Key Takeaways
- To build a crypto exchange from scratch, start by choosing the right model (centralized, decentralized, or hybrid) based on your business goals and target users.
- Successfully creating a crypto exchange platform requires essential systems like a trading engine, wallet infrastructure, user interface, and admin controls.
- A cryptocurrency exchange works by matching buy and sell orders, managing user funds securely, and settling trades in real time.
- Security must be built into the platform from the beginning to protect user assets and prevent operational risks.
- Liquidity is critical for launching a usable crypto exchange, ensuring fast trades, low slippage, and fair pricing.
- The cost and timeline depend on scope, with MVP exchanges taking months and full-scale platforms requiring phased development.
What is a Cryptocurrency Exchange & How does it work?
A cryptocurrency exchange is a platform where users can trade digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other altcoins. The exchange acts as an intermediary that matches buyers and sellers while keeping their funds safe.
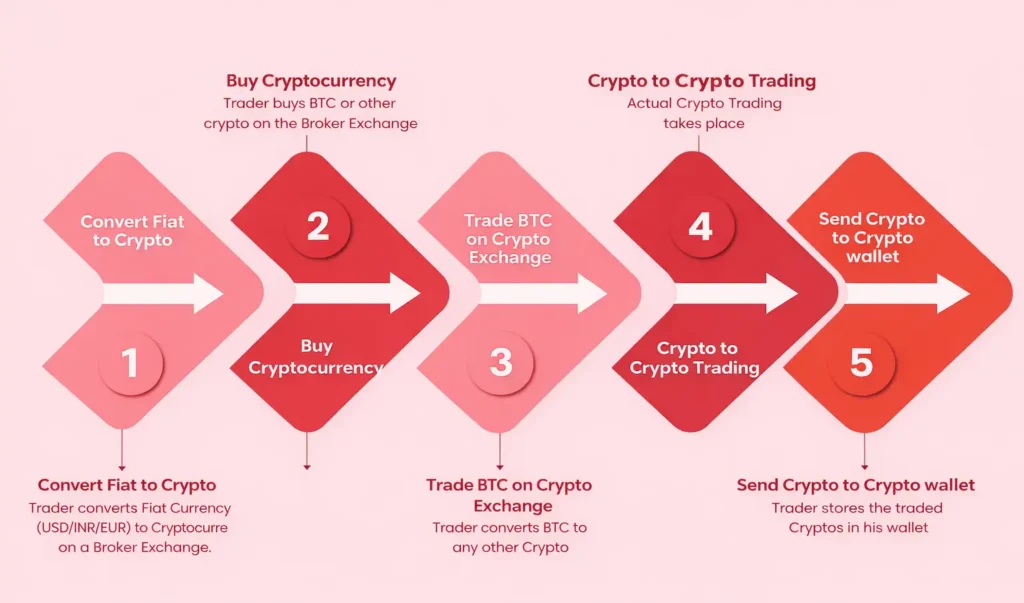
How it works-
- User Accounts- Users first register on the exchange by providing their basic information. Verified accounts are linked to digital wallets where their funds are stored.
- Deposits and Wallets- Users deposit cryptocurrencies or sometimes fiat currency into their wallets. The exchange keeps these funds organized and ready for trading.
- Placing Orders- Users place orders to buy or sell a cryptocurrency. These orders include the amount, price, and type (market or limit order).
- Matching Orders- The exchange’s system checks for matching orders from other users. When a buy order matches a sell order, the trade is executed automatically.
- Updating Balances- Once a trade is completed, the users’ wallets are updated to reflect the new balances. This ensures that all funds are accounted for accurately.
- Security Measures- While trading happens, the exchange continuously monitors transactions to prevent unauthorized access or fraud.
A cryptocurrency exchange is like a marketplace for digital currencies. Users bring their funds, place trades, and the platform ensures everything is executed smoothly and securely. Understanding this flow is crucial before moving on to the next steps of building your own platform.
Why Build a Crypto Exchange Platform?
The cryptocurrency industry has grown into a multi-trillion-dollar market, creating strong opportunities for businesses that want to build or start a crypto exchange platform.
Why are many founders entering this space-
- Over 560 million users worldwide actively own or use cryptocurrency, and this number continues to grow each year.
- The global crypto market is valued at over $2 trillion, showing strong long-term demand for trading platforms.
