Key Takeaways
- ✔ AI Application tools are revolutionizing cybersecurity by enabling real time threat detection, automated incident response, and predictive risk analysis that outperform traditional security methods.
- ✔ Machine learning algorithms on modern AI Platforms can analyze billions of data points every second, identifying malicious patterns and anomalies far faster than human analysts.
- ✔ Organizations adopting AI powered cybersecurity solutions reduce their average breach detection time from 200+ days to mere hours, significantly limiting financial and reputational damage.
- ✔ Behavioral analytics driven by AI enables continuous user monitoring, flagging insider threats and compromised accounts without disrupting normal business operations.
- ✔ The integration of AI into cybersecurity frameworks helps businesses achieve compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS through automated monitoring and reporting.
- ✔ Cybercriminals are also leveraging AI to craft more sophisticated attacks, making it essential for enterprises to deploy equally advanced AI Platforms for defense.
- ✔ Predictive intelligence models allow security teams to anticipate potential vulnerabilities and proactively strengthen defenses before breaches occur.
- ✔ AI powered phishing detection systems now achieve accuracy rates exceeding 98%, dramatically reducing the success rate of social engineering attacks targeting employees.
- ✔ Small and mid sized businesses can now access enterprise grade AI Application tools through cloud based subscription models, democratizing advanced cybersecurity protection.
- ✔ Partnering with experienced providers like Nadcab Labs ensures that AI cybersecurity solutions are properly implemented, continuously optimized, and aligned with evolving business requirements.
Introduction to AI and Cybersecurity
The digital landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and with it comes an equally rapid escalation of cyber threats targeting businesses of all sizes. From data breaches and ransomware attacks to sophisticated phishing campaigns and insider threats, organizations face a relentless barrage of security challenges every single day. Traditional cybersecurity approaches, which rely heavily on static rules and manual oversight, are no longer sufficient to combat the sheer volume and complexity of modern cyberattacks. This is precisely where Artificial Intelligence (AI) enters the picture as a transformative force.
AI Application tools and AI Platforms have emerged as the cornerstone of next generation cybersecurity strategies. By harnessing the power of machine learning, deep neural networks, natural language processing, and behavioral analytics, AI enables security systems to detect, analyze, and respond to threats with a speed and accuracy that was previously impossible. Whether it is identifying a zero day exploit in real time or automating the containment of a ransomware outbreak, AI is fundamentally reshaping how businesses protect their digital assets and maintain operational resilience.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore every facet of AI in cybersecurity, from how it works and the benefits it delivers to the challenges organizations face when implementing these technologies. We will also examine real world examples, compare traditional and AI driven security approaches, discuss the lifecycle of AI powered threat management, and provide actionable best practices that businesses can follow to strengthen their defenses. Whether you are a technology leader, a security professional, or a business owner seeking to understand how AI can fortify your organization, this article has been crafted to serve as your definitive resource.[1]
The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity in the Digital Age
The global digital economy now processes trillions of transactions daily, and virtually every industry depends on connected systems, cloud infrastructure, and data driven decision making. This interconnectedness, while delivering tremendous business value, has also created an enormous attack surface for cybercriminals. According to recent reports, cybercrime is projected to cost the global economy over $10 trillion annually by 2026, making it one of the most significant economic threats facing the modern world.
Several factors are driving the growing urgency of robust cybersecurity. The mass adoption of remote and hybrid work models has dissolved traditional network perimeters, requiring security to extend far beyond the corporate firewall. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has added millions of new endpoints that need continuous protection. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI DSS impose strict compliance requirements, and the penalties for non compliance can be devastating. Furthermore, the sophistication of threat actors continues to increase, with state sponsored hacking groups and organized cybercrime syndicates employing advanced tactics that evolve daily.
Against this backdrop, AI Platforms offer the scalability, adaptability, and intelligence that modern cybersecurity demands. Businesses that fail to adopt AI driven security solutions risk falling behind in an increasingly hostile digital environment where the cost of a single breach can reach millions of dollars and permanently erode customer trust. Understanding the latest market dynamics is essential for making informed security investment decisions.
What is Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity?
Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity refers to the application of intelligent algorithms and computational models to identify, prevent, and respond to cyber threats autonomously or semi autonomously. Unlike traditional security tools that rely on predefined signature databases and rule based logic, AI cybersecurity solutions learn from data, adapt to new threat patterns, and make decisions in real time without requiring constant human intervention.
At its core, AI cybersecurity combines several technological disciplines. Machine Learning (ML) enables systems to improve their threat detection accuracy over time by training on vast datasets of network traffic, malware samples, and attack signatures. Natural Language Processing (NLP) powers the analysis of phishing emails, social media threats, and dark web chatter. Deep Learning networks can identify complex, multi stage attack patterns that traditional tools miss entirely. Behavioral Analytics builds dynamic profiles of users and devices, instantly flagging deviations that may indicate a breach.
Modern AI Application tools deployed in cybersecurity operate across the entire security lifecycle: from preemptive threat hunting and vulnerability assessment to active defense, incident response, and post breach forensics. These tools are embedded within comprehensive AI Platforms that provide unified dashboards, automated workflows, and continuous learning capabilities, enabling security teams to stay ahead of adversaries who are constantly evolving their tactics. Understanding which technologies are trending in this space helps organizations make the right choices for their security stack.

How AI Enhances Threat Detection and Prevention
Threat detection is the foundation of every cybersecurity strategy, and AI is making it faster, smarter, and exponentially more effective. Traditional security tools detect threats by matching incoming data against a database of known threat signatures. While this approach works against known malware and attack patterns, it is virtually blind to novel, never before seen threats. AI Application tools overcome this limitation by using machine learning models that identify threats based on behavior and context rather than signatures alone.
For example, consider a scenario where an employee’s account begins downloading large volumes of sensitive data at 3:00 AM from an unfamiliar location. A signature based system would see nothing unusual because the user has valid credentials. However, an AI powered behavioral analytics engine would immediately flag this activity as anomalous because it deviates from the user’s established patterns. The AI Platform can then trigger an automated response, such as temporarily suspending the account and alerting the security team, all within seconds.
AI also enhances prevention by continuously scanning networks, endpoints, and cloud environments for vulnerabilities. Advanced AI Platforms use predictive models to forecast which systems are most likely to be targeted next, enabling proactive patching and configuration hardening. This shift from reactive to proactive security is one of the most significant advantages AI brings to the cybersecurity domain. As AI Application tools become more sophisticated, their market impact continues to grow substantially across all industries.
Machine Learning for Real Time Cyber Threat Analysis
Machine learning (ML) is the engine that powers most AI cybersecurity solutions. ML algorithms process enormous volumes of security data in real time, learning to distinguish between normal and malicious activity with increasing precision. There are three primary categories of machine learning used in cybersecurity, each serving a distinct purpose in the threat analysis pipeline.
Supervised Learning models are trained on labeled datasets containing examples of both legitimate and malicious network traffic. Once trained, these models can classify new data points with high accuracy. They are particularly effective for malware classification, spam filtering, and intrusion detection. Unsupervised Learning models, on the other hand, analyze data without predefined labels. They excel at discovering hidden patterns and anomalies, making them ideal for detecting zero day attacks and previously unknown threats. Reinforcement Learning represents the most advanced category, where AI systems learn optimal defense strategies through trial and error, continuously improving their response tactics based on the outcomes of previous actions.
The real time processing capability of ML is crucial because cyber attacks often unfold in milliseconds. An AI Application that can analyze network packets, correlate events across multiple data sources, and make threat determinations in microseconds provides a level of protection that no human team could match, regardless of their expertise. Modern AI Platforms leverage GPU accelerated computing and distributed architectures to deliver this speed at enterprise scale.
