Key Takeaways
- AI risk management is essential for organizations deploying AI Applications to protect against data breaches, adversarial attacks, and compliance violations that can cost millions in damages.
- Data poisoning attacks on training datasets represent one of the most dangerous threats to AI Platforms, potentially corrupting model outputs and decision making processes.
- Implementing a layered security approach combining technical controls, governance frameworks, and human oversight provides the strongest protection for AI systems.
- Privacy risks in AI extend beyond traditional data protection, requiring specialized techniques like differential privacy and federated learning to safeguard sensitive information.
- Regulatory compliance for AI is rapidly evolving with frameworks like the EU AI Act mandating specific risk assessments and transparency requirements for high risk AI Applications.
- Model theft and intellectual property protection have become critical concerns as AI Platforms represent significant investments in research, data, and computational resources.
- Bias and fairness risks in AI decisions can lead to legal liability, reputational damage, and real world harm to individuals and communities affected by algorithmic discrimination.
- Continuous monitoring and regular security assessments are necessary because AI threat landscapes evolve rapidly with new attack vectors emerging constantly.
- Building AI resilience requires collaboration between data scientists, security professionals, legal teams, and business stakeholders to address multidimensional risks effectively.
- Organizations that proactively invest in AI risk management gain competitive advantages through enhanced trust, regulatory readiness, and operational stability in their AI deployments.
Introduction to AI Risk Management
Artificial intelligence has transformed how businesses operate, make decisions, and serve customers across virtually every industry. From healthcare diagnostics to financial fraud detection, AI Applications now power critical systems that organizations depend on daily. However, this rapid adoption has created new vulnerabilities and risk categories that traditional cybersecurity approaches cannot adequately address. AI risk management has emerged as a specialized discipline focused on identifying, assessing, and mitigating the unique threats facing machine learning systems and intelligent automation platforms.
The stakes for securing AI systems have never been higher. A single compromised AI model can expose sensitive customer data, generate biased decisions affecting millions of people, or enable sophisticated cyberattacks that bypass conventional defenses. According to recent industry research, over 80 percent of organizations deploying AI Platforms have experienced at least one security incident related to their machine learning infrastructure. These incidents range from data breaches and model manipulation to compliance violations resulting in substantial regulatory penalties.
Understanding AI risk management requires recognizing that artificial intelligence systems face threats at every stage of their lifecycle. From the initial data collection and model training phases through deployment and ongoing operations, vulnerabilities exist that malicious actors can exploit. Additionally, AI systems can create risks even without external attacks through biased outputs, unexpected behaviors, or failures in critical decision making scenarios. Effective risk management must address both intentional threats and unintentional harms arising from AI system design and operation.
This comprehensive guide explores the complete landscape of AI security risks and provides actionable strategies for protecting your AI investments. Whether you are deploying your first machine learning model or managing enterprise scale AI Platforms, understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is essential for sustainable AI success.[1]
Understanding the AI Threat Landscape
The AI threat landscape encompasses a diverse array of attack vectors, vulnerabilities, and risk factors that differ significantly from traditional software security concerns. Machine learning systems introduce novel attack surfaces that security professionals must understand to protect effectively. These threats continue evolving as attackers develop more sophisticated techniques specifically designed to exploit AI system weaknesses.
At the foundation of AI threats lies the data dependency that makes machine learning possible. Unlike conventional software that follows predetermined logic, AI Applications learn patterns from training data and apply those patterns to new inputs. This fundamental characteristic creates opportunities for adversaries to manipulate AI behavior by corrupting training data, crafting malicious inputs, or exploiting model architectures. The same flexibility that makes AI powerful also makes it vulnerable to attacks that traditional security measures cannot detect.
External threat actors targeting AI systems include nation state hackers, organized cybercriminal groups, competitive intelligence operations, and hacktivists seeking to disrupt specific industries or causes. These attackers employ techniques ranging from data poisoning campaigns that subtly corrupt training datasets to adversarial attacks that fool deployed models with specially crafted inputs. The sophistication of these attacks continues increasing as AI security research inadvertently provides blueprints that malicious actors can weaponize.
Internal threats also pose significant risks to AI Platforms. Insider threats from employees, contractors, or partners with access to AI systems can result in model theft, data exfiltration, or sabotage. Additionally, well intentioned data scientists and engineers can inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities through insecure coding practices, insufficient testing, or failure to follow security protocols. Organizations must address both malicious and accidental internal threats within their AI risk management programs.