- Leading exchanges process billions of dollars in daily trading volume, proving that user activity remains high.
- Crypto exchanges generate revenue through trading fees, listings, and premium services, making them scalable business models.
- The global blockchain market is projected to grow from $27.8 billion to over $800 billion, increasing demand for exchange platforms.
As crypto adoption expands, users seek secure, reliable, and user-friendly platforms. This is why many businesses now choose to create their own crypto exchange instead of staying on the sidelines.
How to Start a Cryptocurrency Exchange- Build Options
When planning how to start a cryptocurrency exchange, one of the most important early decisions is how you will build the platform itself. This choice directly affects cost, control, security, scalability, and long-term success.
In practical terms, there are two main ways to create a crypto exchange platform:
- Using a ready-made exchange solution
- Building the exchange platform fully from the ground up
Each option serves a different business goal, so understanding their impact is critical before moving forward.
Using a Ready-Made Crypto Exchange Solution
A ready-made crypto exchange solution allows you to launch an exchange using pre-built software. These platforms typically come with essential features such as a trading system, basic user interface, wallet support, admin controls, and sometimes even initial liquidity access.
This option is often chosen by businesses that want to open a crypto exchange quickly with limited upfront effort.
Benefits of Ready-Made Exchange Platforms
- Quick setup and launch
Since the core system already exists, you can start a crypto exchange much faster. - Lower initial investment
Upfront costs are usually lower compared to building everything independently. - Essential features included
Basic trading, wallets, and admin tools are available from day one.
Limitations to Consider
- Dependence on external providers
Your exchange operations depend on another company’s software and support. - Restricted flexibility
Feature changes, workflow adjustments, and interface updates are often limited. - Scaling difficulties
As user activity and trade volume grow, performance constraints may appear. - Reduced control over security
You rely on the provider’s internal security practices, which may not fully align with your risk tolerance.
While ready-made solutions can help you launch faster, they often create long-term limitations. If the provider discontinues support or changes service terms, your exchange may face operational risks that are outside your control.
Building a Crypto Exchange Platform from Scratch
Building a crypto exchange from scratch means designing and creating every core system independently. This includes the trading logic, wallet management, admin controls, security layers, and user-facing interface.
This approach is suitable for businesses that want full ownership, long-term flexibility, and the ability to scale without restrictions.
Advantages of Starting from the Ground Up
- Full platform control
You own the technology and are not dependent on third-party software decisions. - Flexible feature design
The exchange can be shaped around your business model and user needs. - Scalable foundation
The system can be designed to handle growth in users, trades, and assets. - Distinct user experience
A tailored interface helps differentiate your exchange in a competitive market.
Challenges to Be Aware Of
- Longer preparation time
Building everything independently requires careful planning and testing. - Higher initial cost
Infrastructure, security, and engineering efforts increase early investment.
Despite these challenges, starting from scratch provides long-term stability. You avoid external dependencies, reduce future limitations, and create an exchange platform that can evolve with market demands.
Choosing the Right Approach to Start a Crypto Exchange
If your main goal is to enter the market quickly with minimal setup, a ready-made solution can be a short-term option. However, if you aim to build a reliable, scalable, and long-lasting cryptocurrency exchange, creating the platform from scratch offers stronger long-term value.
The decision should be based on where you want your exchange to be in the future, not just how fast it can be launched today. A strong foundation makes it easier to grow, adapt to regulations, and earn lasting user trust.
Step-by-Step Guide to Build a Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform from Scratch
Building a crypto exchange platform from scratch is not a single technical task. It is a structured process that involves business decisions, system design, security planning, liquidity preparation, compliance readiness, and a controlled launch. This section breaks down the entire journey into clear, actionable steps so founders understand what to do, why it matters, and how each decision affects the final exchange.
This step-by-step approach is designed for startups and businesses that want to create, start, set up, and launch a crypto exchange platform with long-term scalability in mind.
Step 1 – Define Your Crypto Exchange Business Model
The first step in building a crypto exchange platform is deciding what type of exchange you want to create. This decision directly impacts architecture, security design, compliance requirements, and operating costs.
