Key Takeaways
- DEX liquidity incentives are essential mechanisms that attract capital to trading pools, enabling the market depth required for competitive trade execution and platform growth.
- Effective DeFi liquidity incentives balance attractive rewards with sustainability, avoiding excessive token emissions that dilute value and create unsustainable economics.
- Liquidity mining and yield farming in DEX ecosystems have evolved from simple token distributions to sophisticated models incorporating vesting, loyalty multipliers, and governance rights.
- DEX liquidity providers face real risks including impermanent loss, and effective incentive programs must compensate adequately while aligning long-term interests.
- Token rewards for liquidity must be designed to prevent mercenary capital that extracts value without contributing to sustainable platform growth.
- AMM liquidity pools require targeted incentives that direct capital where it creates the most value for traders and the protocol.
- The evolution of DeFi incentive models points toward protocol-owned liquidity, real yield from fees, and reduced reliance on inflationary token emissions.
- Successful liquidity incentive mechanisms directly impact DEX trading volume growth by creating the conditions for competitive pricing and reliable execution.
Liquidity is the lifeblood of decentralized exchanges, and the mechanisms used to attract and retain it determine platform success or failure. Understanding what makes DEX liquidity incentives effective reveals the economic engineering behind successful DeFi platforms. This comprehensive guide explores the strategies, mechanisms, and best practices that transform incentive programs from short-term promotional tools into sustainable competitive advantages.
What Makes DEX Liquidity Incentives Effective?
What makes DEX liquidity incentives effective extends far beyond simply offering high APY numbers. Effective incentives create genuine value alignment between liquidity providers and platforms, build sustainable liquidity that persists beyond promotional periods, and efficiently direct capital to where it creates the most trading value. The difference between effective and ineffective programs often determines whether a DEX thrives or becomes another failed experiment.
Understanding DEX Liquidity Incentives
Understanding DEX liquidity incentives requires examining the fundamental challenge decentralized exchanges face: attracting sufficient capital to enable competitive trading without the market-making infrastructure of centralized platforms. Incentives bridge this gap by compensating providers for the risks and opportunity costs of depositing assets into trading pools.
DEX Liquidity Incentives Explained
DEX liquidity incentives explained simply involve rewarding users who contribute assets to trading pools. These rewards supplement the trading fees that liquidity providers naturally earn, making participation more attractive. Incentives typically come as protocol tokens distributed proportionally to liquidity contribution, though sophisticated programs incorporate multiple reward mechanisms working together.
The mechanics vary by platform but follow common patterns. Users deposit token pairs into AMM liquidity pools, receive LP tokens representing their share, and earn rewards based on their proportional contribution. Building crypto exchanges requires careful incentive design that balances immediate attractiveness with long-term sustainability.
Role of Liquidity Providers in Decentralized Exchanges
The role of DEX liquidity providers extends beyond passive capital supply. Providers essentially become the market makers, enabling trades that would otherwise be impossible. Without their capital, AMM pools cannot function; traders would face infinite slippage or simply no execution capability. This critical role justifies the rewards providers receive.
Providers take real risks including impermanent loss when prices diverge and smart contract vulnerabilities. Understanding how liquidity pools function in decentralized exchanges clarifies why appropriate compensation through incentives is necessary and justified.
Incentive Principle: Effective liquidity incentives create alignment where provider success depends on platform success. Programs that enable extraction without contribution inevitably fail as capital leaves when rewards decrease.
Why Liquidity Incentives Matter for Decentralized Exchange Growth
Why liquidity incentives matter for decentralized exchange growth relates to the competitive dynamics of trading platforms. Liquidity attracts traders through better execution; traders generate fees that reward liquidity providers; satisfied providers maintain or increase deposits. This virtuous cycle depends on initial liquidity that incentives help bootstrap.
Impact on DEX Trading Volume Growth
The impact on DEX trading volume growth from effective incentives can be dramatic. Deeper liquidity enables larger trades with less slippage, attracting institutional and whale traders who bring significant volume. This volume generates fees that support organic rewards, reducing dependence on token emissions over time. The relationship between incentives and volume growth forms a core economic feedback loop.
