If you have ever sent cryptocurrency and wondered where it went, or how long the confirmation would take, you are not alone. Millions of people interact with blockchains daily, yet most have no easy way to verify what actually happened under the hood. That is where block explorers step in. They act as the window into a blockchain, letting anyone see exactly what is going on without relying on a middleman. In this article, we will break down what block explorers are, why they matter, and how they shape the way people, developers, and businesses interact with blockchain networks.
Key Takeaways
- A block explorer is a web-based tool that reads and displays blockchain data in a format anyone can understand.
- Block explorers provide transparency by letting users independently verify transactions, balances, and smart contracts.
- They support security by making fraudulent or suspicious activities visible to the entire network.
- Developers and businesses rely on block explorers for debugging, performance monitoring, and auditing.
- Different blockchains have their own explorers, such as Etherscan for Ethereum, Solscan for Solana, and BscScan for BNB Chain.
- Block explorers play a growing role in DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, and enterprise blockchain applications.
- Without block explorers, the promise of blockchain transparency would remain theoretical rather than practical.
What Exactly is a Block Explorer?
Think of a block explorer as a search engine, but instead of searching websites, it searches a blockchain. When you type a transaction hash, wallet address, or block number into a block explorer, it pulls up detailed information from the blockchain and displays it in a readable format. You can see who sent funds, who received them, how much was transferred, what fees were paid, and whether the transaction has been confirmed.
According to Wikipedia’s article on blockchain explorers, these tools allow users to browse individual blocks, transaction histories, and balances of addresses on a specific blockchain. The concept is straightforward. Blockchains record every transaction in a public ledger. Block explorers simply make that ledger readable for everyday users and professionals alike.
The key distinction is that a block explorer does not store data itself. It reads data directly from the blockchain nodes and then presents it through a user-friendly interface. This means the information you see on a block explorer is the same data that exists on the actual blockchain, just formatted in a way that makes sense to a human being.
How Does a Block Explorer Actually Work?
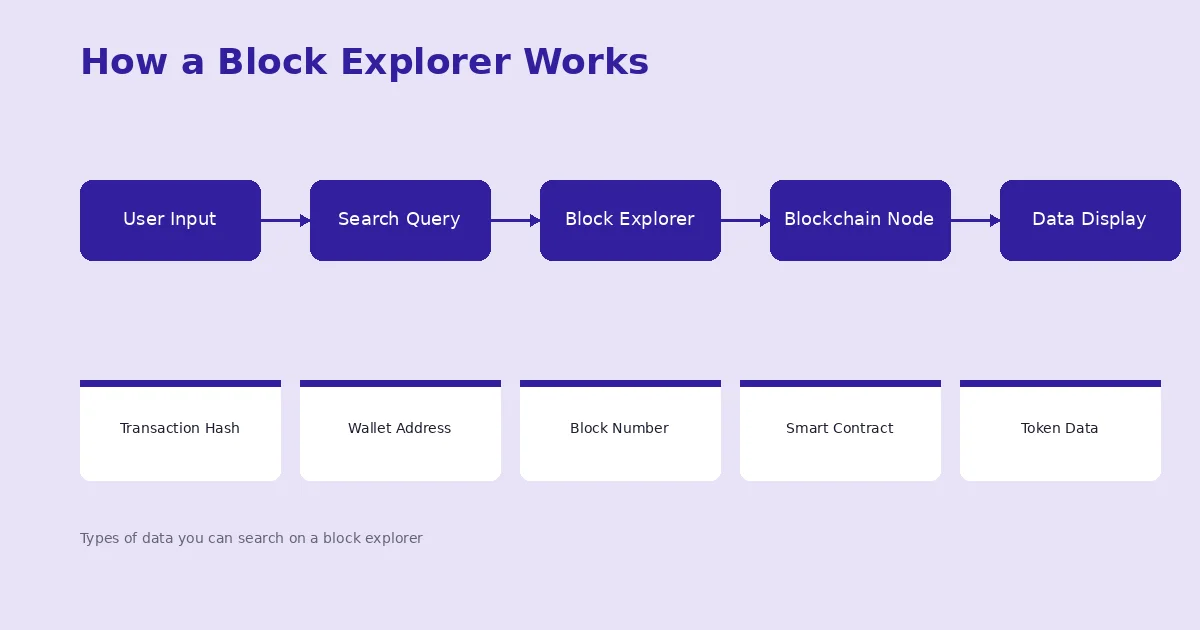
Behind the scenes, a block explorer connects to one or more nodes on a blockchain network. These nodes maintain a full copy of the blockchain, including every transaction ever recorded. The explorer queries these nodes, pulls the raw data, indexes it for fast searching, and then presents it through a clean web interface.