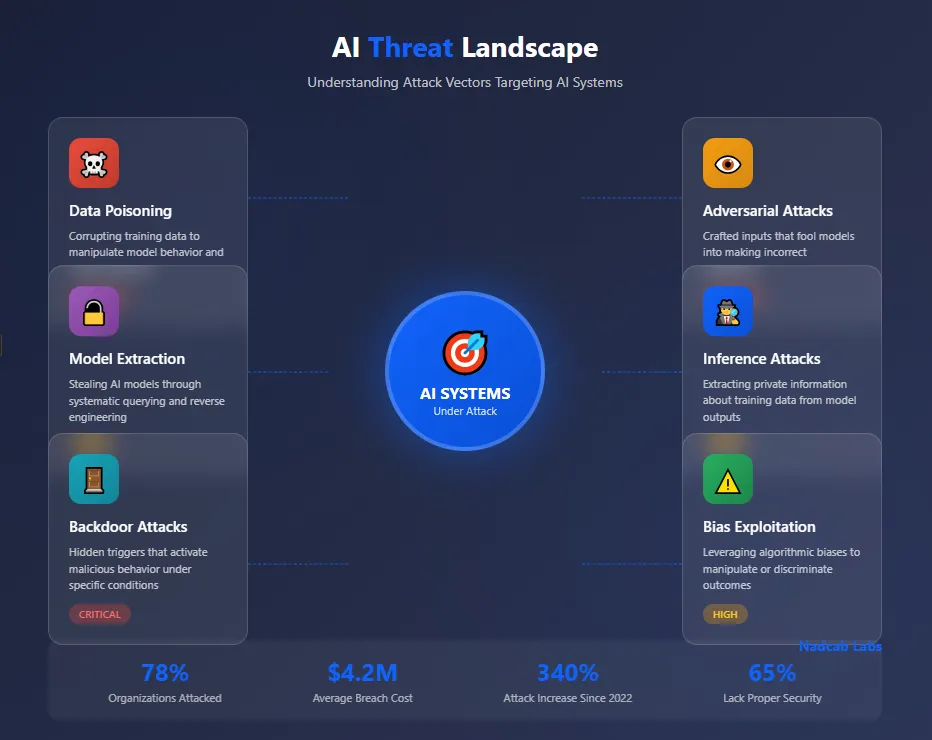
AI Threat Landscape Overview
78%
Organizations faced AI related security incidents in 2024
$4.2M
Average cost of AI system breach for enterprises
340%
Increase in adversarial attacks since 2022
Why Securing AI Systems Is a Business Priority
Securing AI systems has become a strategic business imperative rather than merely a technical concern. Organizations investing millions in AI Applications face significant financial, operational, and reputational risks if those systems are compromised, manipulated, or fail unexpectedly. The business case for AI security extends across multiple dimensions that directly impact organizational success and sustainability.
Financial risks from AI security failures include direct costs like incident response, system remediation, and regulatory fines, as well as indirect costs such as business disruption, lost revenue, and decreased market valuation. Companies that experience publicized AI security incidents often see immediate impacts on stock prices and customer confidence. Insurance coverage for AI related incidents remains limited and expensive, leaving many organizations exposed to substantial uninsured losses when breaches occur.
Regulatory pressure for AI security continues intensifying globally. The European Union AI Act establishes binding requirements for high risk AI Applications including mandatory risk assessments, documentation, and security controls. Similar regulations are emerging in jurisdictions worldwide, creating compliance obligations that organizations must meet to operate legally. Non compliance penalties can reach significant percentages of global revenue, making regulatory risk a board level concern for companies deploying AI Platforms.
Competitive dynamics also drive AI security investments. Organizations that demonstrate strong AI governance and security practices gain advantages in winning enterprise contracts, particularly in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and government. Conversely, companies suffering AI security incidents may find themselves excluded from partnership opportunities and customer relationships that require demonstrated security capabilities. Building and maintaining trust in AI systems has become a competitive differentiator in markets where AI adoption is widespread.
Types of Risks in AI Systems
AI systems face a complex array of risk categories that span technical, operational, ethical, and regulatory domains. Understanding these risk types provides the foundation for developing comprehensive protection strategies. Each category requires specific assessment methodologies and mitigation approaches tailored to its unique characteristics.
| Risk Category | Description | Impact Level | Primary Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Security Risks | Unauthorized access, data breaches, and leakage of training data | Critical | Encryption, access controls, data governance |
| Model Vulnerabilities | Exploitable weaknesses in model architecture and implementation | High | Security testing, architecture review |
| Adversarial Attacks | Malicious inputs designed to deceive AI models | High | Adversarial training, input validation |
| Privacy Risks | Exposure of personal data through model outputs or inference | Critical | Differential privacy, data anonymization |
| Bias and Fairness | Discriminatory outcomes affecting protected groups | High | Fairness testing, diverse training data |
| Operational Risks | System failures, performance degradation, integration issues | Medium | Monitoring, redundancy, testing |
| Regulatory Risks | Non compliance with AI regulations and industry standards | Critical | Compliance programs, documentation |
Data Security Risks in AI Environments
Data serves as the lifeblood of AI Applications, making data security fundamental to overall AI risk management. AI systems typically require vast amounts of data for training, validation, and ongoing operation, creating extensive attack surfaces that adversaries can target. Protecting this data throughout its lifecycle presents unique challenges that extend beyond traditional data security practices.
Training data repositories represent particularly valuable targets for attackers. These datasets often contain sensitive information including personal customer data, proprietary business intelligence, and confidential operational details. A breach of training data can expose not just the raw information but also insights about organizational strategies, customer behaviors, and competitive advantages embedded within the data. Organizations must implement robust access controls, encryption, and monitoring for all training data stores.