Historical data from successful DEX launches shows strong correlation between incentive programs and volume metrics. Platforms that executed well-designed incentive campaigns achieved liquidity levels that sustained trading activity even after reducing rewards, while poorly designed programs saw liquidity and volume collapse together when incentives ended.
Improving Market Depth and Price Stability
Improving market depth and price stability through targeted incentives creates better trading conditions that benefit all participants. Deeper pools mean smaller trades have less price impact, enabling tighter effective spreads. This improved execution attracts traders from competing venues, generating the volume that makes the platform economically viable.
Price stability from deep liquidity also reduces manipulation opportunities. Thin pools can be moved significantly by relatively small trades, enabling exploitation. Incentivized deep liquidity makes manipulation expensive, creating fairer markets that build trust among participants.
Core Liquidity Incentive Mechanisms in DeFi
Core liquidity incentive mechanisms in DeFi have evolved through experimentation across numerous protocols. The fundamental approaches include liquidity mining, yield farming, and token reward distribution, each with variations suited to different platform needs and stages of growth.
Liquidity Mining Models in DEX Platforms
Liquidity mining models in DEX platforms distribute protocol tokens to liquidity providers based on their contribution to designated pools. The simplest models distribute tokens proportionally to LP share over time. More sophisticated models weight rewards by pool importance, incorporate time-locking bonuses, or adjust dynamically based on current liquidity needs.
The effectiveness of liquidity mining depends heavily on token value sustainability. If mining rewards flood the market and crash token prices, the dollar value of rewards decreases, reducing actual incentive effectiveness. Well-designed programs manage emission rates and incorporate mechanisms like vesting to moderate selling pressure.
Yield Farming in DEX Ecosystems
Yield farming in DEX ecosystems extends beyond simple liquidity provision to encompass multi-protocol strategies maximizing returns. Farmers may stake LP tokens for additional rewards, compound earnings automatically, or move capital between platforms chasing optimal yields. This sophisticated participation requires DEXs to design incentives that attract and retain yield farmers while preventing pure extraction.
The yield farming ecosystem has matured significantly since early DeFi experiments. Understanding comprehensive liquidity dynamics in decentralized exchanges helps protocols design farming programs that create genuine value rather than simply redistributing tokens.
Token Rewards for Liquidity Providers
Token rewards for liquidity providers represent the primary incentive mechanism for most DEXs. These rewards supplement trading fees, making liquidity provision profitable even in low-volume conditions. The token rewards also create governance alignment, giving providers voting power over protocol decisions that affect their deposits.
Effective token reward design considers emission schedules, vesting requirements, utility beyond speculation, and long-term dilution impacts. Protocols that simply distribute tokens without these considerations often see rapid value decline that undermines the incentive program itself.
Liquidity Incentive Model Comparison
| Model | Mechanism | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Mining | Proportional token distribution | Easy to understand | Attracts mercenary capital |
| Ve-Token Model | Lock tokens for boosted rewards | Encourages long-term holding | Complex for new users |
| Fee Sharing | Distribute trading fees | Sustainable, no inflation | Requires high volume |
| Protocol-Owned | Protocol owns its liquidity | Permanent liquidity | High capital requirement |
How DEX Liquidity Incentives Work in Practice
How DEX liquidity incentives work in practice involves coordinated smart contract systems that track deposits, calculate rewards, and enable claims. Understanding the practical mechanics helps providers maximize returns while helping protocols design more effective programs.
AMM Liquidity Pools and Incentive Distribution
AMM liquidity pools and incentive distribution work together through staking mechanisms. Users provide liquidity and receive LP tokens representing their share. These LP tokens can then be staked in reward contracts that track deposits and accumulate claimable rewards over time. The separation allows flexible incentive design without modifying core AMM contracts.
Distribution mechanisms vary from simple time-based accrual to sophisticated formulas incorporating deposit size, duration, pool importance, and additional boost factors. Understanding how fee dynamics work in decentralized exchanges provides context for how incentives interact with natural fee generation.
Liquidity Reward Models in Decentralized Exchanges
Liquidity reward models in decentralized exchanges have evolved through multiple generations. Early models simply distributed tokens uniformly. Current best practices incorporate weighted rewards directing capital to priority pools, boost mechanisms for locked positions, and declining emission schedules that reduce inflation over time while maintaining incentive effectiveness.
