes
- Validate transactions
- Produce blocks
- Earn rewards
Nodes ensure that the blockchain is distributed, reliable, and censorship resistant.
6. What Makes Blockchain Transaction Verification Secure?
Blockchain relies on multiple layers of security, combining cryptography, decentralized validation, and consensus rules that prevent unauthorized changes. These layers work together to ensure every transaction is checked, verified, and permanently recorded without relying on a central authority.
1. Cryptography
Every transaction is secured using advanced cryptographic functions.
Introduction to cryptography by NIST:
NIST Cryptographic Standards
2. Decentralization
Thousands of independent nodes verify the same data.
No single entity can alter records.
3. Consensus Mechanisms
Algorithmic agreement ensures trust among participants.
4. Immutable Ledger
Once a block is added, it cannot be changed.
5. Transparency
Every transaction is visible on explorers like:
- Blockchain.com Explorer
- Etherscan
- Solscan
This combination makes blockchain resistant to fraud, hacking, and manipulation.
7. Future Trends in Blockchain Transaction Verification
Blockchain verification continues to evolve. Some promising advancements include stronger cryptographic methods, faster consensus models, enhanced privacy tools, and AI-driven verification techniques that reduce errors, improve scalability, and make transaction validation more efficient for large, global blockchain networks. Some promising advancements include:
1. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)
Allows verifying transactions without revealing sensitive data.
2. Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Networks like Polygon, Optimism, and Arbitrum process transactions faster and cheaper.
3. Sharding
Dividing blockchain into smaller parts for faster verification.
Learn more: Ethereum Sharding Roadmap
4. AI-Assisted Validation
AI can help detect suspicious activities, optimize gas fees, and speed up verification.
5. Green Consensus Models
New low-energy mechanisms such as Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) are emerging.
Final Overview
Blockchain transaction verification is the foundation of trust in decentralized networks. Each step in the process, from confirming digital signatures and checking wallet balances to reaching agreement through methods like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, works together to keep every transaction secure, transparent, and protected from tampering. This layered approach prevents fraud, stops double spending, and maintains the reliability that blockchain is known for.
As the technology continues to advance, verification will become faster, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly. New consensus methods, stronger cryptographic techniques, and better network infrastructure are shaping a future where transaction validation will be even more dependable and scalable across different industries.
To understand how blockchain achieved this level of security, it is helpful to look at its past. You can explore the history of blockchain to see how verification has evolved and why it is such an important part of the technology today.
Businesses and startups looking to build secure digital platforms or explore decentralized applications often rely on teams with deep expertise in blockchain architecture. Partnering with professionals who provide complete blockchain support and blockchain solutions, such as the services offered by Nadcab, helps ensure their systems follow strong verification standards and maintain a high level of security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a blockchain transaction?
A blockchain transaction is a digital action recorded on a decentralized ledger, confirming ownership transfer or execution of data securely without a central authority.
How long does a blockchain transaction take?
A blockchain transaction time depends on network load, fees, and consensus type. It may take seconds or several minutes until confirmed and added to the chain.
Can a blockchain transaction be reversed?
Once confirmed, a blockchain transaction cannot be reversed because the ledger is immutable. Any correction must happen through a new transaction, not editing the previous one.
Why does a blockchain transaction need confirmation?
Confirmation prevents fraud, double spending, and unauthorized transfers. Nodes verify every detail before adding it to the chain, ensuring accuracy, transparency, and network trust.
What affects blockchain transaction fees?
Fees depend on network activity, block space, and transaction size. Higher fees may speed confirmation because validators prioritize profitable transactions.
How do I track a blockchain transaction status?
You can track a blockchain transaction using an explorer like Etherscan or Blockchain.com by entering the transaction hash to view confirmations and details.