Key Takeaways
- A replay attack in blockchain occurs when an attacker intercepts and maliciously rebroadcasts valid transaction data to execute unauthorized transfers, exploiting the lack of transaction uniqueness validation across networks or time periods.
- Blockchain replay attacks most commonly emerge during hard forks and cross-chain operations, where identical transaction formats on different networks allow attackers to duplicate legitimate transfers without additional authorization.
- The primary protection mechanisms against replay attacks include nonce-based transaction sequencing, chain-specific identifiers like EIP-155 in Ethereum, timestamp validation, and cryptographic signature binding to specific network parameters.
- Replay attacks in blockchain can result in substantial financial losses, with victims unknowingly having their transactions duplicated across forked chains, effectively doubling their cryptocurrency expenditures without consent.
- Smart contracts and decentralized applications face particular vulnerability to replay attacks when they fail to implement proper message authentication, nonce tracking, and chain-specific validation in their security architecture.
- The Ethereum and Ethereum Classic fork demonstrated real-world replay attack consequences, prompting industry-wide adoption of standardized replay protection protocols now considered essential in blockchain security best practices.
- Cross-chain replay attacks represent an evolving threat as blockchain interoperability increases, requiring sophisticated protection mechanisms that validate transaction context across multiple network environments.
- Organizations building blockchain systems must incorporate replay attack prevention from the initial design phase, implementing multiple layers of protection including network-level, protocol-level, and application-level security measures.
The expanding blockchain ecosystem has introduced revolutionary capabilities for decentralized transactions, smart contracts, and digital asset management across global financial markets. However, this innovation comes with unique security challenges that demand specialized understanding and protective measures. Among the various blockchain security attacks, replay attacks represent a particularly insidious threat that can compromise transaction integrity and cause significant financial harm to unsuspecting users. These attacks exploit fundamental characteristics of blockchain transaction validation, leveraging the portability of digital signatures across different network contexts. Understanding replay attacks is essential for anyone building, managing, or transacting on blockchain networks, whether handling cryptocurrency exchanges, implementing smart contracts, or managing enterprise blockchain solutions. The consequences of inadequate replay protection have been demonstrated repeatedly throughout blockchain history, from major fork events to cross-chain bridge exploits, resulting in millions in losses and undermined confidence in affected platforms.
What is a Replay Attack in Blockchain?
A replay attack represents a form of network attack where valid data transmission is maliciously intercepted and subsequently retransmitted or delayed to deceive the receiving system into unauthorized actions. In blockchain contexts, this attack vector specifically targets the immutable and transparent nature of distributed ledger transactions. When an attacker captures a legitimate blockchain transaction containing valid cryptographic signatures and transaction data, they can rebroadcast this information to execute duplicate transfers across different blockchain networks or at different times. The fundamental vulnerability lies in how blockchain networks validate transactions through digital signatures without always verifying the specific network context or temporal uniqueness of each operation.
The mechanics of a replay attack in blockchain exploit the fact that digital signatures prove authorization for specific transaction data but do not inherently bind that authorization to a single execution context. This becomes particularly problematic during blockchain forks, where two networks suddenly exist with identical transaction histories but separate futures. A transaction intended for one chain can be captured and replayed on the other chain because both networks recognize the same cryptographic signatures and account structures. The attack succeeds silently, with victims often unaware their transactions have been duplicated until they notice unexpected balance changes or review their transaction history across multiple chains.
Definition of Replay Attack
In formal security terminology, what is a replay attack can be defined as a network assault where an attacker intercepts data transmission between legitimate parties and retransmits the captured data to achieve unauthorized outcomes. The attack relies on the validity and authenticity of the original transmission, which the receiving system cannot distinguish from a malicious replay without additional security mechanisms. In traditional network security, replay attacks might target authentication systems, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access by replaying captured login credentials. The attack succeeds because the receiving system processes the replayed data as if it were a fresh, legitimate request rather than recognizing it as a duplicate of previous communication.
Within blockchain ecosystems, the replay attack definition extends to include the unauthorized rebroadcast of transaction data across different blockchain networks or within the same network at different times. The attack exploits the cryptographic signature’s validity independent of network context or temporal constraints. Unlike traditional replay attacks that might be prevented through session tokens or timestamps, blockchain replay attacks leverage the distributed nature of ledger systems where transaction data exists publicly and signatures remain mathematically valid regardless of when or where they are verified. This characteristic makes blockchain networks particularly susceptible to replay attacks during periods of network uncertainty, such as hard forks or cross-chain operations.
Replay Attacks in Blockchain Explained
Replay attacks in blockchain function by exploiting the portability of cryptographically signed transactions across different execution contexts. When a user initiates a blockchain transaction, they create a data structure containing transfer details such as sender address, recipient address, amount, and additional parameters. This data is then signed using the sender’s private key, creating a digital signature that proves authorization. Under normal circumstances, this signed transaction is broadcast to the intended blockchain network, validated by nodes, and included in a block. However, because the signature is mathematically valid independent of network context, the same signed transaction data can potentially be broadcast to different blockchain networks that recognize the same signature format.
The vulnerability becomes acute when blockchain networks share common origins or compatible transaction formats. Consider a scenario where a blockchain undergoes a hard fork, splitting into two separate networks. Users who held balances on the original chain suddenly have equivalent balances on both resulting chains. If someone sends cryptocurrency on one chain, an attacker who observes this transaction can capture the signed transaction data and rebroadcast it on the other chain. Because both chains recognize the same addresses and signature schemes, the replayed transaction appears valid and gets processed, effectively duplicating the original transfer across both networks without the sender’s knowledge or additional consent. This mechanism has caused significant confusion and financial losses during major blockchain forks throughout the industry’s history.
Why Replay Attacks Are a Serious Blockchain Security Risk
The severity of replay attack crypto threats stems from multiple factors that compound their potential for damage. First, these attacks can be executed with relatively minimal technical expertise once an attacker understands the basic mechanics of transaction broadcasting. Unlike sophisticated exploits requiring deep protocol knowledge or significant computational resources, replay attacks simply involve capturing publicly available transaction data and rebroadcasting it to alternative networks. The transaction data exists openly on the blockchain, eliminating the need for complex interception mechanisms. This accessibility makes replay attacks a common threat that numerous opportunistic actors can attempt during vulnerable periods.
Security Warning: Blockchain networks without proper replay protection mechanisms remain critically vulnerable during fork events and cross-chain operations. Users should verify replay protection status before transacting during these high-risk periods to prevent unauthorized transaction duplication and financial losses.
The financial implications of blockchain replay attacks can be devastating for both individual users and the broader ecosystem. When a replay attack succeeds, victims effectively lose cryptocurrency equivalent to their intended transaction amount on the secondary chain. If someone sends 10 ETH to a friend on one chain and the transaction is replayed on another chain, they have now sent 10 ETH on both chains, doubling their expenditure. For users holding significant balances or executing large transfers, this can result in substantial unintended losses. Beyond direct financial harm, replay attacks undermine trust in blockchain networks, particularly affecting enterprise adoption where security guarantees are paramount. The attacks also create complex recovery challenges, as transactions executed on public blockchains are generally irreversible, leaving victims with limited recourse once a replay attack succeeds.
How Replay Attacks Work in Blockchain Networks
Understanding the technical mechanics of how replay attacks operate requires examining the fundamental components of blockchain transactions and their validation processes. Blockchain transactions consist of several key elements including sender and recipient addresses, transaction amounts, transaction fees, and crucially, digital signatures that authorize the transfer. When a user initiates a transaction, their wallet software constructs this data structure and uses their private key to generate a cryptographic signature. This signature mathematically proves that the holder of the private key authorized this specific transaction data. The signed transaction is then broadcast to the peer-to-peer network where nodes validate the signature against the sender’s public key before including the transaction in the blockchain.