The most effective models combine multiple reward sources: base trading fees, additional token emissions, and bonus rewards for specific behaviors. This layered approach provides consistent base returns supplemented by variable incentives that can be adjusted without disrupting core economics.
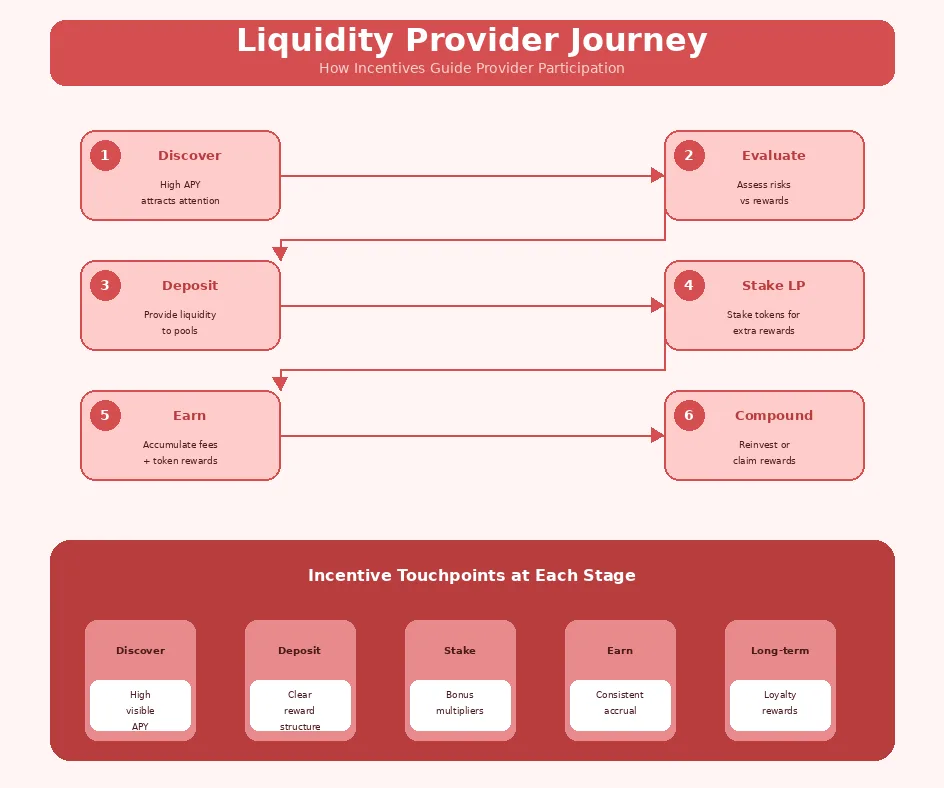
Liquidity Provider Journey Lifecycle
| Stage | Action | Incentive Role | Provider Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Discovery | High APY attracts attention | Interest generated |
| 2 | Deposit | Clear reward structure | LP tokens received |
| 3 | Stake LP | Enable reward accrual | Rewards begin |
| 4 | Earn | Fees + token rewards | Value accumulation |
| 5 | Compound/Claim | Reinvestment options | Returns realized |
| 6 | Long-term Hold | Loyalty multipliers | Enhanced returns |
Effective DeFi Liquidity Incentive Strategies
Effective DeFi liquidity incentive strategies combine multiple mechanisms working together toward sustainable growth. The best strategies evolved through extensive experimentation across the DeFi ecosystem, with successful elements being adopted and refined by subsequent protocols.
Best Liquidity Incentive Strategies in DeFi
Best liquidity incentive strategies in DeFi share common characteristics: they target incentives toward pools that genuinely need liquidity rather than distributing uniformly, incorporate time-locking mechanisms that reward commitment, and transition gradually toward fee-based sustainability. These strategies recognize that different pools have different incentive needs and adjust accordingly.
Targeted incentives might boost new trading pairs that need bootstrapping while reducing rewards for established pairs with organic liquidity. This dynamic allocation maximizes incentive efficiency by directing limited token budgets where they create the most platform value.