Machine Learning Types in Cybersecurity: A Comparison
| Parameter | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning | Reinforcement Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Data | Labeled datasets required | No labels needed | Reward based feedback |
| Best Use Case | Malware classification, spam filtering | Zero day detection, anomaly discovery | Adaptive defense strategies |
| Accuracy | High for known threats | Moderate to high | Improves over time |
| Speed | Fast after training | Moderate | Variable |
| Limitation | Misses novel threats | Higher false positives | Complex to implement |
| Example AI Platform | CrowdStrike Falcon, SentinelOne | Darktrace, Vectra AI | Custom enterprise solutions |
AI Powered Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) have been staples of network security for decades. However, traditional IDS/IPS solutions struggle with modern threats because they rely heavily on known attack signatures and predefined rules. AI powered IDS/IPS represents a quantum leap forward, combining the reliability of signature based detection with the adaptability of machine learning based analysis.
An AI enhanced IDS continuously monitors network traffic, applying deep packet inspection combined with ML models that understand normal traffic patterns. When the system detects a deviation that matches a known attack pattern or exhibits characteristics of a novel threat, it generates an alert with a confidence score. The accompanying IPS component can then take immediate action, such as blocking the malicious traffic, quarantining the affected endpoint, or modifying firewall rules, all without waiting for human intervention.
What makes AI powered IDS/IPS particularly valuable is their ability to reduce false positives. Traditional systems are notorious for generating overwhelming volumes of alerts, many of which turn out to be benign. AI Application tools solve this problem by contextualizing alerts using historical data, user behavior profiles, and threat intelligence feeds. This means security analysts receive fewer but more actionable alerts, allowing them to focus their energy where it matters most. Leading AI Platforms now offer IDS/IPS capabilities that can handle terabytes of network data daily while maintaining detection accuracy above 99%.
Behavioral Analytics and Anomaly Detection
Behavioral analytics is one of the most powerful applications of AI in cybersecurity. It works by establishing a comprehensive baseline of normal behavior for every user, device, and application within an organization’s network. This baseline encompasses patterns such as login times, data access habits, communication frequency, file transfer volumes, and application usage. Once the baseline is established, the AI Application continuously monitors all activity and flags any deviations that exceed predefined thresholds.
The strength of behavioral analytics lies in its ability to detect threats that bypass traditional security controls. Consider a case where an employee’s credentials are stolen through a phishing attack. The attacker might use valid credentials to log in, making their access appear legitimate to conventional security tools. However, a behavioral analytics engine would detect differences in the attacker’s behavior: perhaps they are accessing systems the employee never touches, operating during unusual hours, or transferring data to unfamiliar external locations. The AI Platform can then trigger alerts and automated containment measures before the attacker can exfiltrate sensitive data.
Anomaly detection extends beyond user behavior to encompass network traffic patterns, application performance metrics, and system configurations. AI Platforms that combine User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) with network traffic analysis provide a holistic view of an organization’s security posture, enabling rapid detection of both external attacks and insider threats. This is a powerful example of how AI and human collaboration creates stronger outcomes than either could achieve independently.

Automating Incident Response with AI
When a security breach occurs, every second counts. The faster an organization can detect, contain, and remediate a threat, the less damage it sustains. Unfortunately, manual incident response processes are inherently slow, often taking hours or even days to complete. AI powered Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms are transforming this landscape by enabling near instantaneous automated responses to detected threats.
An AI driven incident response workflow typically follows a structured sequence. First, the AI Application detects a potential threat through its monitoring capabilities. Next, it enriches the alert with contextual information from threat intelligence databases, user behavior profiles, and network topology data. The system then classifies the incident by severity and type, selects the appropriate response playbook, and executes the containment actions automatically. These actions might include isolating a compromised endpoint, revoking compromised credentials, blocking malicious IP addresses, or initiating a forensic data capture for later analysis.
The most advanced AI Platforms support adaptive playbooks that evolve based on the outcomes of previous incidents. If a particular containment strategy proves ineffective, the AI system learns from this experience and adjusts future responses accordingly. This continuous improvement cycle ensures that the organization’s incident response capability becomes more effective over time, even as threat actors change their tactics. For security teams, this means less time spent on repetitive tasks and more bandwidth for strategic threat hunting and security architecture improvements.
Predictive Intelligence and Risk Assessment
One of the most compelling advantages of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to predict threats before they materialize. Predictive intelligence uses machine learning models trained on historical attack data, vulnerability databases, and current threat landscape information to forecast which assets, systems, or users are most likely to be targeted in the near future.