The replay attack exploits a critical characteristic of this process: the digital signature validates the transaction data itself but does not inherently specify which blockchain network should process it. In networks lacking replay protection, the signature remains mathematically valid regardless of which compatible blockchain attempts to verify it. An attacker monitoring blockchain transactions can identify valuable transfers, extract the complete signed transaction data from the blockchain, and rebroadcast it to alternative networks. The alternative network, seeing a properly signed transaction with valid addresses and sufficient balances, processes the transfer as legitimate. This occurs because the blockchain cannot distinguish between the original transaction broadcast and the malicious replay without additional contextual validation mechanisms.
Understanding Blockchain Transactions and Digital Signatures
Blockchain transactions represent digitally signed instructions for state changes within the distributed ledger system. Each transaction contains specific fields defining the operation: the sender’s address derived from their public key, the recipient’s address, the amount to transfer, transaction fees to incentivize validators, and additional data depending on the blockchain’s capabilities. These elements are combined into a specific data structure that gets serialized into a standardized format. The transaction creator then generates a cryptographic hash of this data and signs it using their private key, producing a digital signature that proves authorization without revealing the private key itself.
The security of this system relies on elliptic curve cryptography and hash functions that make it computationally infeasible to forge signatures or derive private keys from public information. When a blockchain node receives a transaction, it extracts the signature, recovers the public key from the signature and transaction data, derives the sender’s address from this public key, and verifies that this address matches the claimed sender and has sufficient balance. If all checks pass, the transaction is considered valid and eligible for inclusion in the blockchain. However, this validation process focuses on cryptographic authenticity and account state rather than network-specific context, creating the vulnerability that replay attacks exploit.
Role of Digital Signature Security
Digital signatures serve as the cornerstone of blockchain security, providing authentication, non-repudiation, and data integrity for all transactions. The cryptographic algorithms underlying these signatures, typically ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) in most blockchains, ensure that only the holder of a private key can create valid signatures for transactions from associated addresses. This mechanism prevents unauthorized transfers and enables trustless operation where parties can verify transaction authenticity without requiring trusted intermediaries. The mathematical properties of elliptic curve cryptography ensure that even slight modifications to transaction data invalidate the signature, protecting against tampering.
However, the very strength of digital signatures contributes to replay attack vulnerability. Because signatures cryptographically bind to transaction data rather than execution context, a valid signature remains valid regardless of when, where, or how many times it is verified. The signature proves that the private key holder authorized specific transaction data but says nothing about the intended destination network or whether the transaction should only execute once. This context-agnostic nature of digital signatures means that additional mechanisms must be implemented at the protocol level to prevent replay attacks. Without such mechanisms, the robust security provided by digital signatures becomes a double-edged sword, enabling replay attacks while simultaneously making blockchain transactions secure against forgery.
Transaction Hash and Signature Reuse
Each blockchain transaction generates a unique cryptographic hash that serves as its identifier within the network. This transaction hash is calculated by applying a cryptographic hash function to the complete transaction data including all fields and the digital signature. The hash provides a fingerprint that uniquely identifies this specific transaction, allowing nodes to reference and track it efficiently. In properly designed systems, each transaction hash should be unique and appear only once in the blockchain’s history. However, the transaction hash alone does not prevent replay attacks because it identifies the transaction data package rather than constraining where or when that package can be executed.
Signature reuse represents the core mechanism enabling replay attacks. When an attacker captures a signed transaction from one blockchain, they possess all components necessary to reconstruct and rebroadcast it on compatible networks. The signature remains cryptographically valid because it was generated correctly for the transaction data using the legitimate sender’s private key. Different blockchain networks processing the same signed transaction will generate identical transaction hashes because the underlying data is identical. This reuse becomes problematic when multiple networks share compatible transaction formats and address systems. The blockchain receiving the replayed transaction has no inherent way to determine whether this is the original execution or a malicious replay without implementing specific anti-replay mechanisms that validate network context or execution history.
Step-by-Step Replay Attack Example in Blockchain
To illustrate how a blockchain replay attack unfolds, consider a practical scenario involving a hard fork event. Imagine a blockchain called Chain A undergoes a contentious hard fork, splitting into Chain A and Chain B. Before the fork, Alice held 100 tokens on Chain A. After the fork, Alice finds herself with 100 tokens on Chain A and 100 tokens on Chain B because both chains share identical transaction history up to the fork point. Alice wants to send 50 tokens to Bob on Chain A for a legitimate business transaction. She constructs a transaction using her wallet, signs it with her private key, and broadcasts it to the Chain A network.
The transaction gets processed on Chain A as intended, transferring 50 tokens from Alice to Bob. However, Carol, an attacker monitoring blockchain activity, observes Alice’s transaction on Chain A. Carol extracts the complete transaction data including Alice’s digital signature from the Chain A blockchain, which is publicly accessible. Carol then takes this exact transaction data and rebroadcasts it to the Chain B network. Because Chain B recognizes the same signature format, address system, and has the same pre-fork balances, it sees Alice’s signature as valid authorization to transfer 50 tokens to Bob on Chain B. The transaction gets processed, and now Alice has unintentionally sent 50 tokens to Bob on both Chain A and Chain B, while she only intended the transfer on Chain A. Alice has effectively lost 50 tokens on Chain B without her knowledge or additional consent, demonstrating the direct financial harm from a replay attack.
Replay Attack Crypto Scenario Explained Simply
To understand replay attack crypto scenarios in simpler terms, think of digital signatures as authorized checks that can be cashed at different banks. Imagine you write a check for $1000 to pay a contractor, sign it, and hand it to them. In the traditional banking system, once this check is cashed at your bank, it cannot be cashed again because the bank records the transaction and marks the check as processed. However, imagine if multiple banks existed that all accepted your checks, and there was no communication between them. The contractor could potentially take your signed check to multiple banks and cash it repeatedly because each bank independently validates your signature without checking if other banks have already processed this check.
This analogy mirrors how blockchain replay attacks function. Your digital signature on a blockchain transaction is like signing a check, but during forks or across compatible chains, multiple “banks” (blockchain networks) exist that all accept your signature. Without replay protection mechanisms, these networks process your signed transaction independently, each executing the transfer you authorized. The difference from traditional banking is that blockchain transactions are broadcast publicly and networks operate independently without centralized coordination to prevent duplicate processing. This creates opportunities for attackers to replay your transactions across multiple networks, causing you to make the same transfer multiple times when you only intended it once. The solution requires building into the transaction itself information that makes it valid only on one specific network, similar to making checks payable only at specific bank branches.
