Key Takeaways
- A hard fork permanently splits a blockchain into two separate chains with different rules, creating independent networks that cannot communicate with each other.
- Hard forks often result in new cryptocurrencies, as seen with Bitcoin Cash emerging from Bitcoin and Ethereum Classic from Ethereum.
- The process requires community consensus, extensive development, rigorous testing, and clear communication before activation.
- Market volatility typically increases around hard fork events, creating both risks and opportunities for investors and traders.
- Professional guidance from experienced blockchain consultants can help businesses navigate the technical and strategic challenges of hard forks.
Blockchain networks do not stay the same forever. They grow, face challenges, and sometimes need major changes to keep working properly. One of the most significant ways a blockchain can change is through something called a hard fork. If you are involved in cryptocurrency, run a business that uses blockchain, or simply want to understand this technology better, knowing how hard forks work is valuable knowledge.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about hard forks. We will cover what they are, why they happen, how they affect blockchain networks, and what real examples look like. By the end, you will have a clear picture of this important blockchain concept.
What Exactly is a Hard Fork in Blockchain?
Think of a blockchain as a digital record book that everyone agrees to use in a specific way. A hard fork happens when the rules for using that record book change so much that the old version and new version can no longer work together. The result is two separate blockchains going their own ways from a specific point forward.
This is different from regular software updates. When your phone gets an update, the new version usually works fine with the old version. But a hard fork creates a permanent split. Computers running the old software will not recognize blocks created by computers running the new software, and vice versa.
According to Wikipedia’s explanation of blockchain forks, a hard fork represents a radical change to a network’s protocol that makes previously invalid blocks and transactions valid, or vice versa. This fundamental incompatibility is what separates hard forks from softer changes to blockchain networks.
For anyone looking to understand the foundations of this technology, exploring how blockchain technology works provides essential background knowledge that makes hard forks easier to grasp.
Hard Fork vs Soft Fork: Understanding the Difference
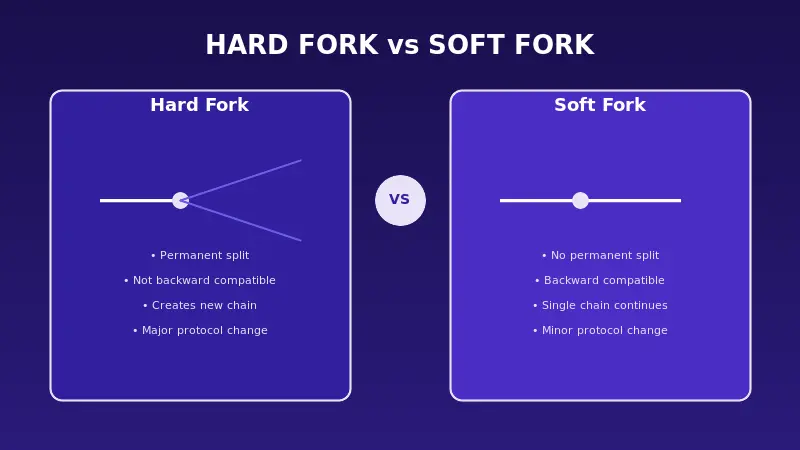
Not all blockchain updates create permanent splits. Soft forks are another type of change that works differently. Understanding both helps clarify why hard forks are such significant events.
| Feature | Hard Fork | Soft Fork |
|---|---|---|
| Backward Compatibility | Not compatible with old nodes | Works with old nodes |
| Chain Split | Creates permanent split | No permanent split |
| Upgrade Requirement | All nodes must upgrade | Only miners need to upgrade |
| Rule Changes | Adds new rules, changes existing rules | Tightens existing rules only |
| Risk Level | Higher risk and complexity | Lower risk |
| New Cryptocurrency | Often creates new coin | Does not create new coin |
The key point is that hard forks represent bigger, more consequential changes. They require more planning, more community agreement, and carry more risk. But they also allow for more significant improvements that soft forks simply cannot achieve.
Why Do Blockchain Networks Need Hard Forks?