Here is a simplified breakdown of the process:
| Step | Action | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | User enters a query | A transaction hash, wallet address, or block number is submitted through the search bar |
| 2 | Explorer queries the node | The block explorer sends a request to a connected blockchain node for the relevant data |
| 3 | Node returns raw data | The node sends back the requested information in its raw, encoded format |
| 4 | Explorer parses and indexes | The data is decoded, organized, and indexed so it can be searched and displayed efficiently |
| 5 | User sees formatted results | The explorer presents the data in a clean, readable interface with charts, labels, and links |
This process happens almost instantly for most blockchains. The speed and accuracy of a block explorer depend on how well it is connected to the network and how its indexing system is built. If you are interested in how nodes function within this system, our detailed guide on Bitcoin nodes in blockchain covers that topic thoroughly.
Why is a Block Explorer Important for Blockchain?
This is the central question, and the answer touches on almost every aspect of how blockchain technology delivers on its promises. A blockchain without a block explorer is like a library without a catalog. The books are there, but good luck finding anything. Let us walk through the specific reasons why these tools are so critical.
1. They Make Transparency Real, Not Just Theoretical
One of the biggest selling points of blockchain is transparency. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger that anyone can access. But accessing raw blockchain data requires technical skills. You would need to run a full node and use command-line tools to parse through blocks and transactions. Most people simply cannot do that.
Block explorers bridge that gap. They turn the abstract promise of transparency into something tangible. A parent sending Bitcoin to their child at college can check the transaction on a block explorer and confirm it went through. An investor can verify that a project actually received the funding it claims. A journalist can trace the movement of funds in a public investigation.
Without block explorers, the transparency that blockchain offers would only be accessible to a small group of highly technical users. That would undermine one of the core values of decentralized technology.
2. Transaction Verification Without Trusting Anyone
In traditional finance, you trust your bank to tell you whether a transfer was successful. If there is a dispute, you call customer service and hope for the best. Blockchain does things differently. Instead of trusting a central authority, you can verify transactions yourself using a block explorer.
Say you paid a supplier in Ethereum. You can take the transaction hash, paste it into Etherscan, and see the exact status. Is it pending? Has it been confirmed? How many confirmations does it have? All of this information is available in seconds, and it comes directly from the blockchain, not from any intermediary.
This self-verification capability is particularly important for cross-border payments, where funds may pass through multiple systems and delays are common. With a block explorer, both the sender and receiver can independently confirm the same transaction without needing to communicate or rely on a third party.
3. Security Monitoring and Fraud Detection
Block explorers are one of the first lines of defense when it comes to spotting suspicious activity on a blockchain. Because every transaction is visible, unusual patterns can be identified and flagged relatively quickly.
For example, if a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) suddenly shows a large outflow of funds to an unknown wallet, community members can spot it on a block explorer and raise the alarm. This type of community-driven surveillance is a unique feature of public blockchains, and block explorers are the tool that makes it possible. You can also read more about how DAOs work in blockchain and why their transparency depends on tools like these.
Security firms and law enforcement agencies also use block explorers as a starting point for tracking stolen funds, analyzing ransomware payments, and building cases against bad actors in the crypto space.
4. An Essential Tool for Developers
If you are building on a blockchain, a block explorer is something you use every single day. When a smart contract does not behave as expected, the first thing a developer does is check the transaction on a block explorer. Did the contract execute correctly? Was there an out-of-gas error? Did the input parameters look right?
Block explorers like Etherscan even let developers verify and publish their smart contract source code, which other developers and users can then review. This creates an open ecosystem where code is auditable by anyone, which significantly raises the bar for quality and security.