Most exchanges fall into three models-
- Centralized Exchange (CEX)-
Operated by a single entity that controls order matching, custody, and user accounts. This model is easier to manage, faster to scale, and more familiar to users, making it a common choice for startups. - Decentralized Exchange (DEX)-
Operates without central custody, relying on smart contracts and user-controlled wallets. While this model offers transparency, it introduces higher technical complexity and user experience challenges. - Hybrid Exchange-
Combines centralized performance with decentralized custody elements, aiming to balance speed, control, and security.
Choosing the right model early prevents costly redesigns later. The goal is not to pick what sounds advanced, but what aligns with your target users, regulatory environment, and long-term business vision.
| Aspect | Centralized Exchange (CEX) | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Hybrid Exchange |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership & Control | Operated and controlled by a single company | No central authority; runs via smart contracts | Platform-controlled trading with partial decentralization |
| Custody of Funds | Exchange holds user funds (custodial) | Users hold their own funds (non-custodial) | Mixed custody model |
| Ease of Use | Very user-friendly for beginners | Requires wallet knowledge and blockchain familiarity | Easier than DEX, slightly complex than CEX |
| Performance & Speed | High-speed order execution | Slower due to on-chain execution | High-speed with optimized settlement |
| Liquidity Availability | Easier to build with market makers | Depends on liquidity pools | Better than DEX, improving over time |
| Security Responsibility | Platform responsible for asset security | Users responsible for their own security | Shared responsibility |
| Regulatory Compliance | Easier to implement KYC/AML | Difficult to enforce regulations | Moderate compliance flexibility |
| Development Complexity | Moderate | High (smart contracts + UX challenges) | High but scalable |
| Cost to Build | Medium to High | High | High |
| Best For | Startups launching their first crypto exchange | DeFi-focused, privacy-driven platforms | Exchanges targeting performance + security balance |
Step 2 – Choose the Right Architecture for Your Exchange Platform
Once the business model is finalized, it’s time to plan and build the architecture for your crypto exchange platform that ensures scalability, security, and smooth trading operations. Architecture determines how different parts of the system communicate, scale, and remain stable under high trading volume.
A modern exchange should be built using a modular architecture, where each core function operates as an independent component. This approach allows easier upgrades, faster issue resolution, and better scalability.
Key architectural principles include-
- Separation of trading, wallet, and user management functions
- Independent scaling of high-load components like order matching
- Fault isolation to prevent system-wide failures
Scalability is especially important. Even if you start small, the platform should be designed to handle sudden spikes in users and trades without downtime. A well-planned architecture ensures your exchange can grow without needing a complete rebuild later.
Step 3 – Core Components Required to Build a Crypto Exchange
Every cryptocurrency exchange is built around a set of essential components that work together to support trading and user operations. Understanding these components helps founders plan development more effectively.
The core components include-
- User Interface (UI)
This is what traders interact with. It includes dashboards, order placement screens, charts, and account management features. A clean and intuitive UI improves user trust and retention. - Trading Engine
Responsible for processing orders, managing order books, and executing trades. It must handle high transaction volumes with low latency. - Wallet System
Manages user deposits, withdrawals, and internal fund transfers. Wallet design impacts both security and user experience. - Admin Panel
Allows operators to monitor activity, manage users, control withdrawals, set trading rules, and respond to security alerts.
Each component serves a specific role, but they must work together seamlessly. Poor integration between components often leads to performance issues, security gaps, and operational inefficiencies.
Step 4 – Building the Matching Engine & Trade Execution Logic
The matching engine is the heart of every crypto exchange you create. It ensures that buy and sell orders are matched efficiently and trades are executed accurately and fairly.
A reliable matching engine must:
- Process orders in real time
- Maintain accurate order books
- Ensure fair price-time priority
- Execute trades without delays or errors
Trade execution logic determines how orders are matched and settled once conditions are met. Even small inefficiencies here can lead to slippage, disputes, or loss of user trust.
At this stage, the focus should be on performance, consistency, and accuracy, not advanced trading strategies. The goal is to ensure that every trade placed on the exchange is executed exactly as expected, even during periods of high market activity.
Step 5 – Wallet Infrastructure & Fund Management Setup
Wallet infrastructure plays a critical role in both security and user confidence. When building a crypto exchange from scratch, you must decide how user funds are stored and managed.
Two common approaches are-
- Custodial wallets, where the exchange controls private keys
- Non-custodial wallets, where users retain control over their assets
Most centralized exchanges use custodial wallets for operational efficiency, while implementing strong internal controls to protect funds.