Data in transit between systems, during model training processes, and when serving predictions also requires protection. AI Platforms often involve distributed architectures where data moves between cloud services, edge devices, and on premises infrastructure. Each data movement creates potential interception points where attackers can capture sensitive information. Implementing end to end encryption and secure communication protocols throughout AI pipelines is essential for maintaining data confidentiality.
Data retention and disposal practices for AI systems require careful consideration. Unlike traditional applications where data can be deleted after processing, AI models may retain implicit information about training data within their learned parameters. This creates scenarios where sensitive data effectively persists even after the original data is deleted. Organizations must develop data governance policies that address these AI specific retention considerations and implement techniques for removing sensitive information from trained models when necessary.
Training Data Integrity and Data Poisoning Threats
Training data integrity represents one of the most critical yet frequently overlooked aspects of AI security. The principle of garbage in, garbage out applies with particular force to machine learning systems, where corrupted or manipulated training data can produce models that behave unpredictably or maliciously. Data poisoning attacks specifically target this vulnerability by introducing carefully crafted malicious data into training pipelines.
Data poisoning attacks can take several forms depending on attacker objectives and access levels. In availability attacks, adversaries inject data designed to degrade overall model performance, making the AI Application unreliable or unusable. Targeted attacks aim to cause specific misclassifications, such as making a fraud detection system fail to identify particular fraudulent patterns. Backdoor attacks insert hidden triggers that cause malicious behavior only when specific conditions are met, allowing compromised models to pass standard testing while remaining exploitable.
Detecting data poisoning presents significant challenges because poisoned data may appear legitimate upon casual inspection. Attackers often design poisoning samples to blend with genuine training data while still achieving their malicious objectives. Organizations must implement statistical analysis, anomaly detection, and data provenance tracking to identify potentially poisoned data before it corrupts model training. Regular auditing of data sources and supply chain security for third party datasets are also essential protection.
Mitigating data poisoning risks requires a defense in depth approach combining preventive and detective controls. Data validation pipelines should verify data integrity at collection points and throughout processing stages. Robust training techniques that are inherently resistant to outliers and anomalies can reduce the impact of poisoning attempts. Maintaining clean reference datasets for comparison and implementing rollback capabilities enables rapid recovery if poisoning is detected after model deployment.
AI Model Vulnerabilities and Exploitation Risks
AI models contain inherent vulnerabilities arising from their architecture, training processes, and deployment configurations. Unlike traditional software, where vulnerabilities typically involve coding errors or design flaws, AI model vulnerabilities often stem from the fundamental mathematics of machine learning algorithms. Understanding these vulnerabilities helps organizations identify and address weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. As highlighted in AI in software testing, integrating AI-driven testing practices can help detect hidden model weaknesses and improve overall system reliability.
Overfitting vulnerabilities occur when models learn training data too precisely, including noise and outliers that should not influence predictions. Overfit models perform well on test data similar to training examples but fail unpredictably on novel inputs. Attackers can exploit this by crafting inputs that trigger the model’s reliance on spurious patterns, causing incorrect outputs that benefit the attacker. Proper regularization, cross validation, and diverse training data help prevent overfitting vulnerabilities.
Model inversion attacks exploit AI Platforms to extract sensitive information about training data. By carefully querying a model and analyzing its responses, attackers can reconstruct training examples or infer private attributes about individuals represented in training datasets. These attacks are particularly concerning for AI Applications trained on medical records, financial data, or other sensitive personal information. Implementing query rate limiting, output perturbation, and differential privacy techniques can reduce model inversion risks.
Membership inference attacks determine whether specific data points were included in a model’s training set. While this may seem like a minor privacy concern, membership inference can reveal sensitive information about individuals. For example, knowing that someone’s data was used to train a disease prediction model could reveal their health status. Organizations deploying AI Applications on sensitive data must implement protections against membership inference as part of their privacy safeguards.
Adversarial Attacks on AI Systems
Adversarial attacks represent a category of threats specifically designed to exploit the unique characteristics of machine learning systems. These attacks involve crafting inputs that appear normal to humans but cause AI models to produce incorrect, unexpected, or malicious outputs. The existence of adversarial examples reveals fundamental limitations in how current AI systems perceive and process information.
Evasion attacks are the most common form of adversarial threat, involving modifications to input data that cause misclassification. In image recognition systems, adding imperceptible noise to photographs can cause AI to misidentify objects, potentially with dangerous consequences in applications like autonomous vehicles or medical imaging. Similarly, adversarial text inputs can fool natural language processing systems, bypassing content filters or manipulating sentiment analysis tools.
Physical adversarial attacks extend these concepts to the real world. Researchers have demonstrated adversarial patches that can be printed and placed in physical environments to fool AI vision systems. Stop signs modified with specific patterns can be misclassified by autonomous vehicle perception systems. Adversarial clothing patterns can prevent person detection systems from recognizing individuals. These physical attacks present serious concerns for AI Applications deployed in safety critical environments.
Defending against adversarial attacks requires multiple complementary approaches. Adversarial training, which includes adversarial examples in the training process, can improve model robustness. Input preprocessing techniques can detect and filter adversarial modifications before they reach the model. Ensemble methods that combine multiple models with different architectures reduce the likelihood that adversarial inputs will fool all models simultaneously. Organizations must continuously update their defenses as researchers discover new adversarial attack techniques.