For teams working on complex blockchain projects, the ability to trace every interaction through a block explorer is invaluable for testing, debugging, and deployment. Organizations offering blockchain development services depend on these explorers daily to deliver reliable solutions to their clients.
5. Monitoring Network Health and Performance
Block explorers do not just show individual transactions. They also provide a bird’s-eye view of the entire network. You can see metrics like total transactions per second, average block time, current gas prices, hash rate, and the number of active validators or miners.
This information is critical for multiple groups. Miners and validators use it to decide whether it is profitable to participate. Traders look at gas fees to time their transactions. Developers monitor network congestion to avoid deploying during peak hours. Researchers analyze these metrics to study the health and growth of blockchain ecosystems.
For example, if you notice that the average gas fee on Ethereum has spiked dramatically, it could signal a popular NFT mint, a DeFi rush, or even a network attack. Block explorers make this data visible in real time, which helps the entire community respond appropriately. Understanding concepts like data availability layers also becomes easier when you can observe how data flows through block explorers.
Key Components That Make Up a Block Explorer
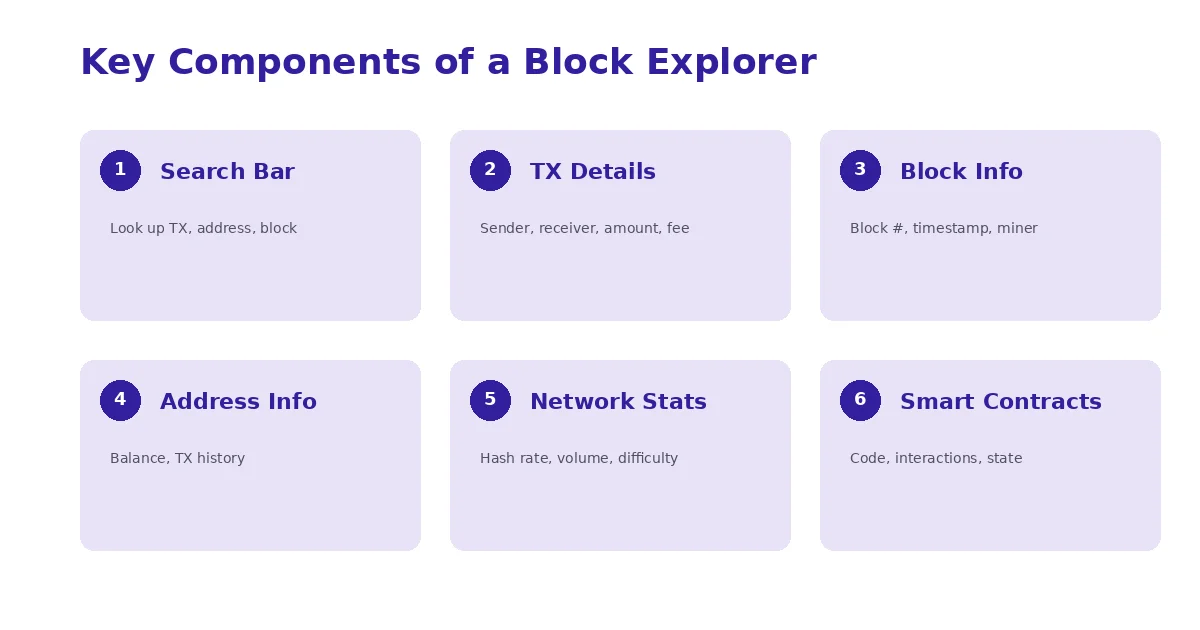
Every block explorer, whether it serves Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, or any other network, is built around a set of core components. Each component serves a specific function, and together they create a complete picture of blockchain activity. Understanding these components helps you get more value out of any explorer you use.
| Component | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Search Bar | Entry point for looking up any blockchain data | Pasting a TX hash to check if a payment went through |
| Transaction Details | Shows sender, receiver, amount, gas fee, status, and timestamp | Confirming a supplier payment with exact amounts and fees |
| Block Information | Displays block number, timestamp, transaction count, and miner/validator | Checking how many transactions were included in a specific block |
| Address Information | Shows balance, transaction history, and token holdings for a wallet | Auditing a project treasury wallet before investing |
| Network Statistics | Real-time data on hash rate, gas prices, and transaction volume | Deciding the best time to send a transaction with low fees |
| Smart Contract Data | Contract source code, interactions, and state variables | Reviewing a DeFi protocol contract before depositing funds |
Some explorers go even further by offering API access, token tracking, analytics dashboards, and even labeling known addresses like exchange wallets or whale accounts. The more mature the blockchain ecosystem, the more feature-rich its explorers tend to be.