Wallet systems typically combine
- Hot wallets for day-to-day transactions
- Cold wallets for long-term asset storage
Fund management processes should include withdrawal approvals, balance reconciliation, and transaction monitoring. A well-designed wallet infrastructure minimizes risk while ensuring users can deposit and withdraw funds smoothly.
Step 6 – Implementing Security Measures Before Launch
Security is not an optional feature when launching a crypto exchange; it is a core requirement. Users trust exchanges with valuable digital assets, and any weakness can result in serious losses.
Key security measures include:
- Strong user authentication and access controls
- Withdrawal limits and approval workflows
- Secure key management and internal permissions
- Continuous monitoring for suspicious activity
Platform-level security must protect both infrastructure and user data. This includes securing APIs, databases, and internal communication channels.
Before launch, security should be treated as an ongoing process, not a one-time setup. The objective is to reduce attack surfaces, limit internal risks, and respond quickly to potential threats. A security-first mindset builds credibility and long-term trust in the exchange.
Step 7 – Liquidity Setup for a New Crypto Exchange
Liquidity determines whether users can actually trade on your exchange. Without sufficient liquidity, even a well-built platform will struggle to attract and retain traders.
Early-stage exchanges typically rely on:
- Initial internal liquidity
- Strategic liquidity partners
- Market-making arrangements
Liquidity ensures tighter spreads, faster trade execution, and better pricing for users. It also improves the overall perception of platform reliability.
The goal at launch is not perfect market depth, but consistent and functional trading activity. Liquidity planning should be aligned with your launch strategy, supported trading pairs, and expected user volume.
Step 8 – Compliance, KYC & Operational Readiness
Compliance is a critical step before opening a crypto exchange to users. Most jurisdictions require exchanges to implement Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes.
Operational readiness includes-
- User verification workflows
- Transaction monitoring procedures
- Record-keeping and reporting systems
Even if regulations vary by region, ignoring compliance can block partnerships, banking access, and future expansion. Building compliance into the platform from the beginning avoids costly changes later.
This step ensures the exchange is not only technically functional but also legally and operationally prepared for launch.
Step 9 – Testing, Deployment & Exchange Launch Process
Before launching a cryptocurrency exchange platform, thorough testing is essential. This includes-
- Functional testing of trading and wallets
- Performance testing under high load
- Security and failure scenario testing
Once testing is complete, the platform is deployed in a controlled environment. A phased launch is often recommended, starting with limited users or trading pairs to monitor system behavior.
The final goal is a stable, secure, and responsive exchange that is ready for real users. A well-executed launch sets the foundation for long-term growth and user trust.
Crypto Exchange Architecture Explained
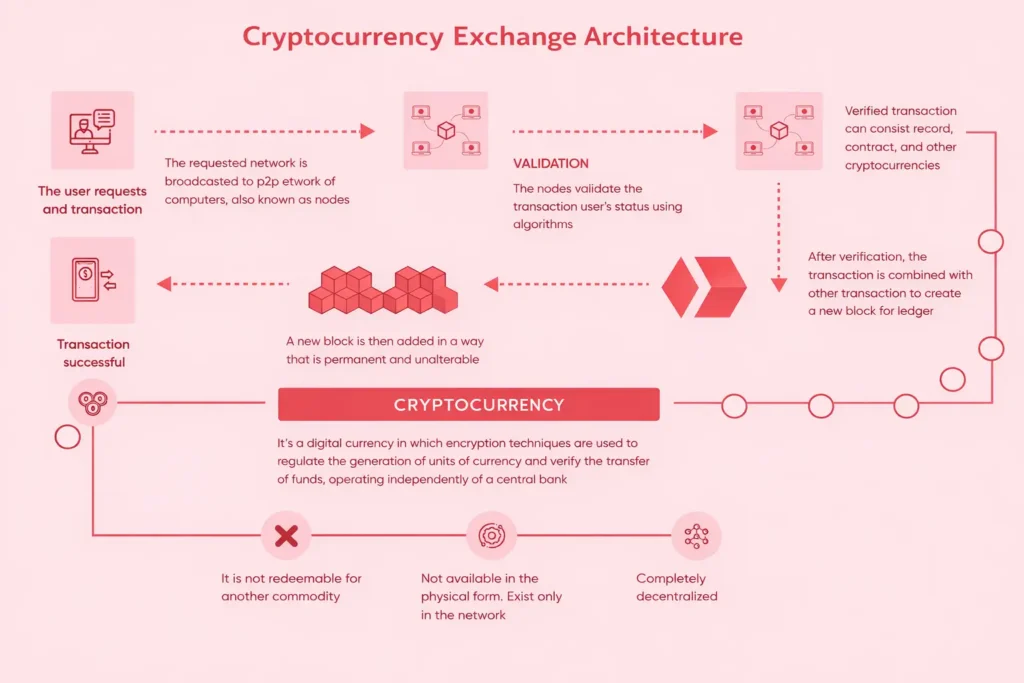
A cryptocurrency exchange architecture defines how different parts of the platform work together to support trading, security, and scalability. At a high level, a crypto exchange is built as a modular system where each layer has a clear responsibility. This approach makes the platform easier to manage, upgrade, and scale as user activity grows.