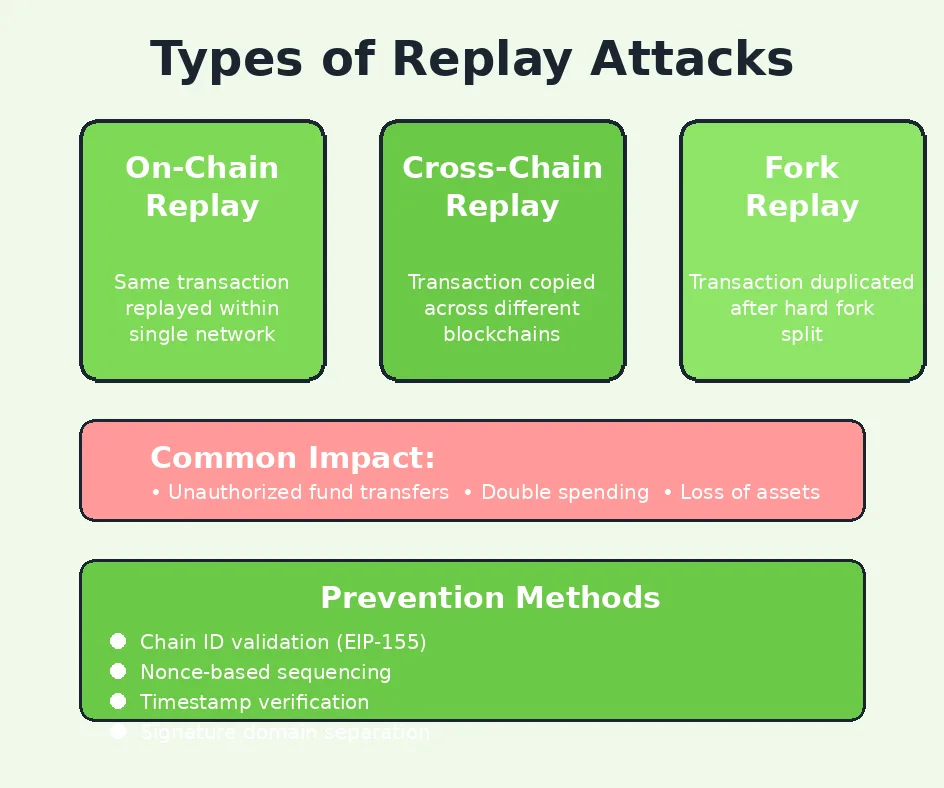
Types of Replay Attacks in Blockchain
Blockchain security attacks through replay mechanisms manifest in several distinct forms, each exploiting different aspects of blockchain architecture and transaction validation. Understanding these variations is essential for implementing comprehensive protection strategies. The primary categories include on-chain replay attacks that occur within a single blockchain network, cross-chain replay attacks that exploit transaction compatibility across different blockchains, and fork-related replay attacks that emerge during network splits. Each type presents unique challenges and requires tailored defensive measures. The sophistication of these attacks has evolved alongside blockchain technology, with attackers continuously identifying new vectors as blockchain interoperability and complexity increase.
| Attack Type | Attack Vector | Common Scenarios | Primary Protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Chain Replay | Transaction rebroadcast within same network | Exploiting missing nonce validation or timestamp checks | Nonce-based sequencing, transaction uniqueness validation |
| Cross-Chain Replay | Transaction replay across different blockchains | Compatible transaction formats between independent chains | Chain-specific identifiers, unique signature schemes |
| Fork Replay | Transaction duplication after network split | Hard forks creating parallel chains with shared history | Post-fork chain ID implementation, replay-safe transactions |
| Smart Contract Replay | Signature reuse in contract calls | Meta-transactions and delegated operations | Message hash tracking, signature expiration |
On-Chain Replay Attacks
On-chain replay attacks occur within a single blockchain network when inadequate transaction uniqueness validation allows the same transaction to be processed multiple times. While modern blockchains implement robust protections against this through nonce mechanisms and transaction hash tracking, vulnerabilities can still emerge in specific scenarios. These attacks typically exploit edge cases in transaction validation logic, particularly in smart contract interactions where external signatures authorize operations. If a contract fails to maintain proper records of processed signatures or messages, an attacker might replay the same signed authorization multiple times to execute unauthorized operations.
The technical manifestation of on-chain replay attacks often involves meta-transaction patterns where users sign messages off-chain that are later submitted by relayers to execute on-chain operations. If the smart contract processing these signatures does not implement proper replay protection such as maintaining a mapping of used signatures or incorporating nonces, the same signature can be submitted repeatedly. Each submission would appear valid because the cryptographic signature remains correct, but the contract would execute the operation multiple times, potentially draining funds or manipulating state. This vulnerability has been discovered in various DeFi protocols and token contracts, particularly those implementing gasless transactions or delegation features where users sign permissions that get executed by third parties.
Cross-Chain Replay Attack
Cross-chain replay attacks exploit transaction format compatibility between different blockchain networks to duplicate transfers across multiple chains. This attack vector becomes relevant when separate blockchain projects use similar or identical transaction structures, signature algorithms, and address formats. For instance, many Ethereum-compatible chains use the same transaction format and ECDSA signature scheme, creating potential for cross-chain replays if additional protections are not implemented. An attacker monitoring transactions on one chain can capture signed transaction data and attempt to broadcast it on another compatible chain, potentially causing unintended transfers if both chains recognize the same addresses and balances.
The severity of cross-chain replay attacks has increased with the proliferation of blockchain networks and the growing emphasis on interoperability. As more chains adopt compatible standards for developer convenience and ecosystem integration, they inadvertently create replay vulnerabilities if chain-specific protections are not properly implemented. This challenge extends to emerging blockchain architectures that emphasize cross-chain communication and asset portability. The solution requires implementing chain identifiers that become part of the transaction signature, ensuring that signatures created for one chain cannot be considered valid on another chain even if the transaction format is compatible. Without such protections, users risk having their transactions replicated across multiple networks whenever they interact with multi-chain ecosystems.
Blockchain Fork Replay Attack
Blockchain fork replay attacks represent perhaps the most historically significant category of replay attack in blockchain, having affected numerous major cryptocurrency networks during contentious splits. When a blockchain undergoes a hard fork, whether for protocol upgrades or due to community disagreements, it may split into two independent chains that share identical transaction history up to the fork point. If these chains do not implement replay protection immediately after the fork, every transaction broadcast to one chain can be captured and replayed on the other chain. This occurs because both chains inherited the same account balances, address system, and transaction validation rules from their common ancestor.
The mechanism of fork replay attacks creates unique challenges because the vulnerability affects an entire user base simultaneously rather than targeting individual accounts. Every user who held balances before the fork now possesses assets on both resulting chains, and any transaction they make potentially affects both chains unless replay protection is active. This creates a period of heightened risk immediately following forks where users must exercise extreme caution. The complexity intensifies when considering that different stakeholders may have different preferences regarding which chain to transact on, making unintended transfers through replay attacks particularly frustrating. The attacks can continue indefinitely until both chains implement strong replay protection or diverge sufficiently in their transaction formats that replays become technically impossible.
Replay Attacks After Hard Forks
The immediate aftermath of hard forks represents the highest-risk period for replay attacks, as networks transition from unified operation to independent existence. During this critical window, both resulting chains may still accept identical transaction formats, creating perfect conditions for replay vulnerabilities. Users attempting to transact on their preferred chain may inadvertently broadcast transactions that get picked up and replayed on the alternative chain. The confusion is compounded by varying levels of replay protection across different wallet software, exchanges, and blockchain infrastructure. Some wallets may automatically implement client-side replay protection by crafting transactions specific to one chain, while others may not, leaving users vulnerable.
The technical solutions to post-fork replay attacks typically involve implementing changes to transaction validation rules that make transactions on one chain invalid on the other. This can be achieved through several mechanisms including modifying the chain identifier that gets included in transaction signatures, implementing different transaction versioning between chains, or requiring specific markers that only one chain recognizes as valid. However, these protections must be carefully coordinated and clearly communicated to users, as improper implementation can create its own complications. The community must reach consensus on replay protection mechanisms, update wallet software, notify exchanges and service providers, and educate users about safe transaction practices during the transition period. This coordination challenge has proven difficult in several historical forks, resulting in extended periods where replay vulnerabilities persisted.