Common Adversarial Attack Types
Evasion Attacks
Modify inputs at inference time to cause misclassification while appearing normal to humans
Poisoning Attacks
Corrupt training data to influence model behavior, creating vulnerabilities for later exploitation
Model Extraction
Query target models systematically to reconstruct functionality or steal intellectual property
Backdoor Attacks
Insert hidden triggers during training that activate malicious behavior under specific conditions
Model Theft and Intellectual Property Protection
AI models represent significant investments in research, data collection, computational resources, and expertise. Protecting these valuable intellectual property assets from theft has become a critical concern as AI Platforms proliferate and the market for pre trained models expands. Model theft can occur through various mechanisms ranging from direct exfiltration to sophisticated extraction attacks.
Direct model theft involves unauthorized copying of model files, weights, and configurations. This can occur through insider threats, compromised systems, or inadequate access controls on model repositories. Organizations must implement strict access management for model artifacts, including encryption at rest, secure transfer protocols, and comprehensive audit logging. Physical security for systems hosting high value models is equally important to prevent direct access by malicious actors.
Model extraction attacks allow adversaries to create functional copies of AI Applications without direct access to model files. By systematically querying a deployed model and observing its outputs, attackers can train surrogate models that replicate the target’s behavior. These attacks are particularly effective against models exposed through APIs or public interfaces. Rate limiting, query logging, and output perturbation can help detect and prevent extraction attempts while maintaining model utility for legitimate users.
Legal protections for AI models remain an evolving area with significant uncertainty. While traditional intellectual property frameworks including patents, copyrights, and trade secrets can provide some protection, their application to trained models involves novel legal questions. Organizations should implement technical protections while also establishing legal frameworks including confidentiality agreements, terms of service restrictions, and contractual protections for model access. Working with legal experts familiar with AI intellectual property issues helps ensure comprehensive protection strategies.
What Can Go Wrong in Digital AI Platforms?
Privacy Risks and Sensitive Data Exposure in AI
Privacy risks in AI Applications extend beyond traditional data protection concerns, encompassing novel threats arising from machine learning’s ability to infer, correlate, and reveal sensitive information. AI systems can expose private data in unexpected ways even when organizations implement standard privacy safeguards. Understanding these AI specific privacy risks is essential for protecting individuals whose data powers machine learning systems. As more businesses explore intelligent automation and blockchain-powered AI ecosystems, initiatives to start an AI-based cryptocurrency project are also raising important questions about how privacy-first AI architectures can be designed from the ground up..
Training data memorization represents a significant privacy concern where AI models inadvertently store and can reproduce sensitive information from training datasets. Large language models have been shown to regurgitate private information including phone numbers, addresses, and other personal details present in their training data. This memorization occurs even when models are trained on data that was intended to be anonymized or aggregated. Techniques like differential privacy and careful data curation help reduce memorization risks.
Inference attacks leverage AI model outputs to deduce sensitive information that was never explicitly provided. By analyzing patterns in model predictions, attackers can infer private attributes about individuals including health conditions, financial status, or personal preferences. These attacks are particularly concerning because they can reveal information even when the underlying data has been properly anonymized. Organizations must consider inference risks when designing AI Platforms that process or output potentially sensitive information.
Federated learning and privacy preserving machine learning techniques offer promising approaches to reduce AI privacy risks. Federated learning enables model training on distributed data without centralizing sensitive information, reducing exposure risks. Homomorphic encryption allows computation on encrypted data, enabling AI processing without exposing plaintext information. While these techniques involve performance tradeoffs, they provide valuable tools for organizations that must balance AI capabilities with strong privacy protections.
Bias, Fairness, and Ethical Risks in AI Decisions
AI systems can perpetuate, amplify, or even create discriminatory outcomes that harm individuals and communities. Bias in AI Applications arises from multiple sources including skewed training data, problematic feature selection, and design choices that embed societal prejudices into algorithmic decision-making. Addressing these ethical risks requires deliberate attention throughout the AI lifecycle from data collection through deployment and monitoring.
Training data bias occurs when datasets do not adequately represent the population on which models will be deployed. Historical data often reflects past discrimination in areas like hiring, lending, and criminal justice, causing AI systems trained on this data to replicate discriminatory patterns. Underrepresentation of certain demographic groups in training data can result in models that perform poorly for those populations. Organizations must audit training data for representativeness and implement techniques to address identified imbalances.
Algorithmic bias can emerge even from balanced datasets through feature selection and model design choices. Proxy variables that correlate with protected characteristics can enable discrimination even when protected attributes are excluded from model inputs. Optimization objectives that prioritize overall accuracy may sacrifice performance for minority groups. Careful feature engineering, fairness aware machine learning techniques, and multi objective optimization help mitigate algorithmic bias sources.
Monitoring deployed AI Platforms for fairness requires ongoing attention as model behavior can drift over time and new bias patterns can emerge. Establishing fairness metrics appropriate to the application context, implementing automated monitoring systems, and conducting regular bias audits help organizations identify and address fairness issues before they cause significant harm. Transparency about AI decision making and providing recourse mechanisms for affected individuals are also important components of ethical AI deployment.