The Lifecycle of a Transaction as Seen on a Block Explorer
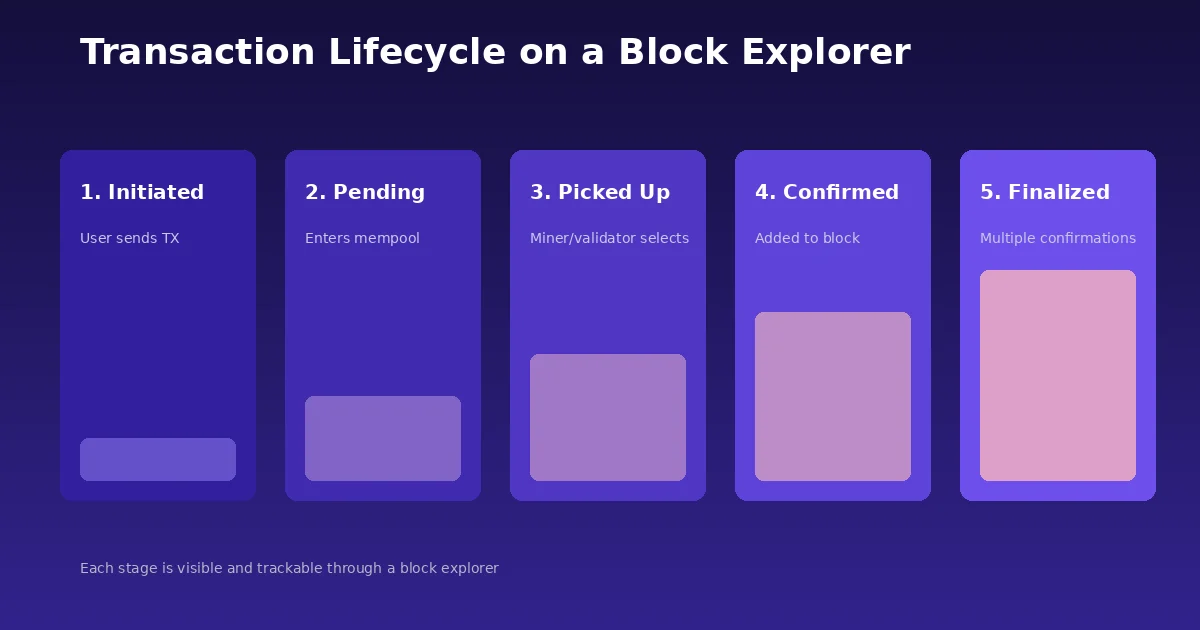
When you send a cryptocurrency transaction, it does not just teleport from your wallet to the recipient. It goes through a series of stages, and a block explorer lets you watch each one in real time. Understanding this lifecycle helps you interpret what you see on a block explorer and troubleshoot issues when they come up.
Stage 1: Transaction Created. You initiate a transaction from your wallet. At this point, the transaction is signed with your private key and broadcast to the network. On a block explorer, it may not appear yet or may show as “unconfirmed.”
Stage 2: Enters the Mempool. The transaction lands in the mempool, which is essentially a waiting room for unconfirmed transactions. Block explorers that support mempool views will show your transaction here, along with details like the gas fee you attached.
Stage 3: Picked Up by a Validator or Miner. Based on the fee you paid and the current network demand, a validator or miner selects your transaction for inclusion in the next block. Higher fees generally mean faster processing.