AI powered risk assessment goes beyond traditional vulnerability scanning. While conventional tools identify known vulnerabilities and assign generic severity scores, AI Application tools consider a much broader set of factors. These include the criticality of the affected asset, the organization’s specific threat profile, the availability of known exploits in the wild, the effectiveness of existing compensating controls, and even geopolitical factors that might influence attack likelihood. By synthesizing these diverse inputs, AI Platforms generate dynamic risk scores that accurately reflect each organization’s unique exposure.
This predictive capability enables security teams to prioritize their efforts efficiently. Instead of trying to patch every vulnerability simultaneously, they can focus resources on the highest risk areas first, dramatically reducing the organization’s overall attack surface. Some AI Platforms even provide attack path analysis, showing the most likely routes an attacker would take through the network and recommending specific mitigations to disrupt those paths. These predictive capabilities are also opening new business opportunities across sectors as AI reshapes the global technology landscape.
AI in Malware Detection and Ransomware Protection
Malware continues to be one of the most prevalent and damaging forms of cyberattack. The volume of new malware variants produced daily is staggering, with some estimates suggesting over 450,000 new samples emerge every day. Traditional antivirus solutions, which rely on signature matching, simply cannot keep pace with this rate of malware evolution. AI Application tools have fundamentally changed the game by enabling detection of malware based on its behavior and code characteristics rather than known signatures.
AI powered malware detection systems analyze executable files using deep learning models that examine thousands of features, including code structure, API call sequences, file metadata, and runtime behavior. These models can identify malicious intent even in files that have never been seen before, effectively neutralizing the zero day advantage that malware authors depend on. The same principles apply to ransomware protection, where AI Platforms monitor for encryption behavior patterns, suspicious file system activity, and known ransomware indicators to block attacks before they can lock down critical data.
A notable example is how modern AI Platforms deploy deception technology alongside malware detection. These systems create decoy files and honeypots that look attractive to ransomware. When the ransomware begins encrypting decoy files, the AI Application detects this activity instantly and terminates the malicious process before it can reach real data. This layered approach, combining predictive detection with deception, provides robust protection against even the most sophisticated ransomware strains.
Combating Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks with AI
Phishing remains the number one vector for cyberattacks, with over 90% of successful breaches beginning with a phishing email. Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities, making them exceptionally difficult to defend against using traditional tools. AI Application tools are proving highly effective in this domain because they can analyze the linguistic, contextual, and behavioral characteristics of communications at a scale and speed that humans cannot match.
AI powered phishing detection systems examine multiple dimensions of every incoming email. NLP models analyze the text for linguistic patterns commonly associated with phishing, such as urgency cues, authority impersonation, and suspicious requests. Computer vision algorithms inspect embedded images, logos, and formatting for signs of brand impersonation. URL analysis modules evaluate links for domain spoofing, redirect chains, and connections to known malicious infrastructure. When combined, these layers of analysis enable AI Platforms to catch phishing attempts that slip past traditional email gateways.
Beyond email, AI is also being deployed to combat social engineering on other channels, including SMS (smishing), voice calls (vishing), and social media platforms. Advanced AI Application tools can even detect deepfake audio and video content used in sophisticated social engineering campaigns, where attackers impersonate executives to authorize fraudulent transactions. This comprehensive, multi channel approach to social engineering defense is becoming essential as attackers diversify their tactics.
Benefits of Integrating AI into Cybersecurity Frameworks
The integration of AI into cybersecurity frameworks delivers transformative benefits that impact every aspect of an organization’s security posture. Beyond the obvious improvements in threat detection and response, AI brings strategic advantages that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and strengthen regulatory compliance.
