Key Takeaways
- Chainalysis reported that global cryptocurrency scam and fraud losses reached at least $9.9 billion in 2024, with fake airdrop campaigns being a major contributor to these losses.
[1] - Wallet drainer malware stole $494 million from over 332,000 wallet addresses in 2024, marking a 67% increase over the previous year, with the largest single theft reaching $55.48 million according to Scam Sniffer.
[2] - The Inferno Drainer scam, as a service tool, stole over $80 million from 134,000 victims by spoofing more than 100 cryptocurrency brands across 16,000 phishing domains, according to Group IB.
[3] - The FBI issued a public service announcement in June 202,5 warning about criminals exploiting NFT airdrop features on the Hedera Hashgraph network to steal cryptocurrency from non-custodial wallets through phishing URLs embedded in transaction memos.
[4] - ScamSniffer found that scammers targeted over 737,000 wallet addresses with fake airdrops impersonating popular projects, including ApeCoin, Pepe, and The Sandbox, to deceive victims into signing malicious transactions.
[5] - Kaspersky issued warnings about fake Hamster Kombat airdrops, noting that scammers exploited the game’s 250 million user base to distribute phishing campaigns designed to steal crypto wallet credentials.
[6] - In 2024, 56.7% of wallet drainer thefts relied on the Permit signature, which authorizes token spending, and 31.9% used the setOwner signature to change smart contract ownership rights, according to Scam Sniffer.
[7] - A single crypto user lost $908,551 in USDC in August 2025 due to a delayed wallet-draining attack that originated from a malicious smart contract approval signed 458 days earlier.
[8] - Telegram operated over 1,500 active scam channels promoting fake airdrops and fraudulent investments, while 56% of all cryptocurrency scams originated from social media platforms in 2025.
[9] - The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center received 41,557 complaints of cryptocurrency investment scams in 2024, a 29% increase from 2023, with reported losses totaling $5.7 billion, representing a 47% jump from the prior year.
[10]
Free tokens. That’s the bait. A promising new blockchain project announces a token giveaway, and all you need to do is connect your wallet, complete a few tasks, or share your details to claim the reward. Sounds simple and exciting. But here’s the reality that thousands of crypto holders learn the hard way every month: not all airdrops are what they seem, and the crypto space is filled with traps disguised as generosity.
An airdrop campaign in the crypto world is a distribution method where blockchain projects send free tokens or NFTs to wallet addresses, usually as part of a marketing push, a community reward, or a strategy to increase token visibility. These campaigns have become one of the most popular ways to build communities and attract early users. But this exact popularity has made them a prime hunting ground for scammers.
Airdrop campaign scams have exploded in frequency over the past two years. What was once a niche trick used by low-level fraudsters has now become a multi-billion-dollar criminal operation. From phishing sites that clone entire crypto platforms and promote token solutions to wallet-draining smart contracts that empty your holdings in seconds, these scams have grown in sophistication and in the financial destruction they leave behind.
This blog breaks down the major types of crypto airdrop scams that are actively running in 2024 and 2025, the real-world losses they have caused, specific cases you should know about, the warning signs that separate a legitimate airdrop from a dangerous one, and the concrete steps you can take to protect yourself. Whether you are a seasoned DeFi user or someone just entering the crypto space, understanding how airdrop fraud in crypto actually works is the first thing standing between you and a potential financial disaster.
The Rising Scale of Crypto Airdrop Scams
The numbers paint a disturbing picture. According to Chainalysis, the global losses from cryptocurrency scams and fraud, which include fake token airdrops, reached at least $9.9 billion in 2024. That figure climbed further in 2025, with reports suggesting losses surging past $12.5 billion. These are not projections or guesses. They come directly from blockchain analysis tracking actual fund movements on the chain.
Scam Sniffer, a Web3 anti-scam platform, published its annual Crypto Phishing Report for 2024, showing that wallet drainer attacks alone were responsible for $494 million in stolen funds from 332,000 affected wallet addresses. That’s a 67% increase from the previous year. The single largest theft in that period was a massive $55.48 million gone in one transaction.
What makes these figures even more alarming is that the number of affected addresses grew only 3.7% compared to 2023, even as total losses jumped by two-thirds. That means scammers are becoming more effective at extracting larger amounts from each victim. They’re not casting a wider net. They’re going deeper into each catch.