At the front end is the user interface, which allows traders to register, deposit funds, place orders, and monitor their balances. This layer communicates with the backend through secure APIs, ensuring that user actions are processed accurately and in real time. Behind the interface sits the core trading logic, which includes order handling and trade execution. This is where buy and sell requests are validated and routed for matching.
Another critical layer is the wallet and fund management system. It is responsible for tracking user balances, handling deposits and withdrawals, and maintaining internal ledgers. Alongside this runs the administrative and monitoring layer, which gives operators visibility into platform activity, risk controls, and system performance.
All these components are connected through a central application layer that manages data flow, access control, and system coordination. At an architectural level, the goal is not complexity, but clarity, each component should do one job well, allowing the exchange to remain stable, scalable, and ready for future growth.
Security Considerations While Creating a Crypto Exchange
Security is one of the most important factors when building a crypto exchange, as user trust depends directly on how well the platform protects funds and data. From the earliest development stages, security must be treated as a core requirement rather than an afterthought.
At a platform level, strong access controls are essential. This includes secure user authentication, role-based permissions, and safeguards around sensitive actions such as withdrawals and account changes. Protecting user data is equally important, which means ensuring that personal and financial information is handled with care and stored securely.
Asset protection is another major concern. An exchange must clearly separate operational systems from fund storage processes to reduce risk exposure. Internal monitoring systems play a key role by tracking unusual activity, enforcing transaction limits, and responding quickly to potential threats.
Beyond technical measures, operational discipline matters just as much. Clear internal processes, controlled access to critical systems, and continuous oversight help reduce human error and misuse. When users see that an exchange prioritizes security at every level, it builds long-term confidence and supports sustainable platform growth.
Liquidity Management for Crypto Exchanges
Liquidity is what makes a crypto exchange usable in real life. Even if your platform is technically sound, users will leave if trades cannot be executed quickly or at fair prices. From a build perspective, liquidity is not just a market concept; it is an operational requirement that must be planned before launch.
Most centralized exchanges rely on order books, where buy and sell orders are matched in real time. Some platforms, especially decentralized ones, use liquidity pools, where assets are pre-deposited to enable instant swaps. While both models serve the same purpose, the choice impacts how your exchange is built, funded, and scaled.
When launching a new exchange, initial liquidity is usually the biggest challenge. Many platforms start with external liquidity providers or market makers to avoid empty order books in the early stages. Others bootstrap liquidity by limiting trading pairs and gradually expanding as volume grows.
From a build standpoint, liquidity management is closely tied to user experience. Tight spreads, low slippage, and fast execution create trust and encourage repeat trading. Without proper liquidity planning, even a well-designed exchange can struggle to retain users after launch.
Cost to Build and Launch a Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform
The cost to build a crypto exchange platform depends on multiple technical and operational factors. There is no single fixed price, because every exchange is built with different goals, features, and scalability requirements.
Development costs usually form the largest portion of the budget. This includes building the trading engine, wallet infrastructure, user interface, admin controls, and backend systems. A basic MVP costs significantly less than a full-scale platform designed for high-volume trading and global users.
Security costs are often underestimated but are critical. Secure wallet architecture, withdrawal controls, access management, and continuous monitoring require both engineering effort and ongoing maintenance. Cutting corners here can lead to long-term losses that far exceed initial savings.