| Benefit | Description | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real Time Detection | AI identifies threats in milliseconds | Reduces breach detection time by up to 95% |
| Reduced False Positives | ML models contextualize alerts | Saves 40%+ analyst time |
| Automated Response | SOAR playbooks execute instantly | Cuts response time from hours to seconds |
| Scalability | AI handles massive data volumes | Supports enterprise growth without linear cost increases |
| Predictive Protection | Forecasts vulnerabilities before exploitation | Enables proactive risk mitigation |
| Compliance Automation | Continuous monitoring and reporting | Simplifies GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS adherence |
| Cost Efficiency | Automates repetitive security tasks | Reduces operational security costs by 30%+ |
These benefits compound over time as AI systems learn and improve. Organizations that invest in AI Platforms today build a security foundation that becomes increasingly effective, creating a competitive advantage in their ability to protect customer data, maintain operational continuity, and demonstrate regulatory compliance to stakeholders and partners.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Cybersecurity
While AI delivers remarkable capabilities in cybersecurity, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations that organizations may encounter during adoption and operation. Understanding these challenges is essential for setting realistic expectations and implementing effective mitigation strategies.
Data Quality and Quantity: AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Organizations with limited or poorly structured security data may find that their AI Application tools produce inconsistent results during the initial deployment phase. Ensuring clean, comprehensive, and representative training data is a prerequisite for effective AI cybersecurity.
Adversarial AI Attacks: Sophisticated threat actors are beginning to use adversarial techniques to fool AI models. By carefully crafting inputs that exploit weaknesses in the model’s training, attackers can sometimes evade detection. This ongoing arms race between offensive and defensive AI requires continuous model updates and adversarial testing.
Skill Gap: Implementing and managing AI Platforms requires specialized expertise that many organizations lack. The cybersecurity skills shortage is already acute, and adding AI competencies to the requirement further narrows the talent pool. Partnering with experienced service providers can help bridge this gap.
Explainability: Many AI models, particularly deep learning systems, operate as “black boxes” that produce accurate results but cannot easily explain their reasoning. In regulated industries, this lack of explainability can create compliance challenges where organizations must demonstrate why certain security decisions were made.
Ethical Concerns and Data Privacy Issues