Ethereum Fork and Replay Attack Risks
The Ethereum and Ethereum Classic fork in 2016 provides the most widely studied example of blockchain replay attack consequences. Following the controversial hard fork that reversed the DAO hack, the blockchain split into two chains: Ethereum (ETH) continuing with the fork and Ethereum Classic (ETC) maintaining the original chain. Initially, neither chain implemented strong replay protection, creating immediate vulnerabilities for users. Transactions broadcast to send ETH on the Ethereum chain could be captured and replayed on the Ethereum Classic chain, and vice versa. This led to widespread confusion and financial losses as users unknowingly made duplicate transactions across both chains.
The Ethereum fork incident catalyzed significant improvements in replay protection standards across the blockchain industry. The vulnerability prompted the creation of EIP-155, which introduced chain-specific transaction signing that prevents cross-chain replay attacks. This proposal made the chain ID a required component of transaction signatures, ensuring that transactions signed for Ethereum could not be valid on Ethereum Classic or any other chain. The implementation of EIP-155 became a template for handling future forks and cross-chain scenarios. However, the transition period revealed numerous complications including exchanges struggling to separate ETH and ETC balances, users accidentally sending funds to wrong chains, and sophisticated attacks exploiting the replay vulnerability for financial gain. These lessons have informed how subsequent forks handle replay protection, with most modern forks implementing chain identifiers from inception.
How Replay Attacks Affect Blockchain and Crypto Users
The impact of replay attacks extends far beyond simple transaction duplication, affecting cryptocurrency transaction security, user confidence, and broader blockchain adoption. When successful, these attacks directly compromise the fundamental promise of blockchain technology that users maintain full control over their assets. The financial consequences manifest immediately as victims discover unexpected transfers they never authorized, effectively doubling their cryptocurrency expenditures or triggering unintended smart contract operations. For individual users, this can mean substantial losses proportional to their transaction amounts, with limited recourse available given blockchain’s irreversible nature.
Beyond direct financial harm, replay attacks create broader market impacts that affect ecosystem health and development. When major replay attack incidents occur, they generate negative publicity that undermines confidence in affected blockchain platforms and cryptocurrency generally. Potential institutional adopters scrutinize security architectures more carefully, and regulatory bodies may cite replay vulnerabilities as evidence of inadequate consumer protection in decentralized systems. The attacks also create operational challenges for exchanges, wallet providers, and other service providers who must implement protective measures, educate users, and potentially process claims related to replay attack losses. These cascading effects make replay protection not merely a technical concern but a fundamental requirement for blockchain viability.
Impact on Cryptocurrency Transaction Security
Replay attacks fundamentally undermine the security guarantees that make cryptocurrency transactions valuable. Users expect that when they digitally sign a transaction authorizing a specific transfer, that authorization executes exactly as intended on the designated network. Replay vulnerabilities violate this expectation by allowing transactions to be duplicated across contexts the user never intended. This creates a breach of transaction integrity where the cryptographic security of digital signatures remains intact, yet the economic outcome diverges from user intent. The psychological impact cannot be understated; users lose confidence in their ability to safely manage digital assets when even properly signed transactions can lead to unexpected consequences.
The security implications extend to how users must approach blockchain interactions during vulnerable periods. Following forks or when transacting on multiple chains, users cannot simply sign and broadcast transactions as they normally would. Instead, they must verify replay protection status, potentially use specialized wallet features, or employ complex workarounds like contract-based transactions that include chain-specific elements. This additional friction degrades user experience and creates barriers to adoption, particularly for less technical users who may not understand the underlying risks. Service providers building crypto exchanges or blockchain platforms must implement additional security layers to protect users, increasing development costs and system complexity while potentially introducing new failure points.
Financial Loss and Double Spending Risks
The direct financial consequences of successful replay attacks can be severe, with victims effectively losing cryptocurrency equivalent to their transaction amounts on secondary chains. Consider a business paying suppliers using cryptocurrency: if a 100 ETH payment gets replayed on Ethereum Classic due to inadequate replay protection, the business has now spent 100 ETH equivalent on both chains when they only intended the payment on one. For organizations managing significant cryptocurrency holdings or conducting regular transactions, replay attacks represent existential financial risks that can result in devastating losses. Unlike traditional payment systems where fraudulent transactions can often be reversed or disputed, blockchain’s immutability means replay attack losses are typically permanent.
While technically distinct from traditional double spending attacks, replay attacks can enable similar outcomes where value is transferred multiple times from a single authorization. The economic impact mirrors double spending from the attacker’s perspective: they potentially receive funds on multiple chains from a single transaction initiated by the victim. This creates complex accounting challenges for businesses and individuals trying to track their cryptocurrency holdings across multiple chains. Organizations must implement robust monitoring systems to detect replay attacks quickly, maintain accurate records across all relevant chains, and develop response procedures for when attacks occur. The financial risk is particularly acute for exchanges, custodial services, and other platforms managing assets on behalf of users, as a single replay attack incident could affect thousands of accounts simultaneously.
Effects on Smart Contracts and dApps
Smart contracts and decentralized applications face unique vulnerabilities to replay attacks that can compromise their functionality and security. Many DeFi protocols, NFT platforms, and Web3 applications rely on off-chain signatures for various operations including gasless transactions, meta-transactions, and delegated operations. When these signatures are not properly protected against replay, attackers can reuse them to execute operations multiple times or in unintended contexts. For example, a signature authorizing a token swap at specific parameters could be replayed multiple times, draining user funds or manipulating market conditions.
The complexity of smart contract replay vulnerabilities stems from the various ways contracts handle external signatures and messages. A properly designed contract must track which signatures have been processed, implement nonce systems for signature sequencing, validate that signatures are intended for the specific contract and chain, and potentially implement time-based expiration for signed authorizations. Failures in any of these areas can create replay vulnerabilities. The problem intensifies in complex DeFi protocols where multiple contracts interact and signatures may flow through several layers of delegation. Similar to other blockchain security threats, replay vulnerabilities in smart contracts require careful architecture and comprehensive testing to prevent exploitation.
Smart Contract Security Vulnerabilities
Smart contract vulnerability to replay attacks typically manifests in functions that accept external signatures as authorization for operations. Common patterns include permit functions that allow users to approve token spending via signatures instead of separate approval transactions, meta-transaction implementations where relayers submit signed user operations, and voting or governance systems where signatures represent votes or proposals. Each of these patterns creates potential replay vectors if not properly secured. The contract must validate not only that the signature is cryptographically valid but also that it has not been used before, is intended for this specific contract instance, and meets any additional context requirements.
Technical implementation of replay protection in smart contracts requires maintaining state that tracks processed signatures or implements nonce systems. A common approach involves maintaining a mapping of signature hashes to boolean values indicating whether each signature has been used. Before processing any signature-authorized operation, the contract checks this mapping and rejects the transaction if the signature has been seen before. Alternatively, nonce-based systems require users to include incrementing nonce values in their signed messages, with the contract rejecting any signature that uses an already-consumed nonce. These protections must be implemented carefully to avoid introducing new vulnerabilities such as denial-of-service vectors where attackers front-run legitimate transactions to consume nonces, or storage exhaustion attacks that manipulate signature tracking mappings.
Replay Attacks in DeFi Applications
Decentralized finance applications face heightened replay attack risks due to their complex interaction patterns and the significant financial value they manage. DeFi protocols frequently implement features like gasless trading, limit orders via signatures, cross-chain operations, and delegated liquidity management, all of which involve users signing messages that get executed later or on different systems. Each of these features creates potential replay vectors. A limit order signature, for instance, might be replayed multiple times if the contract does not properly track executed orders, potentially forcing users to make repeated trades at potentially unfavorable prices.