Comparison: Traditional Security vs AI Security
| Aspect | Traditional Cybersecurity | AI Security |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Assets | Data, systems, networks | Models, training data, inference pipelines |
| Attack Vectors | Malware, phishing, network intrusion | Data poisoning, adversarial inputs, model extraction |
| Vulnerability Sources | Code defects, configuration errors | Training data, model architecture, inference logic |
| Testing Methods | Penetration testing, code review | Adversarial testing, fairness audits, robustness evaluation |
| Monitoring Focus | Intrusion detection, log analysis | Model drift, output anomalies, fairness metrics |
| Compliance Scope | Data protection, industry standards | AI regulations, algorithmic accountability, ethical guidelines |
Operational Risks in AI Deployment and Integration
Deploying AI Platforms into production environments introduces operational risks that can impact system reliability, business continuity, and organizational effectiveness. These risks emerge from the complexities of integrating AI components with existing infrastructure, managing model lifecycles, and ensuring consistent performance under varying conditions. Effective operational risk management requires robust DevOps practices adapted for machine learning systems.
Model degradation over time represents a significant operational concern as deployed AI Applications face changing data distributions and evolving real world conditions. Models trained on historical data may become less accurate as underlying patterns shift, a phenomenon known as concept drift. Without proper monitoring and retraining processes, model performance can decline gradually until systems become unreliable. Implementing automated drift detection and establishing clear retraining triggers help maintain model effectiveness.
Integration failures between AI components and existing systems can cause cascading issues throughout technology stacks. AI models often have specific computational requirements, input format expectations, and latency characteristics that must align with surrounding infrastructure. Version mismatches, API changes, and resource contention can cause AI services to fail or produce incorrect results. Thorough integration testing, staging environments, and gradual rollout strategies reduce integration related operational risks.
Scalability and performance management for AI systems requires specialized approaches beyond traditional application scaling. Machine learning inference can be computationally intensive, and demand patterns may differ significantly from conventional web applications. Organizations must plan for peak loads, implement appropriate caching strategies, and consider edge deployment options to maintain responsive AI services. Capacity planning should account for potential increases in model complexity and expanded use cases over time.
AI Automation and Human Oversight Challenges
Balancing AI automation with appropriate human oversight presents ongoing challenges for organizations deploying intelligent systems. While automation delivers efficiency and consistency benefits, removing humans from decision processes can lead to accountability gaps, missed errors, and inappropriate actions in edge cases. Designing effective human machine collaboration requires thoughtful consideration of where and how humans should remain involved.
Automation complacency occurs when human operators become overly trusting of AI systems, failing to question or verify automated recommendations. As AI Applications prove reliable over time, operators may stop paying attention to outputs, missing situations where AI produces incorrect or inappropriate results. Designing interfaces that maintain human engagement, implementing periodic verification requirements, and rotating responsibilities help prevent complacency from degrading human oversight effectiveness.
Decision authority allocation determines which decisions AI systems can make autonomously and which require human approval. High stakes decisions affecting safety, legal rights, or significant financial consequences typically warrant human involvement regardless of AI confidence levels. Organizations must establish clear policies defining decision thresholds and escalation procedures. These policies should reflect both technical capabilities and ethical considerations about appropriate automation levels for different decision types.
Explainability and interpretability requirements support effective human oversight by enabling operators to understand AI reasoning. Black box models that cannot explain their outputs make meaningful human review difficult or impossible. Investing in explainable AI techniques, providing decision rationale alongside recommendations, and training operators to interpret AI outputs effectively enhances human oversight capabilities. Regulatory requirements increasingly mandate explainability for AI Applications in high impact domains.
AI Driven Cyber Threats and Attack Automation
Artificial intelligence technologies are increasingly weaponized by malicious actors to enhance cyberattack capabilities. AI driven threats can operate at speeds and scales impossible for human attackers, adapting dynamically to defensive measures and discovering novel attack vectors. Organizations must prepare for a threat landscape where adversaries leverage the same AI capabilities being deployed defensively.
Automated vulnerability discovery using machine learning enables attackers to identify exploitable weaknesses in systems faster than manual analysis permits. AI tools can analyze code repositories, scan network configurations, and probe application interfaces to discover vulnerabilities systematically. These capabilities lower the skill barriers for conducting sophisticated attacks while increasing the volume of attempted exploits. Defensive teams must accelerate their own vulnerability management processes to keep pace with AI enhanced threat actors.
AI generated phishing and social engineering attacks achieve unprecedented personalization and believability. Large language models can craft convincing messages tailored to individual targets based on harvested personal information. Deepfake technologies create realistic audio and video that can impersonate executives or trusted contacts. Organizations must enhance security awareness training to address these evolving social engineering threats while implementing technical controls to detect AI generated content.
Adaptive malware using machine learning techniques can evade traditional security tools by modifying its behavior based on environmental observations. AI powered malware can recognize when it is being analyzed in sandbox environments and alter its behavior to avoid detection. Defensive AI systems must be deployed to counter these intelligent threats, creating an ongoing arms race between offensive and defensive AI capabilities. Organizations should assume sophisticated adversaries will employ AI and plan defenses accordingly.
