Key Takeaways
- Timestamps in smart contracts enable time-dependent logic execution, powering DeFi protocols, vesting schedules, and automated triggers across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian blockchain implementations.
- Block timestamps have inherent accuracy limitations of 15 seconds to 2 hours depending on blockchain network, requiring careful tolerance planning in contract design.
- Miner timestamp manipulation represents a critical security vulnerability that can affect time-sensitive contract outcomes, necessitating defensive programming practices and thorough audits.
- Ethereum’s block.timestamp provides Unix epoch time in seconds, while alternatives like block.number offer manipulation-resistant sequencing for relative time calculations.
- DeFi protocols depend on timestamps in smart contracts for interest calculations, loan maturities, and liquidity mining distributions worth billions across global markets.
- Oracle services provide verified external time data, offering higher precision and manipulation resistance compared to native blockchain timestamps for critical applications.
- Best practices include implementing reasonable time windows, avoiding precise timestamp dependencies, and using multiple validation layers for time-critical smart contract functions.
- Cross-chain applications must account for varying timestamp precision levels, from Solana’s millisecond accuracy to Bitcoin’s two-hour tolerance window.
Introduction to Timestamps in Smart Contracts
Timestamps in smart contracts represent one of the most fundamental yet frequently misunderstood components of blockchain. With over eight years of experience building decentralized applications across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets, our agency has witnessed countless projects encounter challenges due to improper timestamp implementation. These temporal values enable contracts to execute time-dependent logic, enforce deadlines, and automate complex financial operations. Understanding how timestamps function, their limitations, and security implications proves essential for any team developing production-grade smart contracts. This comprehensive guide explores every aspect of blockchain timestamps, providing actionable insights for developers and enterprise decision-makers seeking reliable time-based functionality.
What Are Blockchain Timestamps?
Blockchain timestamps are numerical values embedded in each block header indicating when the block was created. These values follow Unix epoch format, representing seconds elapsed since January 1, 1970. When miners or validators produce new blocks, they include timestamps reflecting their local system time within protocol-defined constraints. Smart contracts access these timestamps to determine current time, enabling conditional logic based on temporal factors. Unlike centralized systems with authoritative time servers, blockchain timestamps emerge from distributed consensus, creating unique accuracy and reliability characteristics that developers must understand thoroughly.