The financial stakes in DeFi amplify the consequences of replay vulnerabilities. Protocols managing hundreds of millions or billions in total value locked become attractive targets for attackers seeking to exploit replay vulnerabilities for profit. Historical incidents have demonstrated how signature replay in DeFi can lead to substantial losses, with some attacks draining significant portions of protocol reserves. The complexity of DeFi protocols, where multiple contracts interact and liquidity flows between systems, creates additional attack surface. An attacker might replay signatures not just within a single contract but across different protocol versions, forked chains, or related applications that accept compatible signature formats. Protecting against these sophisticated attack vectors requires comprehensive security architecture that extends beyond individual contract-level protections to encompass protocol-wide signature management and validation frameworks.
Replay Attacks in Ethereum Blockchain
Ethereum has experienced some of the most significant replay attack incidents in blockchain history, making it a valuable case study for understanding these vulnerabilities and their solutions. As the leading smart contract platform, Ethereum’s architecture and evolution have shaped industry approaches to replay protection. The network’s experience with the Ethereum Classic fork, implementation of EIP-155, and ongoing challenges with cross-chain compatibility provide crucial lessons for blockchain security. Understanding Ethereum-specific replay attack vectors helps illuminate broader principles applicable across blockchain platforms.
The Ethereum blockchain’s use of ECDSA signatures and its account-based model create specific characteristics relevant to replay attacks. Ethereum transactions include nonces that prevent on-chain replay within the same network, but additional protections were needed to prevent cross-chain replay. The evolution of Ethereum’s replay protection mechanisms demonstrates how blockchain protocols must adapt to new threat vectors as the ecosystem grows. From the initial lack of chain identifiers through the implementation of EIP-155 and beyond, Ethereum’s journey provides a roadmap for other blockchain projects facing similar challenges.
Replay Attacks in Ethereum Transactions
Ethereum transactions consist of several components including nonce, gas price, gas limit, recipient address, value, data payload, and signature components (v, r, s). The nonce serves as a transaction counter for each account, ensuring that transactions execute in order and cannot be replayed on the same chain. However, before EIP-155, this nonce provided no protection against cross-chain replay because different chains maintained separate nonce counts. An attacker could capture an Ethereum transaction and broadcast it to Ethereum Classic or other compatible chains, where it would appear valid as long as the account had sufficient balance and the nonce matched the account’s current state on that chain.
The vulnerability stemmed from how Ethereum originally structured transaction signatures. The signature covered the transaction data but did not include any chain-specific identifier. This meant that a properly signed transaction for Ethereum was equally valid on any chain using the same signature verification logic and account system. The introduction of the chain ID as part of the signature data resolved this issue by making each transaction cryptographically bound to a specific network. Modern Ethereum transactions include the chain ID in the signature calculation, ensuring that transactions signed for Ethereum mainnet (chain ID 1) cannot be valid on Ethereum Classic (chain ID 61) or any other network, even if all other transaction components are compatible.
ECDSA Signature Replay Risk
The Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) used by Ethereum provides strong cryptographic security for transaction authorization but does not inherently prevent replay attacks. ECDSA signatures prove that the holder of a private key authorized specific message data, but they do not contain information about intended execution context. This characteristic is fundamental to the algorithm rather than an Ethereum-specific limitation. The signature components (r, s, v) mathematically verify against the transaction data and the signer’s public key, but this verification process does not check whether the signature has been used before or on which blockchain it should be valid.
The replay risk with ECDSA signatures extends beyond basic transaction replay to include more subtle vulnerabilities in smart contract interactions. When contracts accept ECDSA signatures for authorization of specific operations, they must implement additional logic to prevent signature reuse. This includes tracking which signatures have been processed, implementing domain separators that bind signatures to specific contract instances, and validating additional parameters that establish the intended context for signature use. The EIP-712 standard addresses some of these concerns by providing structured data signing that includes domain-specific information, making it harder to replay signatures across different contracts or chains. However, proper implementation of these standards remains the responsibility of contract developers, and failures to correctly implement replay protection continue to be discovered in production contracts.
Real-World Replay Attack Examples in Ethereum
The Ethereum and Ethereum Classic split provided the most prominent real-world demonstration of replay attack consequences. In the days and weeks following the fork, numerous users reported unexpected transactions appearing on both chains when they intended to transact on only one. Exchange platforms struggled to separate user balances between ETH and ETC, leading to cases where deposits made on one chain were incorrectly credited or debited from the other chain. The confusion was exacerbated by varying levels of replay protection across different wallet implementations and the initial absence of standardized solutions.
Beyond the ETH/ETC fork, replay attack vulnerabilities have appeared in various Ethereum smart contracts and DeFi protocols. Several DEX implementations have suffered from signature replay issues where limit orders or trading authorizations could be executed multiple times. NFT platforms have faced replay vulnerabilities in minting or transfer authorizations. Cross-chain bridge protocols have discovered replay issues where the same signature could be used to claim assets on multiple chains. These real-world incidents have driven improvements in security standards and increased awareness of replay protection requirements. The cumulative effect has been the evolution of best practices and security tools specifically designed to identify and prevent replay vulnerabilities during contract development and auditing processes.
How to Prevent Replay Attacks in Blockchain
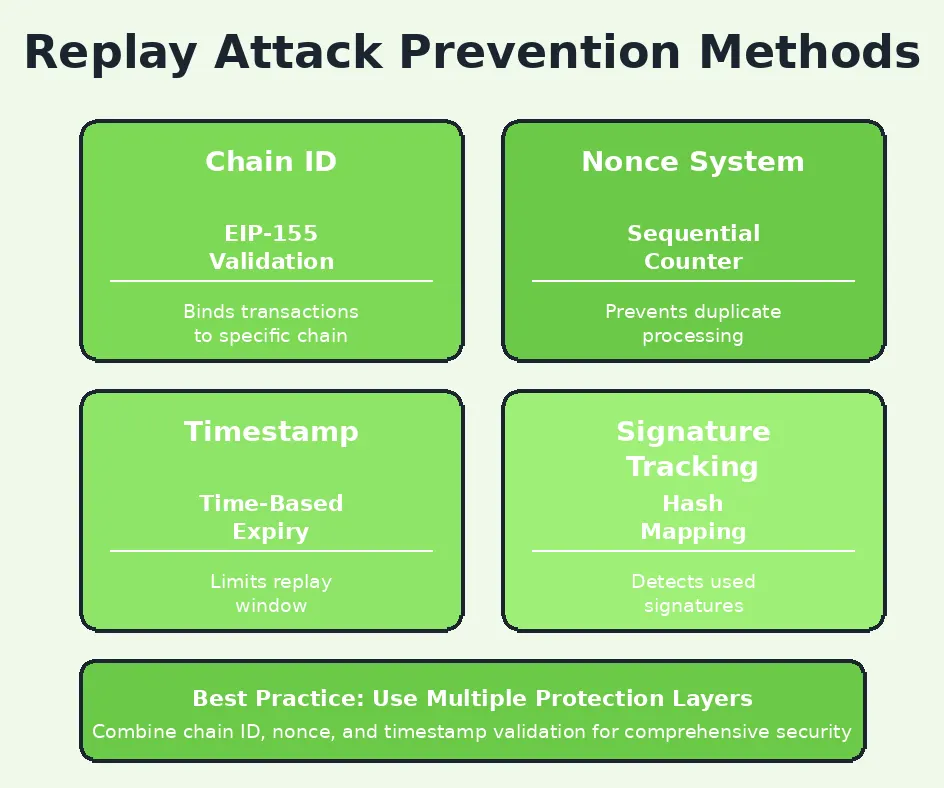
Preventing replay attacks requires implementing multiple layers of protection at different levels of blockchain architecture. Effective replay protection combines protocol-level mechanisms, application-level safeguards, and user-facing tools that work together to ensure transaction uniqueness and context binding. The specific techniques vary depending on the attack vector being addressed, whether on-chain replay, cross-chain replay, or fork-related replay. However, common principles apply across all scenarios: transactions must be cryptographically bound to their intended execution context, systems must track which authorizations have been used, and validation logic must reject duplicate or out-of-context transaction attempts. Organizations implementing comprehensive replay protection benefit from reduced security risks and enhanced user confidence.