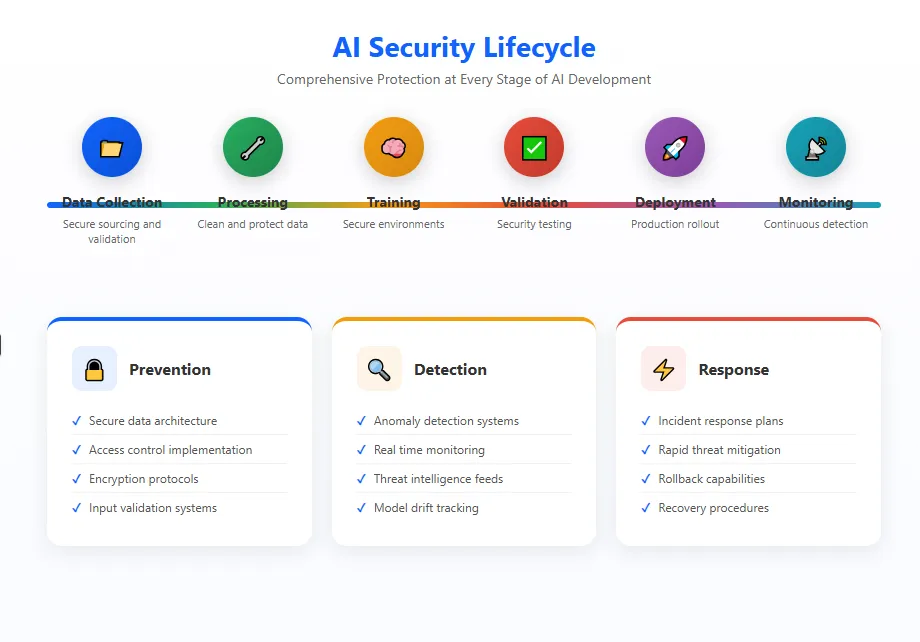
AI Security Lifecycle Stages
1
Data Security
2
Model Training
3
Validation
4
Deployment
5
Monitoring
6
Maintenance
Regulatory, Legal, and Compliance Risks in AI
The regulatory landscape for AI is evolving rapidly as governments worldwide implement frameworks to govern artificial intelligence deployment. Organizations deploying AI Applications must navigate an increasingly complex web of requirements spanning AI specific regulations, data protection laws, sector specific rules, and emerging standards. Non compliance can result in substantial penalties, operational restrictions, and reputational damage.
The European Union AI Act represents the most comprehensive AI regulatory framework currently in force, establishing risk based requirements for AI systems deployed in EU markets. High risk AI Applications in areas like employment, education, and critical infrastructure face mandatory requirements including risk assessments, documentation, human oversight provisions, and accuracy standards. Organizations must classify their AI systems according to risk categories and implement appropriate compliance measures for each classification level.
Data protection regulations including GDPR, CCPA, and similar laws worldwide impose requirements relevant to AI Platforms processing personal data. These regulations establish principles around data minimization, purpose limitation, and individual rights that constrain how AI systems can collect, process, and use personal information. Automated decision making provisions require transparency about algorithmic processing and may mandate human review rights for significant decisions affecting individuals.
Industry specific regulations add additional compliance layers for AI deployed in regulated sectors. Financial services AI must comply with fair lending laws, model risk management guidelines, and algorithmic trading requirements. Healthcare AI faces FDA oversight for medical devices and HIPAA requirements for protected health information. Organizations must coordinate compliance efforts across multiple regulatory frameworks to ensure their AI deployments meet all applicable requirements.
Best Practices for Securing AI Systems
Implementing effective security for AI Platforms requires adopting best practices that address the unique characteristics of machine learning systems while building on established cybersecurity foundations. These practices should be integrated throughout the AI lifecycle from initial planning through ongoing operations and eventual decommissioning.
| Practice Area | Key Actions | Implementation Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Data Protection | Encrypt training data, implement access controls, validate data sources, monitor data pipelines | Immediate |
| Model Security | Secure model storage, implement versioning, protect intellectual property, conduct security testing | Immediate |
| Adversarial Defense | Implement input validation, adversarial training, robustness testing, detection systems | High |
| Privacy Controls | Apply differential privacy, minimize data collection, implement anonymization, conduct privacy impact assessments | High |
| Monitoring and Response | Deploy continuous monitoring, establish incident response procedures, implement anomaly detection | Immediate |
| Governance | Establish AI policies, define roles and responsibilities, implement review processes, maintain documentation | High |
Security by design principles should guide AI Application architecture from the earliest planning stages. Building security into system design is far more effective and economical than attempting to retrofit protections after deployment. Threat modeling exercises help identify potential attack vectors and inform architectural decisions. Security requirements should be specified alongside functional requirements in project planning documents.
Continuous monitoring and testing programs ensure ongoing security as AI systems evolve and threat landscapes change. Automated scanning for vulnerabilities, regular penetration testing, and adversarial red team exercises help identify weaknesses before attackers exploit them. Monitoring should extend beyond traditional security metrics to include AI specific indicators like model drift, output anomalies, and query pattern changes that might indicate attacks in progress.