The deployment of AI in cybersecurity raises important ethical questions that organizations must thoughtfully address. Chief among these is the tension between security monitoring and individual privacy. AI Platforms that perform behavioral analytics necessarily collect and analyze detailed information about user activities, which can feel intrusive to employees and customers alike.
Organizations must establish clear policies that define the scope of AI monitoring, ensure transparency about what data is collected and how it is used, and provide appropriate oversight mechanisms. Data minimization principles should guide the design of AI Application systems, ensuring that only the data necessary for effective security is collected and retained. Regular privacy impact assessments help identify and mitigate potential overreach before it becomes problematic.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for algorithmic bias in AI security systems. If training data contains biases, the AI model may disproportionately flag certain user groups or behaviors as suspicious. Organizations should audit their AI Platforms regularly for bias and ensure that security decisions are fair, consistent, and defensible. Establishing an ethics board or committee to oversee AI cybersecurity practices is becoming a best practice among forward thinking enterprises. The broader question of responsible AI usage is also tied to building a sustainable and equitable technological future.
Traditional Cybersecurity vs AI Powered Cybersecurity
| Parameter | Traditional Cybersecurity | AI Powered Cybersecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Signature based matching | Behavioral and pattern analysis |
| Zero Day Protection | Limited or none | Strong through anomaly detection |
| Response Time | Hours to days | Seconds to minutes |
| False Positive Rate | High (50%+ in many cases) | Low (under 5% with tuned models) |
| Scalability | Linear scaling with infrastructure | Elastic cloud based scaling |
| Adaptability | Requires manual rule updates | Self learning and self improving |
| Operational Cost | High (manual processes) | Lower over time (automation driven) |
| Insider Threat Detection | Weak | Strong through UEBA |
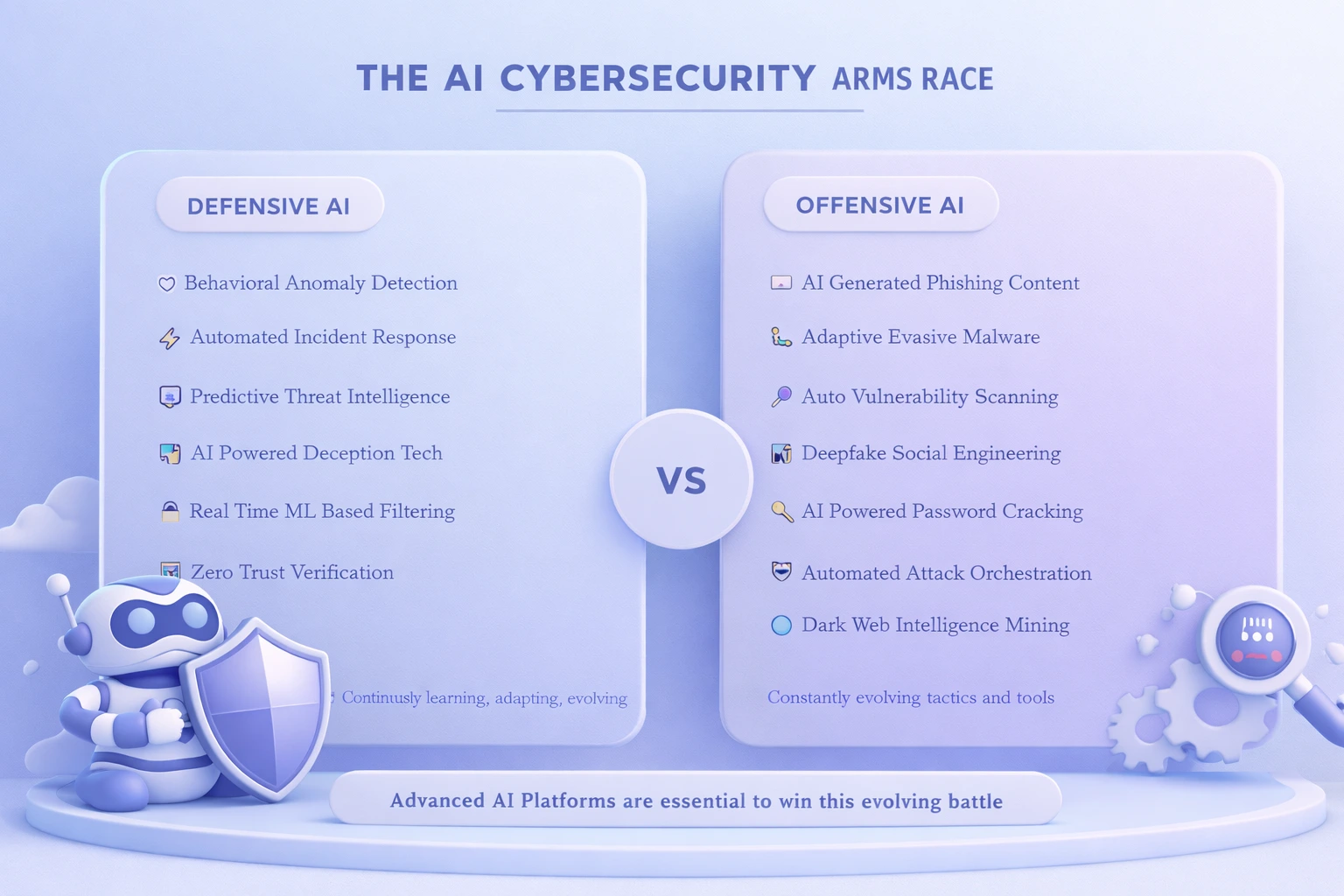
AI vs. AI: How Cybercriminals Use Artificial Intelligence
As defenders embrace AI, attackers are doing the same. Cybercriminals are now leveraging AI to enhance the effectiveness, scale, and sophistication of their attacks. This has created an unprecedented AI arms race in the cybersecurity landscape, where both sides continuously evolve their capabilities to gain an advantage.
Offensive AI applications include automated vulnerability discovery tools that can scan thousands of targets simultaneously, AI generated phishing content that is nearly indistinguishable from legitimate communications, and adaptive malware that changes its behavior in real time to evade detection. Deepfake technology, powered by generative AI, enables convincing impersonation of executives and authority figures, facilitating business email compromise and wire fraud schemes that have cost organizations billions of dollars collectively.