The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) recorded 41,557 complaints of cryptocurrency investment scams in 2024, which was a 29% jump from the 32,094 complaints filed in 2023. Those 2024 complaints accounted for $5.7 billion in reported losses, a 47% increase over the prior year. And in June 2025, the FBI released a specific public service announcement warning about criminals exploiting the NFT airdrop feature on the Hedera Hashgraph network to steal crypto through phishing URLs hidden inside transaction memos.
These numbers show something important: airdrop campaign scams are not declining. They are growing in volume, growing in scale, and growing in the damage they inflict on everyday users.
Recommended Reading:
How Do Airdrop Campaign Scams Actually Work?
Understanding how crypto airdrop scams operate is the foundation of protecting yourself. While tactics vary, the underlying mechanics follow a consistent pattern. Scammers exploit the trust, excitement, and sometimes greed of crypto users by mimicking the language and appearance of real airdrop campaigns. Here’s how the process typically unfolds.
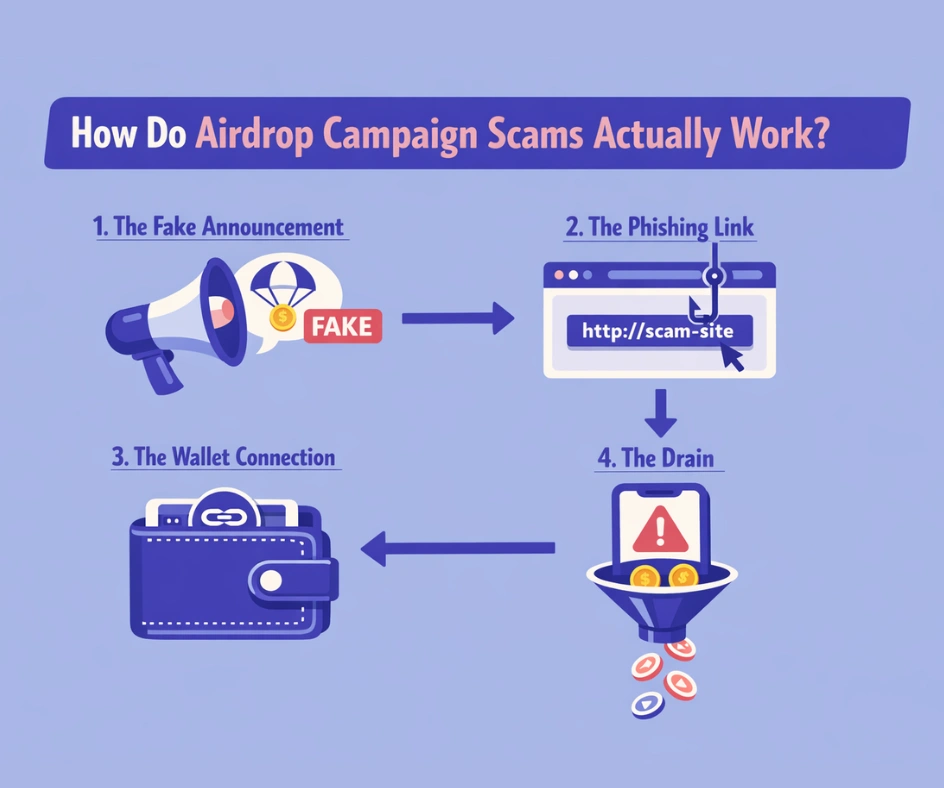
1. The Fake Announcement
Scammers create posts on X (formerly Twitter), Telegram, Discord, and sometimes even through email blasts, announcing a fake airdrop from a well-known project. They use copied branding, project logos, and language that mirrors official communications. Some go as far as setting up entirely fake Telegram groups or Discord servers with hundreds of bots pretending to be active community members.
2. The Phishing Link
The announcement directs users to a website that looks identical to the real project’s site. These phishing airdrop scams use domains that are off by a single character, use alternate extensions like .co instead of .com, or add extra words like “airdrop” or “claim” to the URL. ScamSniffer identified nearly 145,000 malicious web links used in these schemes during 2023 alone.
3. The Wallet Connection
Once on the fake site, users are asked to connect their wallet to “claim” their tokens. This is where the real danger begins. The site either requests the user to sign a malicious transaction, grant unlimited token spending approvals, or provide their seed phrase. Each of these actions opens the door for the scammer to drain the wallet.