Balancing Token Emissions and Sustainability
Balancing token emissions and sustainability represents the central challenge in DeFi incentive design. High emissions attract liquidity but dilute token value; low emissions may fail to bootstrap necessary liquidity. The solution involves carefully calibrated emission schedules that start higher during bootstrapping and decrease as organic activity grows.
Sustainability also requires building genuine utility for reward tokens beyond speculative value. Governance rights, fee sharing, protocol benefits, and ecosystem utility create demand that absorbs emission selling pressure. Tokens without genuine utility inevitably decline regardless of emission management.
Incentive Model Selection Criteria
When designing or evaluating liquidity incentive programs, consider these factors:
- Sustainability: Can the program continue without destroying token value?
- Alignment: Do incentives reward behaviors that benefit the platform long-term?
- Efficiency: Is capital directed to pools that genuinely need liquidity?
- Loyalty: Do mechanisms discourage mercenary capital extraction?
- Simplicity: Can average users understand and participate effectively?
- Flexibility: Can the program adapt to changing market conditions?
How DEXs Attract and Retain Liquidity Providers
How DEXs attract and retain liquidity providers involves both initial incentive attractiveness and ongoing value that encourages sustained participation. Attraction is relatively straightforward through competitive rewards; retention requires deeper alignment and continuous value delivery.
Incentive Design for Long-Term Liquidity
Incentive design for long-term liquidity incorporates mechanisms that specifically reward sustained participation. Time-locked positions earning higher rewards, vesting schedules that release tokens gradually, and loyalty multipliers that increase with deposit duration all encourage providers to maintain positions rather than chase yields elsewhere.
The ve-token model pioneered by Curve exemplifies effective long-term design. Providers lock tokens for up to four years, receiving proportionally higher rewards and governance power. This creates strong incentives for commitment while allowing flexibility in lock duration. Understanding how successful DEX platforms implement retention mechanisms reveals practical approaches.
Reducing Impermanent Loss Through Smart Incentives
Reducing impermanent loss through smart incentives addresses the primary risk that discourages liquidity provision. Some protocols offer impermanent loss protection that compensates providers if they experience losses. Others structure rewards to ensure that incentives consistently exceed expected impermanent loss, making net participation profitable despite the risk.
Concentrated liquidity models introduce new dynamics where providers can earn higher fees from tighter ranges but face increased impermanent loss risk. Incentive programs for these systems must account for the different risk profiles compared to traditional full-range liquidity.
Challenges in Designing DEX Liquidity Incentives
Challenges in designing DEX liquidity incentives stem from competing objectives and complex market dynamics. Programs must attract capital while maintaining sustainability, reward providers fairly while preserving token value, and adapt to changing conditions while providing predictable returns.
Managing Inflation in DeFi Incentive Models
Managing inflation in DeFi incentive models requires careful emission scheduling and demand creation. Protocols that simply distribute tokens without managing supply face inevitable value decline as circulating supply grows. Effective management includes declining emission schedules, token burns, buyback mechanisms, and utility features that create organic demand absorbing new supply.
The challenge intensifies as protocols mature. Early-stage projects can sustain higher emissions when circulating supply is low. As supply grows, the same emission rate creates larger absolute dilution. Transition planning that reduces emissions while maintaining incentive effectiveness requires careful economic modeling.
Preventing Mercenary Liquidity
Preventing mercenary liquidity addresses capital that arrives solely for high initial rewards and leaves immediately when better opportunities appear elsewhere. This behavior extracts value without contributing to sustainable platform growth, often damaging protocols through rapid liquidity withdrawal.
Prevention mechanisms include lock-up requirements, reward vesting, loyalty multipliers, and penalties for early withdrawal. Some protocols implement “rage quit” penalties where early exiters forfeit unvested rewards. The goal is making long-term participation more attractive than short-term extraction.
Investment Warning: High APY incentive programs carry significant risks including token price decline, impermanent loss, and smart contract vulnerabilities. Advertised returns often prove unsustainable. Always assess total risk-adjusted returns rather than focusing solely on headline APY figures.