Liquidity costs are another major consideration. New exchanges often need to allocate capital for market makers or liquidity providers to ensure smooth trading at launch. Without this, user activity drops quickly, regardless of how well the platform is built.
Maintenance and scaling costs continue after launch. Regular updates, performance optimization, customer support systems, and infrastructure scaling all add to long-term expenses. As trading volume grows, so do server, compliance, and operational costs.
In short, building a crypto exchange is not just a one-time development expense. It is a long-term investment that must balance technology, security, liquidity, and sustainability from day one.
Ready to Build Your Own Crypto Exchange Platform?
Plan, Build, and Launch Your Cryptocurrency Exchange with Confidence
How Long Does It Take to Build a Crypto Exchange Platform?
The time required to build a crypto exchange platform depends on the scope of the project and the level of complexity involved. A minimum viable product (MVP) can typically be built within a few months if the focus is on core trading features, basic wallets, and limited assets.
A full-scale exchange platform, however, takes significantly longer. This includes advanced security controls, liquidity integrations, compliance readiness, scalability planning, and extensive testing. Building such a platform often requires multiple development phases rather than a single launch.
Time is also affected by customization needs, third-party integrations, and regulatory preparation. Rushing development usually leads to technical debt or security gaps, which can slow growth later. A realistic timeline prioritizes stability and long-term performance over speed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Starting a Crypto Exchange
One of the most common mistakes when starting a crypto exchange is underestimating security requirements. Basic protections are not enough for platforms that handle real user funds. Weak security design can quickly destroy trust and reputation.
Another frequent issue is liquidity miscalculation. Many new exchanges focus heavily on features but fail to plan how trades will actually happen. Empty order books and high slippage push users away, even if the interface looks polished.
Ignoring compliance and operational readiness is also a major risk. Exchanges that delay KYC, monitoring, or internal controls often face launch delays or forced shutdowns later. Compliance is not just a legal step it directly affects how the platform operates.
Finally, some founders try to do everything at once. Building too many features before validating the core exchange functionality often leads to delays and unnecessary costs. A focused, phased approach usually results in a more stable and scalable platform.
Final Thoughts
Building a cryptocurrency exchange platform is a complex but achievable process when approached strategically. Success depends on more than just writing code; it requires careful planning around architecture, security, liquidity, and long-term operations.
A step-by-step build process helps reduce risk and keeps development aligned with real user needs. Instead of chasing every trend, focusing on reliability, trust, and usability creates a stronger foundation for growth.
Whether you are launching a small MVP or a full-scale exchange, the goal should always be scalability and resilience. A well-built exchange is not defined by how fast it launches, but by how well it performs, adapts, and earns user confidence over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Creating a crypto exchange from scratch involves deciding the exchange type (CEX or DEX), designing the architecture, developing the trading engine, integrating wallets, ensuring liquidity, implementing security measures, and completing compliance checks before launch.
The timeline depends on complexity. A basic MVP can take 3–4 months, while a fully featured platform with advanced security, liquidity integration, and compliance may take 6–9 months.
Costs vary based on features, security, liquidity setup, and compliance requirements. A minimal exchange requires a lower budget, while a fully customized, secure, and compliant platform requires a higher investment.
The easiest approach is to launch a minimal version with essential trading features, basic security, and compliance. This allows founders to test the market and scale the platform gradually without unnecessary complexity.
Security should be built into the platform from the start. Use secure wallets, strong user authentication, fund protection measures, and real-time monitoring to protect both the platform and users’ assets.
Yes. Liquidity ensures smooth trading and prevents failed orders. New exchanges typically integrate external liquidity providers or collaborate with market makers to provide initial liquidity.
Before launching, exchanges must implement KYC and AML procedures and comply with operational regulations in their target market. Meeting these requirements ensures the platform operates legally and builds user trust.
Yes. Non-technical founders can start a crypto exchange by partnering with experienced development teams. Understanding the business model, security needs, and compliance requirements is more important than coding skills.
Core features include user registration, trading interface, matching engine, wallet system, admin dashboard, and monitoring tools. These elements form the foundation of any crypto exchange.
A successful launch requires thorough testing, controlled rollout, monitoring system performance, and gradually scaling features and liquidity as user activity grows. Following these steps ensures a stable and secure platform from day one.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