4. The Drain
Within seconds of signing a malicious approval, funds begin moving out of the user’s wallet. In many cases, the entire balance is gone before the user even realizes what happened. These wallet-draining scams use smart contracts that automate the theft, prioritizing high-value assets like staked tokens, stablecoins, and NFTs.
Major Types of Airdrop Fraud in Crypto
Not all airdrop campaign scams look the same. Scammers have diversified their tactics to cast a wider net and adapt to different types of crypto users. Here are the most common forms of airdrop fraud in crypto that are actively targeting people right now.
1. Phishing Airdrop Scams
This is the most widespread type. Scammers set up fake websites that clone the look of popular crypto projects and ask users to enter private keys, seed phrases, or connect wallets. In January 2024, a major phishing campaign stole almost $600,000 in under 10 hours by sending emails impersonating Cointelegraph, WalletConnect, Token Terminal, and De.Fi. The stolen funds, around $520,000 in ETH, were quickly sent to Railgun’s mixer to hide the trail.
2. Wallet Draining Scams
Wallet-draining scams are a specialized subset of phishing that uses malicious smart contracts. Instead of stealing your password, these scams trick you into signing a transaction that gives the attacker permission to move your tokens. Scam Sniffer’s 2024 report showed that 85.3% of funds lost to wallet drainers, which totaled $152 million, came from Ethereum-based wallets. The most targeted assets were staking tokens (40.9%) and stablecoins (33.5%).
3. Fake Token Airdrops
Fake token airdrops involve scammers sending worthless or malicious tokens directly into users’ wallets. When users try to trade or interact with these tokens, they are redirected to phishing sites or tricked into approving malicious contracts. ScamSniffer’s research found that over 737,000 wallet addresses were targeted with fake airdrops impersonating popular projects such as ApeCoin, Pepe, and The Sandbox. In a related Polygon-based scheme, scammers mimicked 1,354 fraudulent NFTs, causing losses exceeding $1.2 million.
4. Advance Fee Airdrop Scams
In this variation, users are told they’ve qualified for an airdrop but must first pay a “gas fee,” “verification fee,” or “processing charge” in crypto. Once the payment is made, the promised tokens never arrive, and the scammer disappears. One notable example involved a deepfake video of Elon Musk promoting a fake SpaceX Bitcoin giveaway, where users were asked to send 0.1 BTC or more to receive 0.2 BTC in return. Larger senders were falsely promised a 60% bonus.
5. Social Media Impersonation Airdrops
Scammers compromise or impersonate well-known accounts on X, Discord, or YouTube to promote fake airdrops. In one case, Vitalik Buterin’s X account was hacked and used to promote a fake NFT airdrop with a 24-hour deadline, resulting in around $700,000 in collective losses. In late 2024, a deepfake of Binance CEO CZ promoted a fake BNB airdrop that scammed $2 million within hours.
6. Drainer as a Service (DaaS) Scams
These are particularly dangerous because they lower the barrier for criminal entry. Services like Inferno Drainer operated as full-service scam platforms where affiliates could rent phishing kits, draining tools, and hosting services. The operator took 20% of the stolen funds. Group IB identified over 16,000 phishing domains linked to Inferno Drainer, impersonating more than 100 crypto brands. Before its announced shutdown in November 2023, it had stolen over $80 million from 134,000 victims. However, it returned in May 2024 with support for 28 different blockchains, and its lifetime theft total has reportedly reached over $215 million across 200,000 victims.