Best Practice Principle: Effective replay attack prevention requires defense in depth, combining protocol-level protections like chain identifiers and nonces with application-level safeguards such as signature tracking and context validation. No single mechanism provides complete protection; layered security ensures resilience even if individual protections fail.
The implementation of replay protection must consider both immediate threats and long-term security maintenance. Protocols must establish clear standards for transaction formatting that include replay protection from inception rather than attempting to retrofit protections after vulnerabilities emerge. Application developers must understand replay attack vectors relevant to their specific use cases and implement appropriate safeguards in smart contracts and backend systems. Users need access to tools and information that help them transact safely during high-risk periods. This comprehensive approach requires coordination across blockchain infrastructure providers, application developers, wallet creators, and end users to create an ecosystem where replay attacks become practically impossible to execute successfully.
Replay Attack Prevention Techniques
Multiple technical approaches exist for preventing replay attacks, each addressing different aspects of the vulnerability. At the protocol level, chain identifiers provide the foundation for cross-chain replay protection by making transactions cryptographically bound to specific networks. Nonce-based sequencing prevents on-chain replay by ensuring each transaction can only execute once per account. Timestamp validation adds temporal constraints that can limit the window during which signed authorizations remain valid. Signature domain separation ensures that signatures intended for different contracts or purposes cannot be interchanged. These techniques can be combined to create robust protection frameworks that address multiple attack vectors simultaneously.
Application-level replay protection requires careful design of how smart contracts and decentralized applications handle external signatures and authorizations. Contracts should maintain comprehensive tracking of processed signatures using hash-based mappings or similar data structures. Message hashing should include contract addresses and chain identifiers to prevent cross-contract and cross-chain replay. Time-bound authorizations should incorporate expiration timestamps that contracts validate before execution. For complex workflows involving multiple signature verification steps, protocols should implement unique identifiers for each operation and track completion status. These application-level protections complement protocol-level mechanisms to create comprehensive defense against replay attacks targeting specific contracts or applications rather than base-layer transactions.
Role of Nonce in Blockchain Security
The nonce (number used once) represents one of the most fundamental replay protection mechanisms in blockchain systems. In account-based blockchains like Ethereum, each account maintains a nonce counter that increments with every transaction sent from that account. When a user creates a transaction, they must specify the current nonce value for their account. Network nodes validate that incoming transactions contain the expected nonce (matching the account’s current nonce plus one for the next transaction) and reject transactions with incorrect nonce values. This mechanism ensures that transactions execute in strict sequence and prevents any transaction from being processed more than once.
The nonce system provides robust protection against on-chain replay within a single blockchain network but requires careful implementation to function correctly. Users must track their account nonce to construct valid transactions, and wallet software must manage nonces properly when creating multiple pending transactions. If a user sends several transactions quickly, each must use incrementing nonce values, and if any transaction fails or gets dropped, subsequent transactions with higher nonces will remain pending until the gap is filled. This creates some complexity for users and applications but provides strong guarantees against transaction replay. The nonce mechanism does not prevent cross-chain replay by itself, as different chains maintain independent nonce counters, necessitating additional protections like chain identifiers for comprehensive replay safety.
Nonce-Based Transaction Validation
Transaction validation using nonces follows a straightforward process where blockchain nodes verify that each transaction’s nonce matches the sending account’s current nonce value stored in the blockchain state. When a transaction arrives, the node retrieves the account’s current nonce from the state database, compares it to the nonce specified in the transaction, and rejects the transaction if they do not match exactly. If the nonce matches, the node processes the transaction and increments the account’s stored nonce by one, ensuring that this same nonce value will never be valid again for future transactions from that account. This creates an irreversible sequence where each nonce can only be used once.
The implementation of nonce validation must handle various edge cases to maintain security and usability. Nodes must maintain a mempool of pending transactions and handle situations where transactions arrive out of order or with gaps in nonce sequences. Most implementations queue transactions with future nonces until preceding nonces are processed, while rejecting transactions with already-used nonces. Some systems allow transaction replacement where a new transaction with the same nonce but higher gas price can replace a pending transaction, providing a mechanism for users to speed up or cancel transactions. These complexities require careful implementation to prevent vulnerabilities where attackers might manipulate nonce handling to cause denial of service or other security issues.
Chain ID Protection and Replay Safety
Chain identifiers serve as the primary defense against cross-chain replay attacks by making transactions cryptographically specific to individual blockchain networks. Each blockchain network is assigned a unique chain ID number that distinguishes it from all other networks. This identifier becomes part of the transaction data that gets signed, ensuring that signatures created for one chain cannot be mathematically valid on another chain even if all other transaction components are identical. When a node receives a transaction, it verifies that the chain ID embedded in the signature matches its own network’s chain ID, rejecting any transaction signed for a different chain.
The effectiveness of chain ID protection depends on several factors. First, each blockchain network must have a truly unique chain ID with no collisions across the ecosystem. Chain ID registries help coordinate this, though the decentralized nature of blockchain makes absolute enforcement challenging. Second, all network participants including wallet software, nodes, and smart contracts must properly implement chain ID validation. Legacy systems that do not check chain IDs or allow transactions without chain ID signatures remain vulnerable. Third, users must ensure their tools and applications incorporate chain ID correctly in signatures. The widespread adoption of chain ID protection following EIP-155 has dramatically reduced cross-chain replay risks, but ongoing vigilance is required as new networks launch and ecosystem complexity increases.
EIP-155 Replay Protection Explained
Ethereum Improvement Proposal 155 (EIP-155) established the standard for incorporating chain identifiers into Ethereum transaction signatures to prevent cross-chain replay attacks. Introduced in 2016 following the Ethereum Classic fork, EIP-155 modified the transaction signing process to include the chain ID as part of the data being signed. Specifically, when creating the signature, the signer includes the chain ID along with other transaction parameters in the hash that gets signed with their private key. The signature verification process then recovers the chain ID from the signature and validates that it matches the verifying chain’s ID.
The technical implementation of EIP-155 involves modifying the signature’s ‘v’ component to encode the chain ID information. For Ethereum mainnet (chain ID 1), the ‘v’ value becomes either 37 or 38 (calculated as chain_id * 2 + 35 or chain_id * 2 + 36), compared to the original values of 27 or 28 used in legacy transactions. When a node verifies a transaction, it extracts the chain ID from the ‘v’ component and confirms it matches the expected value. This elegant solution maintains backward compatibility with legacy transaction formats while providing strong replay protection for all EIP-155 compliant transactions. The success of EIP-155 in Ethereum has led to its adoption across numerous Ethereum-compatible blockchains and inspired similar approaches in other blockchain ecosystems.
Smart Contract Replay Protection Best Practices
Smart contracts handling external signatures must implement specific protections against signature replay attacks. The first essential practice involves maintaining a mapping or registry of used signatures, typically storing the keccak256 hash of each processed signature as a key in a mapping with a boolean value indicating it has been used. Before processing any signature, the contract checks this mapping and reverts if the signature has been seen before. This prevents the same signature from being used multiple times to execute operations. The storage cost of maintaining this mapping must be considered in contract design, though it represents necessary overhead for security.