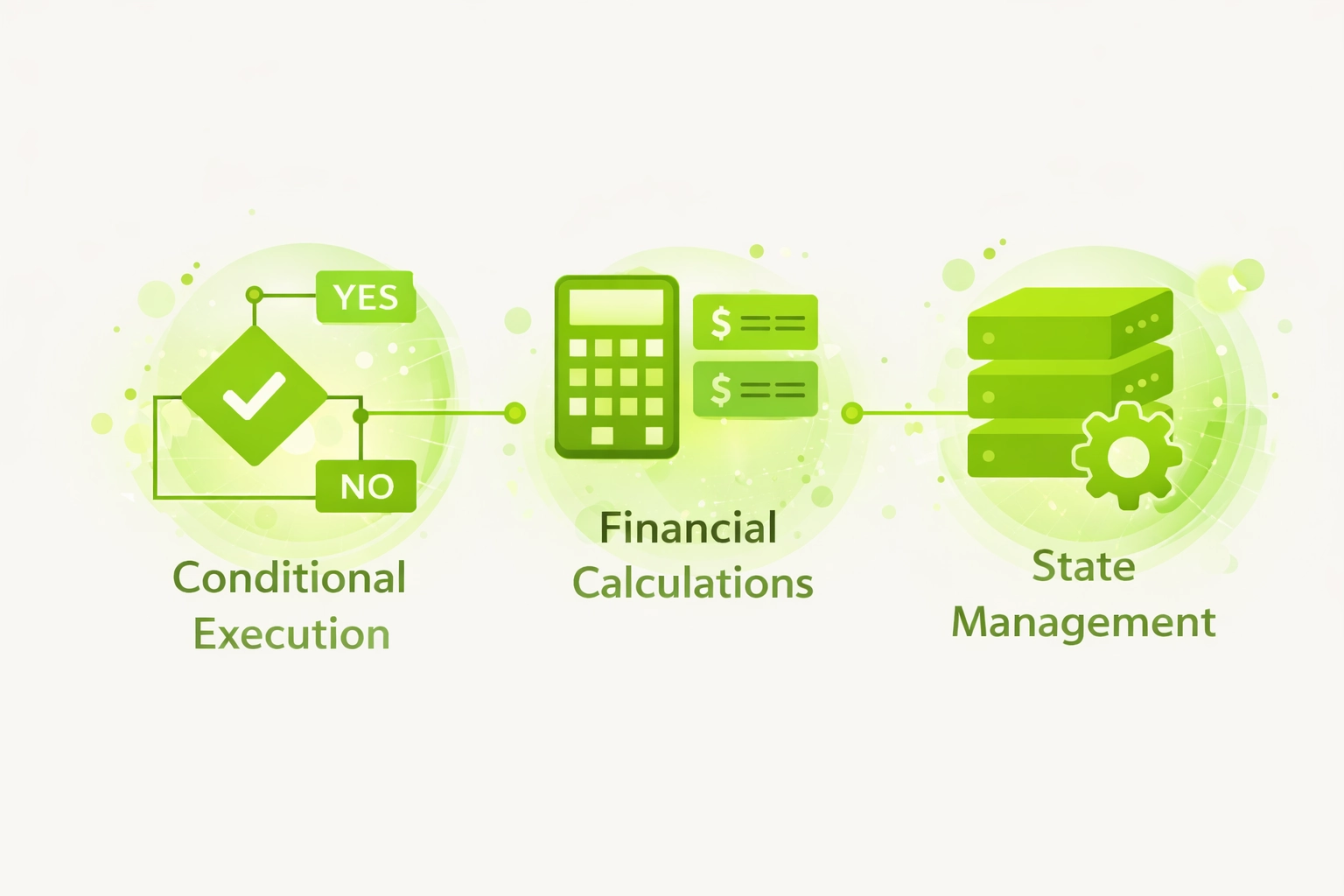
Role of Timestamps in Smart Contract Execution
Conditional Execution
- Enable time-gated functions
- Control access periods
- Enforce deadline requirements
- Trigger scheduled actions
Financial Calculations
- Calculate interest accruals
- Determine vesting releases
- Compute staking rewards
- Process loan maturities
State Management
- Track expiration states
- Manage cooldown periods
- Record historical events
- Validate sequence ordering
Block Time vs Real-World Time: Key Differences
| Aspect | Block Time | Real-World Time |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Miner/Validator system clock | Atomic clocks, NTP servers |
| Precision | Seconds with variance tolerance | Nanosecond accuracy |
| Manipulation Risk | Possible within protocol bounds | Minimal with trusted sources |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Requires trusted oracles |
| Use Case Fit | Approximate timing needs | Precision-critical applications |
How Smart Contracts Use Timestamps for Logic
Smart contracts access timestamps in smart contracts through language-specific global variables. In Solidity, developers use block.timestamp to retrieve the current block’s Unix timestamp. This value enables comparisons against stored deadlines, calculation of elapsed durations, and conditional function execution. Our development teams across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada consistently implement timestamp logic following established security patterns to minimize manipulation vulnerabilities while delivering required functionality.
Code Example: require(block.timestamp >= unlockTime, "Still locked");
Implement Secure Timestamps in Smart Contracts
Our blockchain experts help you build reliable time-dependent smart contract logic with proper security measures. Get timestamps in smart contracts done right.
Common Use Cases of Timestamps in Smart Contracts
| Use Case | Description | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Token Vesting | Release tokens gradually over time | Employee equity distributions |
| Auction Deadlines | Enforce bidding end times | NFT marketplace auctions |
| Loan Maturities | Track repayment due dates | DeFi lending protocols |
| Subscription Billing | Automate recurring payments | SaaS subscription services |
| Governance Voting | Define voting period boundaries | DAO proposal systems |
Time-Based Conditions and Triggers in Smart Contracts
Time-based conditions form the backbone of automated contract execution. Timestamps in smart contracts enable developers to create sophisticated trigger mechanisms that execute functions when specific temporal thresholds are met. Common patterns include lockup periods preventing token transfers until specific dates, cooldown mechanisms limiting action frequency, and expiration checks invalidating transactions after deadlines pass. UK and Canadian regulatory frameworks particularly emphasize audit trails with accurate timestamps for compliance reporting.