Stage 4: Included in a Block. Your transaction is now part of a confirmed block. On the block explorer, you will see it marked as confirmed, with the block number, timestamp, and other details filled in. If you are curious about how addresses link to this process, our article on Bitcoin addresses in blockchain explains the connection clearly.
Stage 5: Finality. Depending on the blockchain, finality may require multiple subsequent blocks to be added on top of the one containing your transaction. Bitcoin, for instance, is generally considered final after six confirmations. Block explorers show the confirmation count so you know exactly where your transaction stands.
This lifecycle is not just academic. Traders use it to time their moves. Businesses use it to confirm payments before shipping goods. Developers use it to identify where a failed transaction went wrong. It is one of the most practical features of any block explorer.
Build With Full Blockchain Transparency
Need a custom block explorer or blockchain solution that gives you complete visibility into your network? Get expert guidance from a team that builds production-grade blockchain tools.
Popular Block Explorers and What They Serve
Not all block explorers are the same. Each one is designed for a specific blockchain or group of blockchains, and they come with different features and strengths. Here is a comparison of the most widely used explorers as of 2025.
| Explorer | Blockchain | Key Strength | Smart Contract Support | Multi-chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etherscan | Ethereum | Deep smart contract analysis, verified contracts | Yes | No |
| Blockchair | Bitcoin, Ethereum, BCH, others | Multi-chain search from one interface | Limited | Yes |
| Blockchain.com | Bitcoin | Clean interface, beginner friendly | No | No |
| BscScan | BNB Smart Chain | Full BNB ecosystem coverage with token tracker | Yes | No |
| Solscan | Solana | Real-time transaction tracking with DeFi insights | Yes | No |
| Polygonscan | Polygon | Ethereum-compatible L2 analysis | Yes | No |
| Cardano Scan | Cardano | Staking rewards tracking and governance data | Yes | No |
Each of these explorers reflects the unique characteristics of its blockchain. Etherscan, for instance, has become the gold standard for Ethereum explorers partly because of its robust smart contract tools. On the other hand, Blockchair stands out for users who work across multiple blockchains and want a single tool to query all of them.
Block Explorer vs. Traditional Banking Tools: A Comparison
People sometimes wonder what makes a block explorer different from their online banking dashboard. Both let you check balances and view transactions. But the similarities end there. The fundamental difference lies in who controls the data and who can access it.
| Feature | Block Explorer | Traditional Banking Dashboard |
|---|---|---|
| Data Access | Public, anyone can view any transaction | Private, only the account holder sees their data |
| Data Control | No single entity controls the data | The bank controls and manages all records |
| Verification | Self-verifiable by anyone, independently | Requires trust in the bank’s systems |
| Availability | 24/7, no downtime for maintenance | Subject to scheduled maintenance and outages |
| Transaction Scope | Shows all transactions on the entire network | Shows only your own account activity |
| Smart Contract Data | Yes, full contract interactions visible | Not applicable |
This comparison highlights a philosophical shift. Traditional banking is built on controlled access and institutional trust. Blockchain, with its block explorers, is built on open access and verifiable data. Neither approach is inherently better for every situation, but for use cases where transparency, auditability, and independence matter, block explorers are the clear winner.
Real-World Use Cases of Block Explorers
Block explorers are not just theoretical tools. They are used every day by millions of people across different industries. Here are some concrete examples of how they add value in real situations.
E-Commerce and Payments. Online stores that accept cryptocurrency use block explorers to confirm that customer payments have been received and confirmed before processing orders. This removes the need for payment processor confirmations and gives merchants real-time certainty about incoming funds.
DeFi Protocol Auditing. Before depositing funds into a decentralized finance protocol, savvy users check the protocol’s smart contracts on a block explorer. They look at the contract code, recent interactions, and total value locked. This kind of due diligence has saved countless users from falling into poorly coded or malicious contracts.
NFT Provenance Tracking. When you buy an NFT, the ownership history is recorded on the blockchain. A block explorer lets you trace every transfer of that NFT from its creation to the present, verifying its authenticity and provenance. This is especially important for high-value digital art and collectibles.
Enterprise Blockchain Auditing. Businesses running private or consortium blockchains use internal block explorers to audit operations, track supply chain movements, and verify compliance. The principles are the same as public explorers, just applied within a controlled network. For a broader view of how enterprises use these systems, our comprehensive guide on enterprise blockchain applications covers the topic in depth.