Additional best practices include implementing domain separation through structured data signing as specified in EIP-712, which includes contract address and chain ID in the signed data. Contracts should validate that signatures are intended specifically for their address and current chain, preventing signatures from being replayed across different contracts or chains. Time-based expiration mechanisms add another layer of protection, where signatures include an expiration timestamp and contracts reject expired signatures. For complex authorization workflows, contracts should implement nonce systems similar to account nonces, requiring signers to include incrementing nonce values that the contract tracks per user. These layered protections ensure comprehensive replay safety while maintaining the flexibility needed for various application patterns.
Best Practices for Blockchain Security Against Replay Attacks
Comprehensive protection against replay attacks requires organizational commitment to security best practices across all aspects of blockchain infrastructure and application layers. Organizations must establish security-first development processes that incorporate replay protection considerations from initial design through deployment and ongoing maintenance. This includes conducting thorough security audits, implementing formal verification where appropriate, maintaining comprehensive testing regimens that specifically target replay vulnerabilities, and establishing incident response procedures for detected attacks. The investment in proper security architecture pays dividends through reduced vulnerability to attacks and enhanced reputation in security-conscious markets.
| Security Layer | Protection Mechanism | Implementation Priority | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol Level | Chain ID validation, nonce enforcement, timestamp checks | Critical – Must implement before launch | Monitor for protocol updates and vulnerabilities |
| Application Level | Signature tracking, domain separation, message expiration | High – Essential for all signature handling | Regular audits and pattern updates |
| Infrastructure Level | Network monitoring, anomaly detection, transaction validation | Medium – Enhances detection capabilities | Continuous monitoring and alerting system updates |
| User Interface Level | Transaction preview, chain verification, safety warnings | Medium – Improves user awareness | User education and interface improvements |
Secure Smart Contract Development
Secure smart contract creation begins with incorporating replay protection considerations during the initial design phase rather than attempting to retrofit security after implementation. Developers must identify all points where contracts accept external signatures or process user-submitted data that could be replayed. Each such interaction point requires specific protections appropriate to its use case. For simple approval signatures, hash-based tracking of used signatures may suffice. For complex authorization workflows, comprehensive nonce systems and domain separation become necessary. The design phase should produce detailed security specifications that explicitly address replay attack vectors and document the protections being implemented.
Implementation requires following established patterns and standards rather than creating custom security mechanisms that may contain subtle flaws. Developers should leverage well-tested libraries like OpenZeppelin that provide secure implementations of common patterns including signature validation and replay protection. Code should undergo comprehensive testing including specific test cases that attempt replay attacks under various scenarios. Formal verification can mathematically prove that replay protections function correctly across all possible states. Before deployment, contracts should undergo professional security audits by firms specializing in blockchain security who can identify replay vulnerabilities that developers may have overlooked. This rigorous approach ensures that contracts resist replay attacks from launch rather than discovering vulnerabilities in production.
Improving Blockchain Network Security
Network-level security improvements create a foundation of replay protection that benefits all applications built on the platform. Blockchain protocols should implement comprehensive chain identifier systems from inception, ensuring every transaction includes and validates chain-specific data. The protocol should enforce nonce sequencing strictly, rejecting any transaction that attempts to reuse a nonce or skip nonces in the sequence. Transaction validation logic must verify all replay protection mechanisms before accepting transactions into the mempool or including them in blocks. These protocol-level protections provide baseline security that individual applications can build upon.
Network operators and validators play crucial roles in maintaining replay protection effectiveness. They must run up-to-date node software that implements current security standards and properly validates all replay protection mechanisms. Validators should monitor for suspicious transaction patterns that might indicate replay attack attempts, such as unusual volumes of rejected transactions with invalid chain IDs or duplicate nonces. Network governance should prioritize security updates that address newly discovered replay attack vectors, implementing and activating protections quickly when vulnerabilities are identified. This ongoing vigilance ensures that network-level protections remain effective as attack techniques evolve and the blockchain ecosystem grows more complex.
Regular Audits to Prevent Blockchain Security Attacks
Systematic security auditing represents an essential component of comprehensive replay attack prevention. Organizations should conduct regular audits of their blockchain infrastructure, smart contracts, and applications to identify potential replay vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. These audits should encompass both automated analysis using security scanning tools and manual review by experienced security professionals who understand blockchain-specific attack vectors. Audit scope must include transaction handling logic, signature verification code, state management systems, and any integration points with external chains or protocols where replay risks might emerge.
The audit process should follow structured methodologies that systematically examine each component of the system for replay vulnerabilities. Auditors should verify that all transactions include and validate chain identifiers, confirm that nonce systems function correctly, check that smart contracts properly track used signatures, validate domain separation implementations, and test that replay protection mechanisms work correctly under various scenarios including fork situations and cross-chain operations. Findings should be documented comprehensively with severity ratings and specific remediation recommendations. Organizations must then prioritize and implement fixes for identified vulnerabilities, with critical replay attack risks addressed immediately. Regular re-audits ensure that new code changes have not introduced vulnerabilities and that existing protections remain effective as the system evolves.
Future of Blockchain Security and Replay Attack Protection
The evolution of blockchain technology continues to introduce new challenges and opportunities for replay attack protection. As the ecosystem moves toward greater cross-chain interoperability, more sophisticated smart contract applications, and novel consensus mechanisms, replay attack vectors will continue to evolve. Future protection mechanisms must anticipate these developments and provide security frameworks that adapt to changing threat landscapes. The industry is moving toward standardized security frameworks that incorporate replay protection as a fundamental requirement rather than an optional addition, reflecting growing maturity in blockchain security practices.
Emerging technologies including zero-knowledge proofs, threshold signatures, and quantum-resistant cryptography will influence how replay protection is implemented in future blockchain systems. These advanced cryptographic techniques can provide more elegant and efficient replay protection while enabling new capabilities. The development of cross-chain communication protocols requires sophisticated replay protection that works across heterogeneous blockchain environments with different security models. As blockchain adoption expands into regulated industries and critical infrastructure, the standards for replay protection will likely increase, with formal verification and provable security guarantees becoming expected rather than exceptional.
Advanced Cryptographic Security Measures
Next-generation cryptographic techniques offer promising approaches to enhancing replay protection while improving other security properties. Zero-knowledge proofs enable verification of transaction validity without revealing transaction details, and can incorporate replay protection directly into proof construction. A transaction could prove not only its correctness but also its uniqueness and chain-specific validity, with the proof itself preventing replay across different contexts. Threshold signature schemes allow distributed transaction authorization where multiple parties must cooperate to create valid signatures, and these schemes can incorporate built-in replay protection through unique signature binding to specific network and temporal contexts.
Post-quantum cryptography represents another frontier that will reshape blockchain security including replay protection. As quantum computers advance, current cryptographic algorithms including ECDSA may become vulnerable, necessitating migration to quantum-resistant alternatives. These new signature schemes must incorporate replay protection from their design, learning from the challenges experienced with current systems. The transition to quantum-resistant cryptography provides an opportunity to rethink transaction structure and security mechanisms, potentially enabling more robust replay protection as an inherent property of the cryptographic primitives rather than an additional layer built on top. Research in this area continues to advance, with several candidate algorithms showing promise for blockchain applications.
Cross-Chain Security and Replay Protection
The growing emphasis on blockchain interoperability creates complex new requirements for replay protection. Cross-chain bridges, atomic swaps, and other interoperability protocols must ensure that operations intended for one chain cannot be replayed on another, even when those operations involve coordination across multiple chains. This requires sophisticated security architectures where replay protection encompasses not just individual transactions but entire multi-chain workflows. Each step in a cross-chain operation must be bound to its specific chain context while also linking to related operations on other chains to prevent partial replays or reordering attacks.