Building a Comprehensive AI Risk Management Framework
A comprehensive AI risk management framework provides the structure and processes needed to systematically identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks across AI platforms. Effective frameworks integrate technical controls with governance mechanisms, establishing clear accountability and enabling consistent risk management across the organization. Building such a framework requires commitment from leadership and collaboration across technical, business, and legal functions. Real-world implementations, such as the Sharpe AI crypto trading platform case study, demonstrate how structured AI governance and risk controls can be applied in high-stakes, production-grade AI environments.
Risk identification processes should systematically examine all aspects of AI systems for potential vulnerabilities and threats. This includes technical assessments of data, models, and infrastructure as well as analysis of operational, ethical, and compliance risks. Threat intelligence feeds help identify emerging risks from the broader AI security landscape. Regular risk identification exercises ensure new threats are captured as the AI environment evolves.
Risk assessment methodologies for AI should evaluate both likelihood and potential impact of identified risks. Quantitative methods can estimate financial impacts and probability based on historical data and industry benchmarks. Qualitative assessments capture risks that are difficult to quantify including reputational harm and ethical concerns. Risk assessment results inform prioritization decisions and resource allocation for mitigation efforts.
Governance structures establish accountability for AI risk management across organizational levels. Board and executive oversight ensures strategic alignment and appropriate resource allocation. Risk committees provide ongoing monitoring and escalation mechanisms. Clear role definitions specify responsibilities for data scientists, security teams, compliance functions, and business owners. Documentation requirements create audit trails and support regulatory compliance demonstrations.
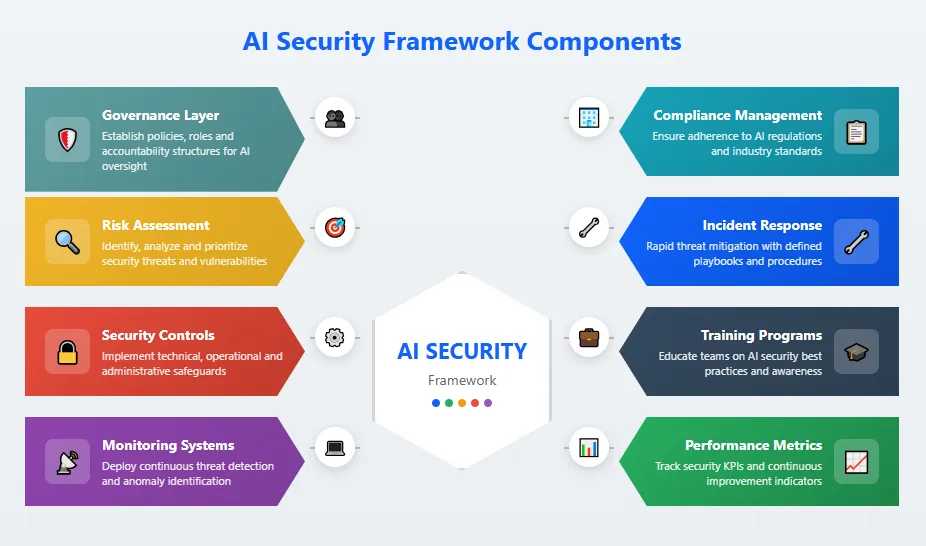
AI Risk Management Framework Components
Governance
Policies, roles, accountability structures
Risk Assessment
Identification, analysis, prioritization
Controls
Technical and operational safeguards
Monitoring
Continuous oversight and detection
Future Trends in AI Security and Risk Management
The field of AI security continues evolving rapidly as both threats and defensive capabilities advance. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations prepare for future challenges and opportunities in protecting their AI investments. Forward looking risk management strategies should account for these developments while maintaining focus on current operational needs.
Automated AI security tools leveraging machine learning for defense are becoming increasingly sophisticated. These tools can detect adversarial attacks in real time, identify anomalous model behaviors, and automatically respond to security incidents. The integration of AI into security operations promises faster threat detection and response, though it also creates new attack surfaces as adversaries target the defensive AI systems themselves.
Regulatory requirements for AI will continue expanding and becoming more prescriptive. Organizations should expect mandatory security standards, certification requirements, and audit obligations for AI Applications in high risk domains. Proactive compliance investments position organizations to meet these requirements without operational disruption. Participation in standards development processes allows organizations to influence emerging requirements and prepare for their implementation.
Privacy enhancing technologies for AI are maturing rapidly, enabling new approaches to protecting sensitive data while maintaining AI utility. Advances in federated learning, secure multi party computation, and homomorphic encryption are making privacy preserving AI increasingly practical for production deployments. Organizations investing in these technologies now will be well positioned as privacy expectations and requirements for AI Platforms continue intensifying.
Ready to Secure Your AI Systems?
Partner with experts who understand AI security inside and out. Protect your investments and build trust with comprehensive risk management solutions.
Conclusion: Creating Resilient and Secure AI Systems
Building resilient and secure AI systems requires comprehensive approaches that address technical vulnerabilities, operational risks, ethical considerations, and regulatory requirements. Organizations that invest proactively in AI risk management position themselves for sustainable success with artificial intelligence while protecting against the significant costs of security failures. The strategies and best practices outlined in this guide provide a foundation for developing robust AI security programs tailored to specific organizational contexts and risk profiles.