Tax Reporting. Crypto users in many jurisdictions need to report their transactions for tax purposes. Block explorers provide a transparent record of every transaction associated with a wallet address, making it easier to compile accurate tax reports.
Block Explorers in Development and Testing
For blockchain developers, block explorers on testnets are just as important as those on mainnets. When you are building a decentralized application, you deploy it first to a testnet, a replica of the main blockchain used for testing purposes. Testnet block explorers let you verify that your smart contracts behave correctly, that transactions are processed as expected, and that edge cases are handled properly.
Developers often start their testing by using blockchain faucets to get free testnet tokens, then use block explorers to monitor how those tokens move through their applications. This testing workflow is a standard part of blockchain development and would be significantly harder without explorers.
Teams building on platforms like Solana, which is known for its high throughput and growing ecosystem, rely heavily on Solscan during development. If you are curious about how Solana is expanding into new markets, our article on how the Solana blockchain is transforming the gig economy provides an interesting perspective.
Advanced Features Found in Modern Block Explorers
The earliest block explorers were basic. They showed transaction data and not much else. Modern explorers have evolved into sophisticated platforms with features that serve everyone from casual users to institutional analysts.
Token Tracking. Most explorers now track not just the native cryptocurrency but also every token built on that blockchain. On Etherscan, for example, you can see all ERC-20 and ERC-721 tokens held by any address. This is critical for DeFi users who interact with dozens of tokens across multiple protocols.
Internal Transactions. When a smart contract calls another smart contract, it creates what is known as an internal transaction. These are not directly visible on the blockchain in the same way regular transactions are, but block explorers can parse and display them. This is important for understanding the full impact of complex DeFi interactions.
Address Labeling. Explorers like Etherscan maintain databases of labeled addresses, identifying wallets belonging to major exchanges, known scammers, bridges, and protocol treasuries. This labeling gives context to otherwise anonymous blockchain data. Understanding how these addresses work at a structural level is key, and our write-up on account trie in blockchain digs into the technical side of address management.
API Access. Many block explorers offer API endpoints that developers can use to programmatically query blockchain data. This is essential for building applications that rely on real-time blockchain information, such as portfolio trackers, alert systems, and analytics dashboards.
Gas Fee Estimators. Some explorers include tools that estimate the current gas fees needed for a transaction to be processed within a certain timeframe. This helps users avoid overpaying or underpaying for transaction processing.
Block Explorers in Blockchain Gaming and Emerging Sectors
The role of block explorers is expanding as blockchain technology moves into new industries. In blockchain gaming, for instance, players earn in-game assets that exist as tokens on a blockchain. Block explorers let players verify their asset ownership, track marketplace transactions, and confirm that game rewards have been distributed correctly.
This transparency is particularly important in play-to-earn models, where real money is at stake. Players want to know that the game economy is functioning as promised, and block explorers give them the tools to check. For a closer look at how blockchain gaming projects are built and supported, see our article on how Nadcab Labs supports blockchain gaming projects.
Beyond gaming, block explorers are becoming relevant in areas like supply chain management, healthcare data sharing, and decentralized identity. Wherever blockchain is used, block explorers will follow, because the need for transparency and verification is universal.
What to Look for When Choosing a Block Explorer
Not every block explorer is built the same way, and choosing the right one depends on your needs. Here are the factors that matter most when picking an explorer for regular use.
Accuracy and Real-Time Data. The explorer should pull data directly from reliable nodes and update in real time. Delayed data can lead to wrong conclusions, especially for time-sensitive transactions.
User Interface. A good block explorer should be usable by both technical and non-technical people. Clear labeling, intuitive navigation, and responsive design all contribute to a better experience.
Search Capabilities. You should be able to search by transaction hash, wallet address, block number, token name, and contract address. The more search options, the more useful the explorer becomes.
API Availability. If you plan to build applications that consume blockchain data, API access is essential. Check whether the explorer offers free and paid API tiers, and what rate limits apply.