Several situations push blockchain communities toward hard forks. Each reason reflects a different need that the existing blockchain cannot meet without fundamental changes.
Adding New Capabilities: Blockchains sometimes need features that their original design did not include. Smart contracts, faster transaction processing, or new security measures might require rule changes so significant that only a hard fork can implement them. The history of blockchain shows how these networks have continuously adapted through such upgrades.
Fixing Critical Problems: Security vulnerabilities or major bugs sometimes require immediate, drastic action. When a flaw threatens the entire network, a hard fork can quickly implement fixes. The Ethereum community faced this exact situation after a major hack, and their response shaped blockchain governance discussions for years afterward.
Resolving Community Disagreements: Not everyone in a blockchain community agrees on how the network should develop. When disagreements become too deep to resolve through compromise, a hard fork allows different groups to pursue their own visions. This is democracy in action, blockchain style.
Improving Performance: As more people use a blockchain, it can become slow and expensive. Hard forks can change how the network processes transactions, making it faster and more efficient for everyone.
The Complete Hard Fork Process
Hard forks do not happen overnight. They follow a structured process that can take months or even years from initial proposal to final activation. Understanding this process helps explain why hard forks are such major events in the blockchain world.
Stage 1: Proposal and Discussion
Everything starts with someone suggesting a change. This proposal explains what needs to change, why it matters, and how it would work technically. The community then discusses the proposal, asking questions, raising concerns, and suggesting modifications. This stage can last weeks or months depending on how controversial the proposed changes are.
Stage 2: Building Consensus
For a hard fork to succeed, enough people need to support it. This includes developers who write the code, miners who validate transactions, and users who actually use the network. Getting everyone aligned is often the hardest part of the process. Without broad support, a hard fork might fail or create an unwanted permanent split.
Stage 3: Development
Once there is agreement, developers start writing the actual code. This involves creating new software that implements the proposed changes while maintaining everything else that works well. The development phase requires careful attention to detail because mistakes can have serious consequences.
Stage 4: Testing
Before any code goes live, it must be tested thoroughly. Developers create test networks that simulate real conditions without risking actual assets. They look for bugs, security holes, and unexpected behavior. Only after extensive testing does the new code get approved for deployment.
Stage 5: Activation
Finally, the hard fork goes live on a specific date or at a specific block number. Everyone who wants to continue using the network must upgrade their software before this point. After activation, the old chain and new chain operate independently.
How Hard Forks Affect Blockchain Networks
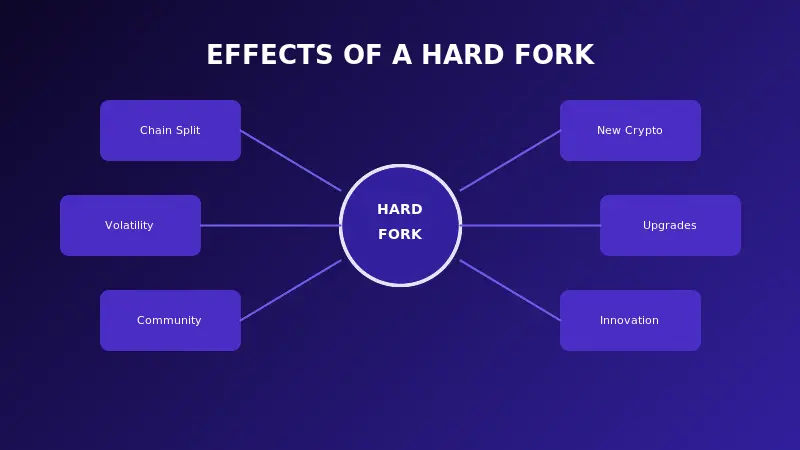
The effects of a hard fork ripple through every part of the blockchain ecosystem. Some effects are immediate while others unfold over months or years.
Creation of Two Independent Networks
The most visible effect is the split itself. Where one blockchain existed before, now two exist. Each chain has its own transaction history from the fork point forward. Each chain has its own community, developers, and governance. They may evolve in completely different directions over time.