Major Airdrop Scam Types and Their Real World Impact
| Scam Type | How It Works | Documented Losses / Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Airdrop Scams | Cloned websites ask for seed phrases, private keys, or wallet connections to steal credentials | $600,000 stolen in one phishing campaign in under 10 hours (January 2024) |
| Wallet Draining Scams | Malicious smart contracts trick users into signing approvals that drain wallet funds automatically | $494 million from 332,000 wallets in 2024 (Scam Sniffer) |
| Fake Token Airdrops | Worthless or malicious tokens sent to wallets that redirect users to phishing sites when interacted with | 737,000+ wallet addresses targeted; $1.2 million lost in Polygon NFT scam |
| Advance Fee Scams | Victims told to pay gas fees or verification charges before receiving airdrop tokens that never arrive | Deepfake Elon Musk SpaceX BTC scam tricked users into sending 0.1 BTC+ |
| Social Media Impersonation | Hacked or fake accounts of public figures promote fraudulent airdrops on X, YouTube, and Discord | $700,000 lost via hacked Vitalik Buterin X account; $2 million via deepfake CZ BNB airdrop |
| Drainer as a Service (DaaS) | Criminal platforms offer ready-made phishing kits and draining tools for a % cut of stolen funds | Inferno Drainer stole $80M+ from 134,000 victims across 16,000 phishing domains |
| Delayed Drain Attacks | Malicious approvals lie dormant for months before activating to drain funds when balances grow | $908,551 USDC drained in August 2025 from an approval signed 458 days earlier |
Real World Cases of Airdrop Campaign Scams
Theory is one thing, but seeing how airdrop campaign scams play out in practice hits differently. Here are several documented cases that show just how creative and destructive these scams have become.
The Hamster Kombat Airdrop Fraud
Hamster Kombat, a Telegram-based tap-to-earn game launched in March 2024, exploded in popularity and attracted over 250 million players. The game lets users earn HMSTR tokens through completing daily tasks and upgrades. But that massive user base also attracted scammers. Kaspersky issued public warnings about fake Hamster Kombat airdrops that were specifically designed to steal crypto wallet credentials from unsuspecting players. These phishing airdrop scams impersonated the game’s official branding and directed users to fraudulent claim pages where their login information was harvested.
The Wall Street Pepe Clone
Wall Street Pepe ($WEPE), an Ethereum-based memecoin, became a target when scammers cloned the project’s official website. The fake site promised airdrops and encouraged users to connect their wallets and sign transactions. Those who did found their wallets emptied through draining contracts. This case shows how crypto airdrop scams specifically target trending memecoins to exploit the fear of missing out that new investors commonly experience.
The $32.4 Million Inferno Drainer Heist
In one of the most devastating individual losses tied to the wallet-draining scams ecosystem, a crypto whale lost 12,083 Spark Wrapped Ether tokens (spWETH), valued at approximately $32.4 million. The attack was linked to the Inferno Drainer service. The victim unknowingly signed a malicious Permit transaction that granted the attacker full control over their wallet. Following the attack, the victim sent a blockchain message offering the thief 20% of the stolen amount (roughly $6.5 million) in exchange for returning the rest.
The Delayed Drain That Took $908,000
This case shook the crypto community because of its patience. In August 2025, a user lost $908,551 in USDC to a delayed wallet-draining attack. The theft was traced back to a malicious ERC 20 token approval the victim had signed 458 days earlier, on April 30, 2024. The scammer monitored the wallet for over a year, waiting until a substantial balance appeared before executing the drain. The funds were sent to an address identified as “pink-drainer.eth,” a known malicious actor in scam monitoring circles. This highlights an often overlooked danger: dormant approvals that silently wait for the right moment.
The FBI Hedera Hashgraph Warning
In June 2025, the FBI released a specific public service announcement about a growing scam exploiting the NFT airdrop feature on the Hedera Hashgraph network. Criminals were sending unsolicited NFTs or tokens into users’ non-custodial wallets. Each airdrop came with a “memo” containing a URL that appeared to be a claim link. When users clicked it, they were directed to phishing sites or malicious dApps that asked for login credentials and seed phrases. This case is notable because it represents federal law enforcement formally flagging airdrop fraud in crypto as a distinct and growing threat category.
The Google Play Crypto Drainer
Check Point Research uncovered the first known case of a crypto drainer exclusively targeting mobile users. A malicious app published on Google Play impersonated the WalletConnect protocol and stayed undetected for over five months, accumulating more than 10,000 downloads. It victimized over 150 users with losses exceeding $70,000 before being removed. The app used the MS Drainer toolkit, one of the most advanced malicious toolkits available, supporting multiple EVM blockchains, including Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum, Fantom, and Optimism.
Recommended Reading:
The Role of Social Media in Spreading Phishing Airdrop Scams
Social media is not just a channel for these scams. It is the engine that powers them. According to data from cryptocurrency fraud trend reports, 56% of all cryptocurrency scams in 2025 originated from social media platforms, including Instagram, Telegram, and X. Meta platforms like Facebook and Instagram alone drove 38% of reported crypto scam leads.