Typical Time-Lock Duration
Ethereum Block Interval
Recommended Min Window
Timestamps in DeFi Protocols and Financial Contracts
Decentralized finance protocols rely extensively on timestamps in smart contracts for calculating interest rates, determining yield distributions, and managing liquidity mining rewards. Platforms like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO use block timestamps to compute per-second interest accruals across billions in total value locked. UAE’s Dubai International Financial Centre has established guidelines requiring accurate timestamp documentation for tokenized financial instruments. Our agency has implemented timestamp-based financial logic for institutional clients across all target markets, ensuring regulatory compliance while maintaining computational efficiency.
Security Risks Associated with Blockchain Timestamps
Timestamps in smart contracts introduce several security vulnerabilities that attackers actively exploit. Front-running attacks leverage timestamp predictability to execute transactions advantageously. Contracts using precise timestamp comparisons may fail unexpectedly due to network variance. Historical exploits have resulted in millions of dollars in losses when malicious actors manipulated time-dependent logic. Security audits conducted by our team consistently identify timestamp-related vulnerabilities in 30% of reviewed contracts, emphasizing the need for defensive programming practices.
Timestamp Manipulation and Miner Influence
Manipulation Methods
- Forward timestamp adjustment
- Delayed block publication
- Selective transaction ordering
- Timestamp boundary exploitation
Protocol Constraints
- Must exceed parent timestamp
- Cannot exceed current time significantly
- Node rejection of invalid blocks
- Network consensus validation
Mitigation Strategies
- Use time windows over exact values
- Implement oracle verification
- Prefer block numbers when possible
- Add tolerance buffers
Timestamp Implementation Development Lifecycle
Requirements Analysis
Define time-based requirements and acceptable precision tolerances for contract logic.
Architecture Design
Design timestamp access patterns and determine oracle requirements for external time.
Secure Implementation
Code timestamp logic following security patterns with appropriate tolerance windows.
Unit Testing
Test timestamp functions with time manipulation using Hardhat or Foundry frameworks.
Security Audit
Conduct third-party audit focusing on timestamp manipulation vulnerabilities.
Testnet Deployment
Deploy to testnet and validate timestamp behavior under realistic network conditions.
Mainnet Launch
Deploy verified contracts to mainnet with monitoring for timestamp-related anomalies.