Effective AI security is not a one time achievement but an ongoing commitment that must evolve alongside advancing threats and changing technologies. Continuous monitoring, regular assessments, and adaptive defenses are essential for maintaining protection over time. Organizations should establish clear governance structures with defined accountability for AI risk management, ensuring that security receives appropriate attention and resources as AI deployments expand.
The interdisciplinary nature of AI risk management demands collaboration across technical, business, legal, and ethical domains. Data scientists, security professionals, compliance officers, and business leaders must work together to identify risks comprehensively and implement balanced mitigation strategies. This collaborative approach ensures that security measures support rather than impede AI value creation while maintaining appropriate protection levels.
Nadcab Labs brings over 8 years of specialized expertise in AI Application security and risk management, helping organizations worldwide protect their machine learning investments. Our team combines deep technical knowledge of AI Platforms with extensive experience in cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and enterprise risk management. We have successfully secured AI deployments across industries including financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, and technology, developing proven methodologies for addressing the unique challenges of machine learning security. From comprehensive risk assessments and security architecture reviews to ongoing monitoring solutions and incident response capabilities, Nadcab Labs delivers the expertise organizations need to deploy AI confidently. Our authoritative approach to AI security reflects lessons learned from hundreds of engagements, ensuring that clients benefit from battle tested strategies and current best practices in this rapidly evolving field.
Frequently Asked Questions
The cost of implementing an AI risk management system varies based on business size, complexity, and chosen solutions. Small businesses can expect to invest between $10,000 to $50,000 for basic AI security measures, including vulnerability assessments and monitoring tools. Cloud based AI Platforms often offer scalable pricing models, allowing businesses to start small and expand as needed. Ongoing maintenance and updates typically add 15 to 20 percent annually.
Yes, specialized cyber insurance policies now cover AI related risks, including data breaches, algorithmic failures, and third party liability. Insurers evaluate factors like AI Application complexity, data handling practices, and existing security measures. Premiums depend on industry, AI deployment scale, and risk history. Many providers require businesses to demonstrate compliance with recognized AI security frameworks before offering coverage. This emerging insurance market continues expanding as AI adoption grows.
A comprehensive AI security audit typically takes 4 to 12 weeks depending on system complexity and scope. Initial assessment and planning require 1 to 2 weeks, followed by technical vulnerability scanning taking 2 to 4 weeks. Penetration testing and adversarial attack simulations add another 2 to 3 weeks. Final reporting and remediation planning complete the process. Organizations with multiple AI Platforms or complex integrations may require extended timelines.
AI security professionals should pursue certifications like Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and specialized AI credentials like the Certified AI Security Professional (CAISP). Machine learning specific certifications from major cloud providers also add value. Data privacy certifications such as CIPP and CIPM complement technical skills. Organizations increasingly prefer candidates combining cybersecurity expertise with AI Application development knowledge.
Startups should prioritize foundational security measures first, including secure data storage, access controls, and encryption. Implementing open source security tools reduces costs while maintaining protection. Focus on protecting training data integrity before expanding to model security. Cloud based AI Platforms often include built in security features that reduce additional investment needs. Regular security training for team members provides high return on minimal investment.
Legal liability for AI caused financial harm depends on jurisdiction, deployment context, and demonstrated negligence. Companies may face lawsuits under product liability, negligence, or consumer protection laws. Courts increasingly examine whether reasonable AI risk management practices were implemented. Documentation of security measures and risk assessments becomes crucial evidence. Regulatory penalties may apply separately from civil liability, especially in financial services and healthcare sectors.
Open source AI models can achieve enterprise grade security with proper implementation. Organizations must conduct thorough code reviews, implement additional security layers, and maintain regular updates. Custom security wrappers and monitoring systems enhance protection. Many enterprises successfully deploy secured open source models alongside proprietary AI Platforms. The key lies in dedicating resources to ongoing security maintenance rather than relying solely on community updates.
AI systems should undergo continuous monitoring with formal security assessments quarterly. Critical AI Applications in high risk sectors require monthly penetration testing. Model retraining cycles should include security validation before deployment. Patch management should follow a 30 day maximum window for critical vulnerabilities. Real time threat intelligence feeds help identify emerging risks between scheduled assessments. Annual comprehensive audits provide strategic security planning input.
Employee training forms a critical defense layer against AI security threats, addressing human factors in data handling and system access. Initial onboarding should include AI security fundamentals, followed by quarterly refresher sessions. Role specific training for data scientists and engineers should occur monthly. Simulated phishing and social engineering exercises help maintain awareness. Organizations using AI Platforms should update training whenever new features or integrations are deployed.
Measuring AI security ROI involves quantifying prevented losses, compliance cost savings, and operational efficiency gains. Track metrics like incident frequency reduction, mean time to detection, and remediation costs. Calculate potential breach costs using industry benchmarks and compare against security investments. Customer trust metrics and contract win rates often improve with demonstrated AI Application security. Most organizations see positive ROI within 18 to 24 months of implementing comprehensive AI risk management programs.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.