Telegram has become a particularly fertile ground for airdrop campaign scams. Reports indicate that the platform hosted over 1,500 active scam channels promoting fake airdrops and fraudulent investment opportunities. Scammers use these channels to build credibility through bot-generated engagement, fake testimonials, and urgency-driven messaging.
On X, the playbook involves creating accounts that closely mimic verified crypto projects or well-known figures. These fake accounts post airdrop announcements with links to phishing sites. Scam Sniffer tracked a significant increase in the use of compromised Twitter accounts and bots to push crypto drainer links throughout 2024. Some scammers even purchased X advertisements to promote their phishing pages, using paid traffic to reach a broader audience.
YouTube has not been spared either. Fraudulent livestreams impersonating Bitcoin giveaways defrauded viewers of $120 million, according to fraud trend reports. These streams used AI-generated deepfake videos of public figures like Elon Musk and other crypto personalities to create an illusion of legitimacy.
The combination of platform reach, lack of immediate verification systems, and the speed at which crypto transactions finalize makes social media the perfect distribution network for phishing airdrop scams.
Wallet Draining Scams: The Silent Killer
Wallet-draining scams deserve their own spotlight because of how devastatingly effective they are. Unlike traditional phishing, where scammers need your password, wallet drainers only need you to sign a single transaction. That signature, often disguised as a routine “claim” or “approve” action, is enough to hand over complete control of your tokens.
Here’s what makes them so dangerous:
1. The Permit Exploit
In 2024, 56.7% of wallet drainer thefts used the “Permit” signature type. This function, part of the EIP 2612 standard, allows users to authorize token spending through an off-chain signature. Scammers exploit this by embedding permit requests into their fake airdrop claim pages. Because it happens off-chain, it doesn’t trigger the usual on-chain warnings that wallets provide.
2. The setOwner Takeover
Another 31.9% of thefts relied on the “setOwner” function, which changes the ownership or administrative rights of a smart contract. Once ownership is transferred, the attacker has free rein over all assets managed by that contract.
3. The Mobile Attack Vector
Check Point Research uncovered the first case of a crypto drainer targeting only mobile users through a fake WalletConnect app on Google Play. The app remained live for over five months and was downloaded more than 10,000 times before removal. It used the MS Drainer toolkit and victimized over 150 users.
4. The Dormant Approval Threat
As the $908,551 USDC case showed, malicious approvals can sit dormant in your wallet for months or even years. The scammer waits, monitors your balance through on-chain data, and strikes when the value peaks. This makes regular audit of token approvals using tools like Etherscan’s Token Approval Checker not just a good practice but a necessity.
5. The Evolving Evasion Techniques
Scam Sniffer documented that in 2024, drainer operators increasingly used fake CAPTCHA pages, Cloudflare impersonation, IPFS hosting to avoid takedowns, and Google Ads to drive legitimate-looking traffic to phishing sites. These techniques make it harder for both security tools and users to identify the threat until it is too late.
Warning Signs of a Fake Airdrop
Knowing the red flags is half the battle when it comes to crypto airdrop scams. Here are the most consistent warning signs that an airdrop is fraudulent:
1. No Official Announcement from the Project
If the airdrop was not announced through the project’s verified website, verified X account, or official Discord/Telegram channels, treat it with extreme suspicion. Scammers promote fake token airdrops through unsolicited DMs, unofficial groups, and hastily assembled websites.
2. Requests for Private Keys or Seed Phrases
No real airdrop will ever ask for your private key, seed phrase, or wallet password. These are the master keys to your crypto holdings. Any request for them is an immediate disqualifier.
3. Suspicious or Lookalike URLs
Check the URL carefully. Scam sites often have subtle differences from the real thing: extra characters, missing letters, different domain extensions, or added words like “claim” or “airdrop” in the address. A single character difference in a URL can redirect you from a real platform to a fake page.
4. Grammar Errors and High-Pressure Language
Phrases like “Claim Now Or Lose Out!” or “Final Chance For Free Tokens!” are textbook scam tactics. Real projects communicate professionally and don’t create panic to push users into hasty decisions.
5. Unrealistic Reward Promises
If an airdrop promises you thousands of dollars worth of tokens just for clicking a link or connecting a wallet, that’s a warning sign. Legitimate airdrop campaigns have defined criteria, often tied to prior usage of the protocol, holding certain tokens, or genuine community participation.