Future cross-chain protocols will likely implement standardized replay protection frameworks that work across diverse blockchain architectures. These frameworks might include universal chain identifiers that work across all connected chains, cross-chain nonce systems that prevent replay across bridge operations, and cryptographic commitments that bind multi-chain operations together atomically. The security of these systems must account for the lowest common denominator in security across all connected chains, as vulnerabilities in any single chain could potentially compromise cross-chain operations. As the industry matures, we can expect consolidation around proven cross-chain security patterns that make replay protection a solved problem for interoperability scenarios.
Evolving Standards for Blockchain Security Risks
Industry standards for blockchain security continue to evolve, incorporating lessons learned from past replay attacks and other security incidents. Organizations like the Ethereum Foundation, various industry consortiums, and regulatory bodies are establishing best practices and compliance frameworks that specify minimum security requirements including replay protection. These standards help organizations understand what security measures they must implement and provide benchmarks for evaluating blockchain platforms and applications. As standards mature and gain widespread adoption, baseline security improves across the ecosystem, making previously common vulnerabilities increasingly rare.
Future standards will likely mandate replay protection as a fundamental security requirement rather than an optional enhancement. Smart contract development frameworks may enforce replay protection patterns through compiler checks or static analysis tools that reject code lacking appropriate safeguards. Blockchain protocols might implement stricter validation rules that refuse to process transactions lacking modern replay protection mechanisms. Industry certification programs could emerge that verify applications and platforms meet security standards including comprehensive replay attack resistance. This standardization raises the minimum security bar across the ecosystem while reducing the burden on individual developers who can rely on established patterns and tools rather than implementing custom solutions.
Final Thoughts on Replay Attacks in Blockchain
Replay attacks represent a fundamental security challenge that every blockchain system must address through careful protocol design and implementation. The unique characteristics of blockchain technology including transaction transparency, signature portability, and network decentralization create specific vulnerabilities that traditional security models do not fully address. Understanding replay attack mechanisms, their potential consequences, and proven protection techniques is essential for anyone building, operating, or using blockchain systems. The industry has made significant progress in developing robust replay protection mechanisms, but ongoing vigilance remains necessary as new attack vectors emerge with technological evolution and increased ecosystem complexity.
The lessons learned from historical replay attack incidents have shaped current best practices and security standards across the blockchain industry. From the Ethereum Classic fork that demonstrated the severity of cross-chain replay risks to ongoing discoveries of smart contract replay vulnerabilities in DeFi protocols, each incident has contributed to our collective understanding of these threats. Organizations that prioritize security from inception, implement comprehensive replay protection across all layers of their systems, conduct regular audits, and stay informed about emerging threats position themselves for success in the blockchain ecosystem. As the technology matures and adoption expands, the standard for security including replay protection will continue rising, separating professional implementations from amateur efforts.
Why Understanding Replay Attacks is Important for Crypto Projects
For projects building blockchain-based solutions, understanding replay attacks transcends academic interest to become a practical necessity that directly impacts project viability and user trust. Projects that fail to implement adequate replay protection risk catastrophic security failures that can destroy user confidence, trigger regulatory scrutiny, and result in substantial financial losses. In competitive markets where users have numerous platform options, security reputation becomes a key differentiator. Projects known for robust security including comprehensive replay attack protection attract users, partners, and investment, while those with security vulnerabilities struggle to gain traction regardless of other merits.
The technical understanding of replay attacks also influences broader architectural decisions. Projects must consider replay protection requirements when designing transaction formats, choosing cryptographic algorithms, implementing cross-chain capabilities, and structuring smart contract interactions. These decisions made during early design phases have long-lasting consequences that can be difficult or impossible to change later without disruptive forks or migrations. Projects that deeply understand replay attack mechanics can make informed architectural choices that provide strong protection while maintaining the flexibility needed for innovation and growth. This security-aware design thinking represents a hallmark of mature blockchain projects built to last.
Secure Your Blockchain Against Replay Attacks
Build secure, replay-protected blockchain solutions with expert smart contract development, security audits, and enterprise-grade protection by a trusted blockchain development company.
Launch Your Exchange Now
Building Secure Blockchain Systems from Day One
The most effective approach to replay attack protection involves incorporating security considerations from the very beginning of blockchain system design rather than attempting to add protections after the fact. Initial architecture should specify exactly how transactions will be made unique and context-specific, how signatures will be bound to intended execution environments, and how the system will handle edge cases like forks or cross-chain scenarios. Security requirements should receive equal priority with functional requirements during the design phase, with technical specifications explicitly addressing replay attack vectors and the mechanisms being implemented to prevent them.
Organizations building blockchain systems should invest in security expertise from project inception, engaging professionals who understand blockchain-specific attack vectors including replay attacks. The design team should include security architects who can identify potential vulnerabilities and specify appropriate protections. Implementation should follow secure coding practices with comprehensive testing that specifically targets replay attack scenarios. Before launch, systems should undergo thorough security audits by independent firms specializing in blockchain security. This disciplined approach to security-first construction creates systems that resist replay attacks and other threats from launch, providing users with the security guarantees they require. The incremental cost of proper security implementation is minimal compared to the catastrophic costs of security failures after deployment, making security investment a clear priority for any serious blockchain project.
Frequently Asked Questions
A replay attack occurs when a malicious actor intercepts a valid data transmission and fraudulently repeats or delays it to deceive the receiving system. In blockchain contexts, attackers copy legitimate transaction data and rebroadcast it to execute unauthorized transfers or operations. This attack exploits the lack of transaction uniqueness validation, allowing the same digital signature to be reused across different networks or time periods, potentially causing significant financial losses.
Replay attacks in blockchain happen when an attacker captures a legitimate transaction from one blockchain network and rebroadcasts it on another network, particularly after hard forks or on cross-chain platforms. The attack succeeds because both chains may recognize the same digital signatures and transaction formats. Without proper replay protection mechanisms like unique chain identifiers or transaction nonces, the blockchain cannot distinguish between the original transaction and its malicious duplicate, executing both transfers.
Yes, replay attacks can directly result in cryptocurrency theft. When an attacker successfully replays a transaction, they can force unintended transfers from victims’ wallets on forked or parallel chains. For instance, if you send funds on one chain after a fork, an attacker might replay that transaction on the other chain without your consent, effectively doubling your expenditure. This vulnerability has caused millions in losses during major blockchain forks throughout crypto history.
A replay attack involves reusing valid transaction data across different networks or time periods, while a double spend attack attempts to spend the same cryptocurrency twice on the same network by exploiting consensus delays. Replay attacks exploit transaction portability between chains, whereas double spending attacks target the blockchain’s consensus mechanism itself. Both threaten transaction integrity but through fundamentally different attack vectors requiring distinct prevention strategies.
EIP-155 prevents replay attacks by incorporating a unique chain identifier into transaction signatures, making each transaction specific to one blockchain network. This Ethereum Improvement Proposal ensures that transactions signed for one chain cannot be validly executed on another, even if both chains share common origins. The chain ID becomes part of the cryptographic signature, so any attempt to replay the transaction on a different network results in signature verification failure and transaction rejection.
A nonce (number used once) is a sequential counter included in each blockchain transaction that ensures uniqueness and ordering. Each account maintains its own nonce value that increments with every transaction, preventing the same transaction from being processed multiple times. If an attacker attempts to replay a transaction, the blockchain rejects it because the nonce has already been used. This mechanism provides temporal protection, ensuring transactions can only be executed once in the correct sequence.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