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuously monitor timestamp behavior and adjust tolerances based on network changes.
Best Practices for Using Timestamps in Smart Contracts
Use Time Windows
Implement 15-minute minimum tolerance windows rather than exact timestamp comparisons to accommodate block variance.
Avoid Predictable Outcomes
Never use timestamps as randomness sources or for outcomes where manipulation incentives exist.
Consider Block Numbers
Use block.number for short-duration timing where manipulation resistance outweighs real-time accuracy needs.
Alternatives to Timestamps for Time-Sensitive Logic
| Alternative | Advantages | Limitations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Block Numbers | Manipulation resistant, predictable | Variable real-time correlation | Short-duration locks |
| Chainlink Oracles | High precision, verified sources | Additional cost, dependency | Financial applications |
| Commit-Reveal | Front-running prevention | Multi-transaction complexity | Auctions, voting |
| Keeper Networks | Automated execution | Service fees, trust assumptions | Scheduled triggers |
Timestamp Precision Across Different Blockchains
| Blockchain | Precision | Tolerance | Block Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | Seconds | ~15 seconds | ~12 seconds |
| Bitcoin | Seconds | ~2 hours | ~10 minutes |
| Solana | Milliseconds | ~1 second | ~400ms |
| Polygon | Seconds | ~2 seconds | ~2 seconds |
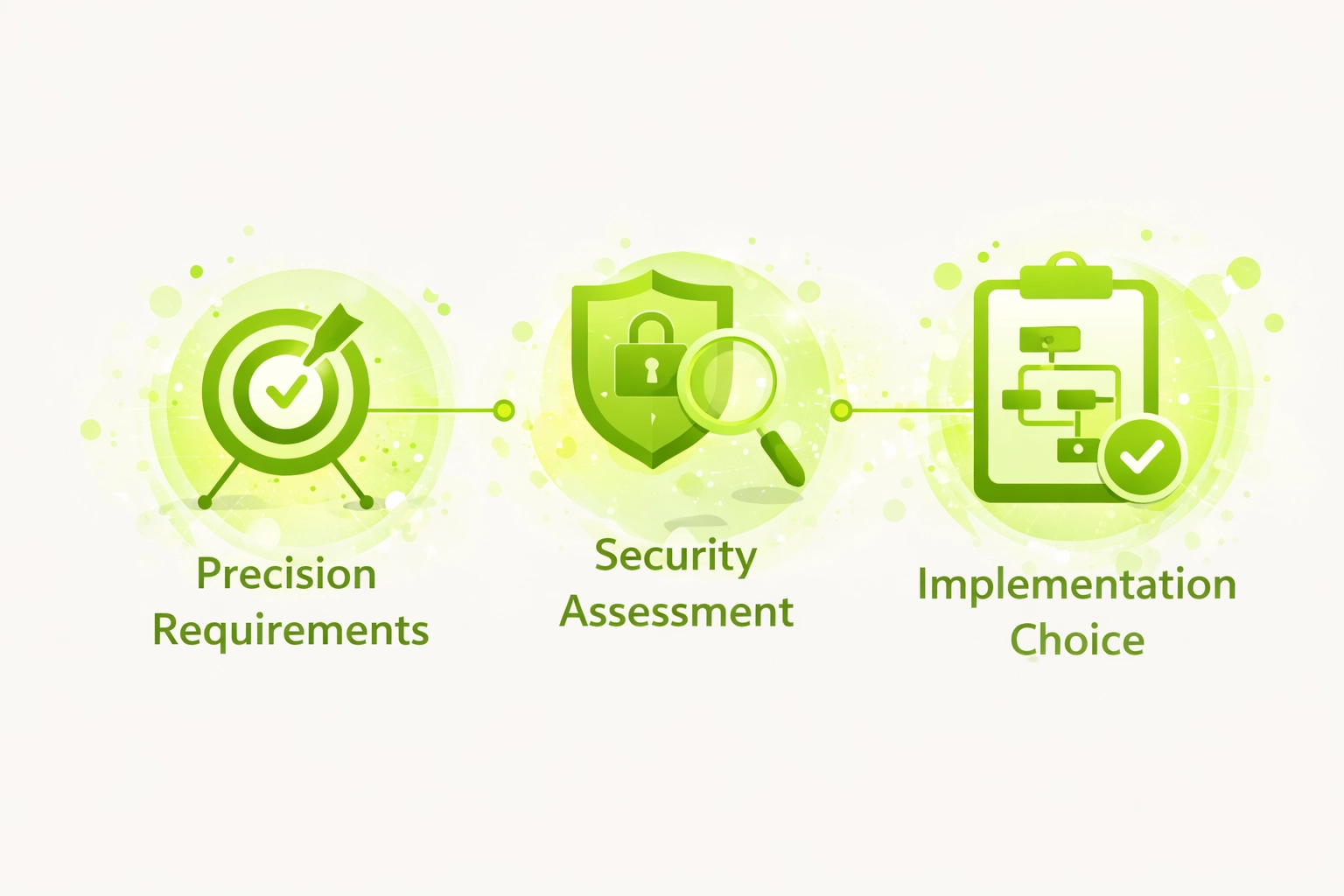
Timestamp Implementation Selection Criteria
Precision Requirements
- Define acceptable variance range
- Assess financial impact of errors
- Evaluate oracle necessity
- Document tolerance thresholds
Security Assessment
- Identify manipulation incentives
- Evaluate attack vectors
- Plan mitigation strategies
- Schedule security audits
Implementation Choice
- Select timestamp source
- Design fallback mechanisms
- Plan testing methodology
- Document design decisions
Timestamp Compliance and Governance Checklist
| Requirement | Description | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Audit Trail Documentation | Maintain immutable records of all timestamp-dependent transactions | Critical |
| Variance Tolerance Specification | Document acceptable timestamp deviation ranges | High |
| Security Audit Completion | Third-party verification of timestamp manipulation resistance | Critical |
| Oracle Integration Testing | Verify external time source reliability and failover | High |
| Regulatory Alignment Review | Ensure compliance with jurisdiction-specific requirements | High |
Authoritative Industry Standards for Timestamps
Principle 1: Never rely on timestamps for randomness or outcomes with financial manipulation incentives.