6. No Whitepaper, Roadmap, or Team Information
Projects that exist only to promote an airdrop with no verifiable team, no whitepaper, no development roadmap, and no codebase are almost always scams. Real blockchain projects have a public track record.
7. Unusual Token Approval Requests
When a site asks you to approve unlimited spending of specific tokens or sign transactions you don’t fully understand, stop immediately. These approvals are the mechanism through which wallet draining scams operate.
Red Flags vs Legitimate Airdrop Signs: A Comparison
| Indicator | Legitimate Airdrop | Scam Airdrop |
|---|---|---|
| Announcement Source | Official project website, verified social accounts | Unsolicited DMs, unofficial Telegram groups, unknown emails |
| Information Requested | Public wallet address only | Private keys, seed phrases, passwords, and upfront payment |
| Website URL | Matches the official domain exactly | Misspelled, extra characters, alternate domain extensions |
| Urgency Level | Clear timeline, no panic language | “Act now!” “Last chance!” “Claim before it expires!” |
| Reward Claims | Proportional to activity or holding period | Outrageous amounts for minimal or no effort |
| Project Transparency | Whitepaper, doxxed team, GitHub repository, audit reports | No team info, no whitepaper, no verifiable history |
| Transaction Requests | Simple claim, no unusual token approvals | Unlimited spending approvals, Permit signatures, and ownership transfers |
How to Protect Yourself from Airdrop Campaign Scams
Protection against airdrop campaign scams starts with habits and tools. Here is a practical breakdown of the most effective defenses available right now.
1. Verify Every Airdrop Through Official Channels
Before clicking any link or connecting any wallet, go to the project’s official website manually (type the URL yourself, don’t follow links). Check their official X account, Discord, or Telegram for matching announcements. If the airdrop is only being promoted through DMs or unofficial channels, it is almost certainly a scam.
2. Never Share Your Private Key or Seed Phrase
This is the golden rule of crypto. Your seed phrase is the master password to everything you own on chain. Legitimate airdrop campaigns will never ask for it. Period.
3. Use a Dedicated Wallet for Airdrop Interactions
Create a separate wallet specifically for interacting with airdrops and unknown dApps. Keep only a minimal amount of funds in this wallet. This way, even if a scam slips through your defenses, the damage is limited to the contents of that wallet rather than your entire portfolio.
4. Regularly Audit Your Token Approvals
Use tools like Etherscan’s Token Approval Checker or Revoke. Cash to regularly review and revoke any token approvals you no longer need. The delayed drain case that cost $908,551 could have been prevented if the dormant approval had been caught and revoked in time.
5. Install Security Extensions and Wallet Guards
Tools like ScamSniffer, Pocket Universe, and Wallet Guard can warn you before you sign a malicious transaction. These browser extensions analyze transactions in real time and flag suspicious activity. ScamSniffer has already identified over 100,000 malicious domains through its open source blacklist.
6. Use Hardware Wallets for Significant Holdings
Hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor keep your private keys offline, making them immune to web-based phishing attacks. Never approve airdrop-related transactions on mobile browsers connected to your primary wallet.
7. Enable Two Factor Authentication Everywhere
Protect your exchange accounts, email, and any crypto-related platforms with app-based two-factor authentication (not SMS, which can be SIM swapped). This adds a layer that scammers cannot bypass through phishing alone.
8. Read Transactions Before Signing
Get into the habit of reading every transaction prompt carefully before clicking “confirm.” If a transaction asks you to approve unlimited spending for a token, or if the action description doesn’t match what you expected, reject it immediately. Simulate transactions using tools built into wallets like Rabby or MetaMask’s transaction preview feature.
9. Report and Block Suspicious Accounts
If you encounter a fake airdrop on social media, report the account and block it. The FBI encourages victims and witnesses of airdrop scams to submit reports to the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) at ic3.gov. This helps law enforcement track and eventually dismantle scam operations.
10. Stay Informed Through Community Channels
Follow trusted security accounts like ScamSniffer, CertiK Alert, PeckShield, and SlowMist on social media. Subreddits like r/CryptoCurrency frequently share real-time alerts about active scams. Community vigilance is one of the most effective defenses against phishing airdrop scams.
Recommended Reading:
The Changing Landscape: How Airdrops Are Evolving to Fight Fraud
Not all the news is bad. The industry is adapting. Legitimate airdrop campaigns are shifting their models to reduce exploitation by scammers and bots alike.