Birth of New Cryptocurrencies
When a hard fork happens, anyone holding coins on the original chain typically receives an equal amount on the new chain. This creates a new cryptocurrency that may develop its own value and market. Some of these new coins become significant players in the crypto market while others fade away.
Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices often swing wildly around hard fork events. Uncertainty about which chain will succeed, speculation about new coins, and general market excitement all contribute to price movements. Traders see both opportunities and risks during these periods.
Technical Disruptions
Applications built on the blockchain need updates to work with the new rules. Wallets, exchanges, and other services must adapt. This transition period can cause temporary inconveniences for users who rely on these services.
Navigate Hard Fork Changes Successfully
Hard forks bring complexity to blockchain operations. Get expert guidance to adapt your systems, protect your assets, and take advantage of new opportunities.
Real Examples of Blockchain Hard Forks
Theory becomes clearer with concrete examples. Several hard forks have shaped the cryptocurrency landscape we see today.
| Hard Fork Event | Year | Original Chain | New Chain | Primary Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The DAO Fork | 2016 | Ethereum | Ethereum Classic | Reverse major hack |
| Bitcoin Scaling | 2017 | Bitcoin | Bitcoin Cash | Increase block size |
| Hash War | 2018 | Bitcoin Cash | Bitcoin SV | Vision disagreement |
| Shelley Upgrade | 2020 | Cardano | N/A (planned) | Decentralization |
| Alonzo Upgrade | 2021 | Cardano | N/A (planned) | Smart contracts |
The Ethereum and Ethereum Classic Split
In 2016, hackers exploited a vulnerability in The DAO, a decentralized investment fund built on Ethereum, stealing millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency. The Ethereum community faced a difficult choice: accept the theft or change the blockchain’s history to return the stolen funds.
Most community members chose to hard fork and reverse the hack. But some believed that blockchains should be immutable, meaning their history should never change regardless of circumstances. This philosophical disagreement led to two chains: Ethereum (which reversed the hack) and Ethereum Classic (which kept the original history).
Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin’s block size limit of 1 megabyte caused problems as the network grew. Transactions became slow and expensive during busy periods. The community debated solutions for years without reaching agreement.
In 2017, one group decided to increase the block size through a hard fork, creating Bitcoin Cash with 8 megabyte blocks (later increased to 32 megabytes). The original Bitcoin continued with its smaller blocks but implemented other scaling solutions. Both chains survive today with different approaches to the same fundamental problem.
Cardano’s Planned Upgrades
Not all hard forks create permanent splits. Cardano has used hard forks as planned upgrades to add new features. The Shelley hard fork improved decentralization while the Alonzo hard fork added smart contract capabilities. Because the community agreed on these changes, no competing chains emerged.
Challenges Businesses Face During Hard Forks
Organizations that use blockchain technology face specific challenges when hard forks occur. These challenges require careful planning and often professional guidance to navigate successfully.
System Updates: Any software that interacts with the blockchain needs updates. This includes payment systems, inventory tracking, supply chain applications, and more. The updates must happen before the fork to avoid disruptions.
Asset Management: Businesses holding cryptocurrency must decide how to handle coins on both chains. Selling, holding, or converting these assets requires strategic thinking about tax implications, market timing, and operational needs.
Vendor Coordination: Companies that rely on blockchain service providers need those providers to update their systems as well. Any weak link in the chain can cause problems.
Staff Training: Employees who work with blockchain systems need to understand the changes and how to handle them. This education takes time and resources.
Working with a blockchain based company that has experience with hard forks can significantly reduce these challenges. Professional guidance helps ensure smooth transitions and minimizes business disruption.
Impact on Different Stakeholders
Hard forks affect various participants in the blockchain ecosystem differently. Understanding these varied impacts helps stakeholders prepare appropriately.
| Stakeholder | Primary Impact | Required Action |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Users | Wallet updates, potential new coins | Update software, secure private keys |
| Miners | Choose which chain to support | Update mining software, evaluate profitability |
| Developers | Code updates, new opportunities | Adapt applications, learn new features |
| Exchanges | Support both chains, manage listings | Update systems, communicate with users |
| Businesses | System updates, strategic decisions | Plan transition, seek professional guidance |
Expert Guidance for Hard Fork Navigation
Hard forks introduce complexity that many organizations are not equipped to handle alone. This is where professional blockchain consulting becomes valuable. Experienced consultants bring knowledge gained from handling multiple hard forks across different blockchain networks.