Community Trust. Stick with explorers that have a strong track record and community trust. Explorers backed by established teams, such as Etherscan or Solscan, are generally more reliable than lesser-known alternatives.
The Future of Block Explorers
Block explorers have come a long way from simple transaction lookup tools. The future looks even more interesting. As blockchains become more complex and interconnected, explorers will need to keep up.
Cross-chain explorers are already emerging, allowing users to track assets as they move between different blockchains. This is becoming increasingly important as bridging and multi-chain strategies grow in popularity.
AI-powered analytics layers are being added to some explorers, helping users identify patterns, flag anomalies, and generate reports without needing deep technical knowledge. Privacy-preserving blockchains like Monero and Zcash present unique challenges for explorers, pushing innovation in how to balance transparency with confidentiality.
We are also seeing block explorers integrate with wallet applications directly, so users do not need to leave their wallet to check transaction details. This kind of seamless integration will make explorers even more central to the blockchain experience.
Final Thoughts
Block explorers are not glamorous tools. They do not get the same attention as new DeFi protocols or NFT drops. But they are arguably one of the most important pieces of infrastructure in the entire blockchain ecosystem. Without them, the transparency and verifiability that make blockchain valuable would be inaccessible to most people.
Whether you are a casual crypto user checking if your transfer went through, a developer debugging a smart contract, or a business integrating blockchain into your operations, block explorers are the tool that keeps everything visible and accountable. As the blockchain industry continues to grow and diversify, the role of block explorers will only become more central to how we interact with decentralized networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
A block explorer is used to search, view, and verify data stored on a blockchain network. It allows users to look up specific transactions by entering a transaction hash, check wallet balances by searching an address, and view the contents of individual blocks. Beyond basic lookups, block explorers provide network statistics, smart contract details, and token tracking features. They serve as the primary transparency tool for blockchain, enabling anyone to independently confirm that transactions occurred as expected without relying on a centralized authority.
Yes, you can track transactions on any public blockchain using the appropriate block explorer for that network. For Bitcoin, you would use Blockchain.com Explorer or Blockchair. For Ethereum transactions, Etherscan is the most popular choice. Solscan covers Solana, BscScan covers BNB Smart Chain, and Polygonscan handles Polygon. The only limitation is that privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Monero intentionally obscure transaction details, so their explorers show limited information compared to fully transparent blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Most block explorers are completely free to use for basic searches, transaction tracking, and address lookups. Explorers like Etherscan, Solscan, and Blockchair all offer free web interfaces that anyone can access without creating an account. However, some advanced features come with costs. API access for developers, for instance, often has a free tier with rate limits and paid plans for higher usage. Premium analytics, exported reports, and enterprise-level features may also require a subscription. For everyday users checking transactions and balances, though, block explorers are free.
Block explorers contribute to blockchain security by making all on-chain activity visible and auditable. When suspicious transactions occur, such as large unauthorized fund movements from a protocol or exchange, community members and security researchers can spot them immediately through a block explorer. Security firms use explorers to trace stolen funds across wallets and exchanges. Developers verify smart contract behavior and check for unexpected interactions. Address labeling features help users identify known scam addresses before sending funds to them. This open surveillance model is a core part of how public blockchains maintain trust.
A crypto wallet and a block explorer serve fundamentally different purposes. A wallet is a tool for managing your own cryptocurrency. It stores your private keys, lets you send and receive funds, and interacts with decentralized applications. A block explorer, on the other hand, is a read-only tool for viewing blockchain data. It does not hold any funds or private keys, and it cannot initiate transactions. Think of a wallet as your personal bank account and a block explorer as a public ledger viewer. You use your wallet to act on the blockchain and a block explorer to observe what has happened on it.
Yes, block explorers can be built for private and enterprise blockchains, though they function differently from public ones. On a public blockchain, anyone can access the explorer and view all data. On a private or consortium blockchain, the explorer is typically restricted to authorized participants within the network. Enterprise block explorers provide the same core features, including transaction tracking, block details, and address lookups, but access is controlled through authentication and permissions. Companies use these internal explorers for supply chain auditing, compliance monitoring, and operational oversight within their private blockchain networks.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