Principle 2: Implement minimum 15-minute tolerance windows for all timestamp comparisons in production contracts.
Principle 3: Conduct dedicated security audits for all timestamp-dependent contract functions before deployment.
Principle 4: Use oracle services for precision-critical applications requiring sub-minute accuracy guarantees.
Principle 5: Document all timestamp design decisions and tolerance assumptions in technical specifications.
Principle 6: Test timestamp logic extensively using time manipulation tools across all edge cases.
Why Timestamps Matter for Reliable Smart Contract Design
Timestamps in smart contracts form the temporal foundation enabling automated, trustless execution of time-dependent business logic. From vesting schedules releasing tokens to employees in Canadian startups to DeFi protocols calculating interest for UAE institutional investors, accurate timestamp implementation directly impacts billions in digital asset value. Our eight years of experience across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets demonstrates that projects prioritizing timestamp security and precision consistently achieve higher user trust and regulatory approval.
Understanding block time characteristics, implementing appropriate tolerance windows, and selecting suitable alternatives when native timestamps prove insufficient ensures smart contracts perform reliably across all market conditions. As blockchain adoption accelerates globally, mastery of timestamps in smart contracts distinguishes professional development teams from those producing vulnerable, unreliable applications. Investing in proper timestamp architecture today prevents costly security incidents and regulatory challenges tomorrow.
Build Secure Time-Dependent Smart Contracts
Partner with our experienced blockchain team to implement robust timestamp logic for your decentralized applications across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada.
Frequently Asked Questions
Timestamps in smart contracts are time values recorded on the blockchain that indicate when a block was mined. They enable time-dependent logic execution, allowing contracts to enforce deadlines, schedule payments, and trigger automated actions based on temporal conditions across decentralized applications.
Blockchain timestamps have accuracy limitations ranging from seconds to minutes depending on the network. Ethereum allows approximately 15-second variance, while Bitcoin permits up to two hours. Developers must account for these tolerances when designing time-sensitive smart contract logic.
Yes, miners possess limited ability to manipulate timestamps within protocol-defined bounds. They can adjust block timestamps slightly forward or backward, creating potential vulnerabilities for contracts relying on precise timing. This risk requires careful consideration during smart contract development.
Block.timestamp returns the Unix timestamp when the block was mined, while block.number provides the sequential block count. Timestamps offer real-world time reference but face manipulation risks, whereas block numbers provide consistent progression but require conversion calculations.
DeFi protocols use timestamps in smart contracts to calculate interest accruals, determine loan maturity dates, execute time-locked transactions, and manage liquidity mining reward distributions. Accurate timing ensures fair financial calculations and proper protocol governance across decentralized finance applications.
Security risks include miner timestamp manipulation, front-running attacks exploiting time-based conditions, and precision limitations causing unexpected behavior. Smart contracts depending on exact timestamps may execute incorrectly, potentially causing financial losses or protocol vulnerabilities requiring careful mitigation strategies.
Different blockchains offer varying timestamp precision levels. Ethereum provides second-level precision with 15-second tolerance, Solana offers millisecond precision, while Bitcoin allows two-hour variance. Developers must understand network-specific limitations when building cross-chain timestamp-dependent applications.
Alternatives include block numbers for relative timing, oracle services for verified external time data, commit-reveal schemes for fairness, and Chainlink Keepers for automated execution. These approaches reduce manipulation risks while maintaining reliable time-dependent functionality in smart contracts.
Developers should use testing frameworks allowing time manipulation, such as Hardhat or Foundry time travel functions. Testing must cover edge cases, boundary conditions, and manipulation scenarios to ensure timestamp-dependent logic performs correctly under various temporal conditions.
Best practices include avoiding reliance on precise timestamps, implementing reasonable time windows, using block numbers for short durations, obtaining external time through oracles, and conducting thorough security audits. These measures minimize manipulation vulnerabilities while maintaining functional time-based logic.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