Nadcab Labs has spent over 8 years working with blockchain technology, guiding businesses through numerous hard fork events. This deep experience means understanding not just the technical aspects but also the strategic and operational considerations that affect business outcomes.
The value of professional guidance extends beyond simply updating software. Consultants help organizations understand the implications of different choices, develop contingency plans, and execute transitions smoothly. They bring perspective from similar situations and can anticipate problems before they occur.
For businesses building custom blockchain solutions, hard fork considerations should be part of the development process from the start. Planning for future upgrades and changes makes them easier to handle when they occur.
The Future of Blockchain Evolution
Hard forks will continue to be part of blockchain technology’s evolution. As networks mature and face new challenges, some will require fundamental changes that only hard forks can deliver. The key is approaching these events with preparation, understanding, and appropriate support.
The blockchain industry has learned from past hard forks. Governance mechanisms have improved, communication practices have matured, and technical processes have become more refined. Future hard forks will likely be smoother than those of the past, though they will never be entirely without challenges.
For anyone involved with blockchain technology, staying informed about potential hard forks affecting the networks they use is essential. Early awareness allows for better preparation and reduces the risk of being caught off guard by major changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
When a hard fork occurs, you typically receive an equivalent amount of the new cryptocurrency on the forked chain. Your original coins remain on the original chain. However, you need to take precautions to protect both. Before the fork, ensure your coins are in a wallet where you control the private keys, not on an exchange. After the fork, you will have coins on both chains that you can manage separately. Some exchanges handle this automatically, but relying on your own wallet gives you more control over the process and timing of accessing your forked coins.
The entire hard fork process from initial proposal to activation can take anywhere from several months to over a year. The proposal and discussion phase might last a few weeks to several months depending on controversy. Building consensus often takes the longest time, sometimes requiring multiple rounds of negotiation. Development and testing typically need three to six months minimum for major changes. The actual activation happens at a predetermined block number or date. Contentious forks where community agreement is difficult can stretch the process considerably longer than planned upgrades.
Once a hard fork activates, it cannot be simply reversed. The blockchain has permanently split into two independent networks. However, the community could theoretically execute another hard fork to undo changes or even merge back with the original chain, though this would require overwhelming consensus and is extremely rare. In practice, hard forks create permanent separate paths. The only real reversal happens when one chain loses all support and becomes abandoned, which effectively means everyone moved to the other chain rather than actually reversing the fork itself.
Opposition to hard forks often stems from philosophical differences rather than purely technical concerns. Some believe blockchains should prioritize immutability and resist changes even for improvements. Others may disagree about what constitutes an improvement. Miners might oppose changes that affect their profitability. Developers who built applications on the current system might not want to update their code. Some community members distrust the motivations of those proposing changes. The decentralized nature of blockchain means everyone has a voice, and genuine disagreements about the network’s future direction are common and expected.
Smart contracts are affected differently depending on what the hard fork changes. If the fork only changes consensus mechanisms or block parameters, most smart contracts continue working normally on both chains. However, if the fork changes the programming language, execution environment, or fundamental operations, smart contracts may need updates. After a fork, the same smart contract exists on both chains and executes independently. This can create interesting situations where a contract behaves differently on each chain due to different network conditions, user bases, or subsequent updates to the chains.
Replay protection prevents transactions made on one chain from being copied and executed on the other chain after a fork. Without replay protection, sending coins on one chain could allow someone to replay that transaction on the other chain, effectively stealing your coins on the second chain. Well-designed hard forks include replay protection to prevent this attack. This is implemented by making transactions on each chain incompatible with the other. When a fork lacks replay protection, users must take extra precautions like splitting their coins using specialized techniques before making any transactions.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.