Activity-based airdrops are replacing the old “sign up and receive” model. Projects like Optimism and LayerZero have moved toward retroactive distribution methods that reward users based on their past on-chain activity, such as staking, governance participation, or protocol usage. This makes it much harder for scammers to create fake claim campaigns because eligibility is tied to verifiable blockchain history rather than simple form submissions.
Anti-Sybil systems are now implemented by more than 85% of projects according to CoinLaw data. These systems detect bot farms and fake wallet clusters that try to game airdrop distributions. While not perfect, they significantly raise the cost and complexity for scammers trying to intercept or replicate legitimate campaigns.
AI-powered monitoring is also entering the picture. Some projects are beginning to integrate machine learning models that scan for phishing domains, impersonation accounts, and suspicious smart contract patterns in real time. This proactive approach aims to shut down scam infrastructure before it reaches victims.
The SEC and the EU’s MiCA regulatory framework are adding legal pressure as well. As crypto regulations tighten, the ability of scammers to operate openly on exchanges and through advertising platforms is being curtailed. While enforcement remains slow, the direction is clear: regulatory bodies are treating airdrop fraud in crypto with increasing seriousness.
Blockchain analysis firms like Chainalysis, SlowMist, and Scam Sniffer are making real progress in identifying and flagging malicious infrastructure. Scam Sniffer’s open source blacklist now contains close to 100,000 malicious domains, and the company scanned nearly 12 million URLs during 2023 alone. These community-driven efforts are creating a growing database of known threats that wallets and browsers can use to protect users before they ever reach a phishing page.
The shift from passive, open airdrops to verified, activity-based distributions is perhaps the most important long-term change. By requiring users to have pa rovable on-chain history before becoming eligible, projects are making it structurally harder for scammers to create convincing fakes. This doesn’t eliminate the threat, but it narrows the window of opportunity considerably.
What Regulators and Law Enforcement Are Doing
Government agencies are taking notice. The FBI’s public service announcement in June 2025 about the Hedera Hashgraph airdrop scam was a clear signal that federal law enforcement views airdrop campaign scams as a distinct category of cybercrime worth addressing directly. The FBI specifically recommended that users verify any unsolicited airdrop with the official provider, never share seed phrases or one-time passwords unless they initiated the contact, and monitor their crypto accounts for unauthorized activity.
The FBI’s Operation Level Up, launched in January 2024, has notified 5,831 victims of cryptocurrency investment fraud as of April 2025. The operation reported that 77% of those contacted were unaware they had been scammed. It helped save victims over $359 million in potential additional losses and referred 59 victims to FBI victim specialists for suicide intervention, underscoring the personal devastation these scams can cause.
California’s Department of Financial Protection and Innovation (DFPI) maintains a dedicated Crypto Scam Tracker that includes a specific category for “Crypto Giveaway/Airdrop Scams.” The DFPI defines these as schemes where scammers compromise or impersonate public figures, often using AI deepfakes, to promote fake giveaways that are either attempts to steal crypto directly or phishing operations targeting private wallet information.
On the international front, Europol’s operations have targeted crypto laundering networks, and Interpol’s HAECHI VI operation recovered $439 million and blocked 68,000 bank accounts connected to crypto fraud. The EU’s MiCA regulation, now in effect, is creating a compliance framework that makes it harder for fraudulent projects to advertise or list tokens on regulated platforms within Europe.
Despite these efforts, enforcement remains challenging. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrency, the speed of transactions, and the use of privacy mixers and cross-chain bridges make it difficult to track and recover stolen funds. Prevention through user education remains the most effective line of defense against crypto airdrop scams.
Blockchain Security Solutions Built for the Real World
The following projects reflect how blockchain security, smart contract auditing, and wallet protection are already being applied in production environments. Each implementation showcases the principles discussed throughout this article, from smart contract verification and multi-chain security to decentralized governance and fraud prevention infrastructure.
🔐
Rubic: Multi-Chain Decentralized Exchange with MEV Protection
Built a decentralized exchange aggregating over 200 DEXs across 80+ blockchain networks with Private RPC and MEV bot protection. The platform prevents front running and transaction manipulation, providing users with protected trade execution and fraud prevention across every supported chain.