Incentive Effectiveness Factors
| Factor | Effective Approach | Ineffective Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Rate | Declining schedule over time | Constant high emissions |
| Targeting | Directed to priority pools | Uniform distribution |
| Lock Requirements | Tiered with loyalty bonuses | No commitment required |
| Token Utility | Governance + fee sharing | Speculation only |
| Sustainability | Transition to fee-based | Permanent emission dependence |
Future of Liquidity Incentives in Decentralized Exchanges
The future of liquidity incentives in decentralized exchanges points toward more sophisticated, sustainable models that learn from early DeFi experiments. The industry is moving beyond simple token distributions toward comprehensive economic systems that align all stakeholders.
Evolution of DeFi Liquidity Incentive Mechanisms
The evolution of DeFi liquidity incentive mechanisms shows clear progression from simple to sophisticated. Early programs distributed tokens uniformly; current best practices incorporate dynamic targeting, loyalty mechanics, and sustainability features. Future evolution will likely emphasize real yield from protocol revenue over inflationary emissions.
Protocol-owned liquidity represents one evolutionary direction where protocols acquire permanent liquidity rather than renting it through ongoing incentives. This approach eliminates mercenary capital concerns entirely by owning the liquidity outright. Understanding how modern exchange platforms implement advanced incentive systems reveals emerging best practices.
Build a High-Liquidity DEX with Proven Incentive Models
Launch a powerful DEX with smart liquidity incentives that attract providers, boost trading volume, and ensure long-term growth, built by expert DEX developers.
Launch Your Exchange Now
Next-Generation Incentives for Sustainable DEX Growth
Next-generation incentives for sustainable DEX growth will likely combine multiple mechanisms: base fee sharing that rewards proportionally to actual trading facilitated, bonus emissions for priority pools that genuinely need bootstrapping, and governance power that makes long-term holders the decision-makers.
Real yield models that distribute actual protocol revenue rather than newly minted tokens represent a significant evolution. When rewards come from genuine economic activity rather than inflation, sustainability concerns diminish. The challenge is building sufficient trading volume to generate meaningful fee-based rewards.
Future Outlook: The most successful DEX incentive programs will be those that create genuine alignment between providers and protocols, transitioning from promotional token distributions to sustainable fee-sharing models as platforms mature.
DEX liquidity incentives have evolved from simple promotional tools into sophisticated economic systems that determine platform success. Effective incentives balance attractiveness with sustainability, target capital efficiently, and create genuine alignment between providers and protocols. As the DeFi ecosystem matures, the distinction between platforms with effective incentive design and those without will become increasingly stark.
Understanding what makes incentives effective enables better participation decisions for providers and better program design for protocols. The principles of sustainability, alignment, and efficiency apply regardless of specific implementation details. Platforms that master incentive design build the liquidity foundation for long-term success, while those that rely on unsustainable promotional models face inevitable decline.
Frequently Asked Questions
DEX liquidity incentives are rewards offered to users who provide liquidity to decentralized exchange trading pools. These incentives typically include token rewards, fee sharing, and yield farming opportunities designed to attract capital to the platform. By compensating liquidity providers for the risks they take, DEXs can build the market depth necessary for efficient trading.
Liquidity mining programs distribute protocol tokens to users who deposit assets into liquidity pools. The rewards are typically calculated based on the proportion of liquidity provided relative to the total pool and the duration of participation. These programs create additional yield beyond trading fees, making liquidity provision more attractive during the critical bootstrapping phase of new DEX platforms.
Liquidity mining specifically refers to earning tokens by providing liquidity to DEX pools, while yield farming encompasses broader strategies for maximizing returns across DeFi protocols. Yield farming may involve moving assets between multiple platforms, staking LP tokens, and compounding rewards. Liquidity mining is one component within the broader yield farming ecosystem.
DEXs need liquidity incentives because without sufficient liquidity, traders face high slippage and poor execution, making the platform uncompetitive. Incentives compensate liquidity providers for impermanent loss risk and opportunity cost of locking capital. During the early stages especially, aggressive incentives help bootstrap liquidity that creates the network effects necessary for long-term platform success.
Effective liquidity incentives balance attractive rewards with long-term sustainability, target capital to pools that genuinely need depth, and align provider interests with platform success. The best programs reward loyalty over mercenary capital, incorporate mechanisms to reduce selling pressure from emissions, and adjust dynamically based on market conditions and protocol needs.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