🛡️
RoninChain: Gaming Blockchain with Post-Hack Security Overhaul
Developed a gaming-focused Layer 1 blockchain that underwent comprehensive security enhancements following a major bridge hack. The platform now features validator diversity, robust slashing mechanisms, DPoS consensus, and continuous security audits to protect millions of NFT transactions and user assets.
Protect Your Blockchain Project from Smart Contract Exploits:
We bring 8+ years of blockchain expertise to smart contract auditing and Web3 security. Our specialized team handles everything from vulnerability detection to multi-chain security implementation, ensuring your platform is built to protect user assets and prevent exploits. Whether you need a DeFi security audit or a wallet protection solution, we deliver results that matter.
Conclusion
Airdrop campaign scams are not a minor inconvenience on the fringes of the crypto world. They are a multi-billion-dollar criminal industry that is growing more sophisticated with every passing quarter. The $9.9 billion in scam losses reported by Chainalysis for 2024, the $494 million drained through wallet drainer malware that same year, the FBI’s formal warnings about NFT airdrop exploitation, and the continued evolution of Drainer as a Service platforms like Inferno Drainer all point to the same conclusion: this is a threat that demands serious attention from every crypto user.
The good news is that the tools and knowledge needed to avoid these scams are available. Verifying airdrops through official project channels, never sharing private keys or seed phrases, using dedicated wallets for unknown interactions, regularly auditing token approvals, installing browser security extensions, and staying informed through trusted community sources can collectively reduce your risk significantly. None of these steps is complicated, but they require discipline and consistency.
The crypto industry itself is moving in the right direction. Activity-based airdrop models, anti-Sybil systems, AI-powered threat detection, and stronger regulatory frameworks are all making it harder for scammers to operate. But these structural improvements take time to mature. In the meantime, the responsibility for protection falls on individual users. Every wallet connection, every transaction signature, and every link click is a potential point of vulnerability.
The single most important takeaway from everything covered in this blog is this: if something promises free money for almost no effort, and it asks you to connect your wallet or share your credentials to receive it, the overwhelming probability is that it’s a crypto airdrop scam. The cost of verifying before acting is zero. The cost of acting without verifying can be everything in your wallet.
Frequently Asked Questions
An airdrop campaign scam is a fraudulent scheme where criminals impersonate real blockchain projects and promise free tokens to trick users into connecting their wallets, sharing private keys, or signing malicious transactions. These scams are designed to steal cryptocurrency from victims’ wallets, and they often use phishing websites, fake social media accounts, and cloned project branding to appear legitimate.
The most common signs of a fake token airdrop include: the lack of any announcement on the project’s official website or verified social media accounts, requests for private keys or seed phrases, URLs with subtle misspellings or unusual domain extensions, high-pressure language like “claim now or lose forever,” unrealistic reward promises, and no verifiable project team or documentation. Always cross-check any airdrop announcement directly on the project’s official channels before interacting.
Immediately use a tool like Revoke. Cash or Etherscan’s Token Approval Checker to review and revoke any token approvals you may have granted. Transfer your remaining assets to a new wallet as quickly as possible. Do not interact further with the suspicious site. If you have lost funds, document the transaction hashes, phishing URL, and any other details, then report the incident to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) at ic3.gov.
Yes. Wallet draining scams do not need your private key. They work by tricking you into signing a transaction that grants the attacker permission to move your tokens. This is done through malicious Permit signatures, setOwner functions, or unlimited token spending approvals. A single signed transaction is enough to drain your entire wallet balance without ever having access to your seed phrase.
Yes, several tools can significantly reduce your risk. ScamSniffer offers a browser extension that detects phishing websites and malicious transactions in real time. Pocket Universe and Wallet Guard provide transaction simulation before you sign. Revoke. Cash allows you to audit and revoke unnecessary token approvals. Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor keep your keys offline. Using a combination of these tools alongside basic verification habits provides strong protection.
Several factors are driving the growth. The Drainer as a Service model (DaaS) has lowered the barrier for entry, allowing even non-technical criminals to run sophisticated scams using pre-built kits. Social media platforms still struggle to prevent impersonation accounts and paid phishing ads. AI deepfakes are making fake endorsements more convincing. And the growing number of new crypto users unfamiliar with on-chain security practices creates a constantly expanding pool of potential victims. While defensive tools are improving, the attackers are evolving just as fast.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