This escalation underscores the critical importance of deploying robust AI Platforms for defense. Organizations that rely solely on traditional security tools are at a significant disadvantage against AI powered attacks. The key to winning this AI vs. AI battle lies in continuous model training, threat intelligence sharing across industry peers, and investment in advanced AI Application tools that can detect and counter AI generated threats. It also highlights the need for human oversight, as security professionals must guide AI systems and make strategic decisions that pure automation cannot handle.
Future Trends in AI and Cybersecurity
The intersection of AI and cybersecurity is evolving rapidly, and several emerging trends are poised to shape the landscape over the coming years. Understanding these trends is crucial for organizations that want to stay ahead of the curve and build future proof security strategies.
Autonomous Security Operations Centers (SOCs): The future SOC will be largely autonomous, with AI systems handling the vast majority of detection, investigation, and response activities. Human analysts will transition from alert processors to strategic advisors who oversee AI operations and handle the most complex, novel threats that require creative problem solving.
Federated Learning for Collaborative Defense: AI models will increasingly be trained using federated learning techniques, where organizations contribute to shared threat intelligence without exposing their proprietary data. This approach enables the creation of more robust AI Platforms that benefit from collective knowledge while preserving individual data privacy.
Quantum Resistant AI Security: As quantum computing advances, current encryption methods may become vulnerable. AI Application tools are being designed to identify quantum related threats and support the transition to post quantum cryptographic standards, ensuring long term data protection.
AI Driven Zero Trust Architectures: The zero trust security model, which assumes no user or device should be inherently trusted, is becoming the standard framework for enterprise security. AI Platforms play a central role by continuously verifying identities, assessing risk levels, and enforcing access policies dynamically based on real time context.
Explainable AI (XAI) in Security: Regulatory requirements and organizational governance demands are driving the adoption of explainable AI models that can clearly articulate the reasoning behind their security decisions. This transparency is essential for building trust in AI cybersecurity systems and meeting compliance requirements.
Best Practices for Implementing AI Driven Security Solutions
Successfully implementing AI in cybersecurity requires a thoughtful, structured approach that aligns technology investments with organizational goals and risk tolerance. The following best practices provide a roadmap for organizations seeking to integrate AI Application tools into their security frameworks effectively.
Start with a comprehensive security assessment to identify your organization’s specific threat landscape, existing security gaps, and compliance requirements. This assessment provides the foundation for selecting the right AI Platforms and tools that address your most critical needs.
Invest in data quality and infrastructure. AI models require high quality, well organized data to deliver accurate results. Ensure your network monitoring tools, endpoint agents, and log management systems are properly configured to feed clean data into your AI Application tools. Establish data governance policies that define data retention, access controls, and privacy protections.
Adopt a phased implementation approach rather than attempting a full scale deployment at once. Begin with a pilot project in a contained environment, measure results against clear success criteria, and gradually expand scope based on demonstrated value. This approach reduces risk and allows your team to build expertise incrementally.
Ensure human oversight and accountability. AI should augment your security team, not replace it. Establish clear escalation procedures, define roles and responsibilities for AI oversight, and ensure that critical security decisions always involve human review. Regular audits of AI system performance help identify issues before they impact security effectiveness.
Continuously train and update AI models. The threat landscape evolves constantly, and AI models must evolve with it. Establish processes for regular model retraining using fresh threat data, adversarial testing to identify potential weaknesses, and performance monitoring to ensure detection accuracy remains high. Leading AI Platforms provide automated model update capabilities that simplify this process.
Choose experienced implementation partners. The complexity of AI cybersecurity demands specialized expertise. Partnering with providers who have deep experience in both AI and cybersecurity ensures that your implementation follows proven methodologies, avoids common pitfalls, and delivers maximum value from your investment.
The Evolving Role of AI in Strengthening Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence has moved from a futuristic concept to an indispensable reality in the world of cybersecurity. As cyber threats grow in volume, velocity, and sophistication, AI Application tools and AI Platforms provide the only viable path to maintaining robust defenses at scale. From real time threat detection and behavioral analytics to automated incident response and predictive intelligence, AI is reshaping every dimension of how organizations protect their digital ecosystems. The businesses that embrace this transformation today will be the ones that thrive in an increasingly hostile digital landscape tomorrow.
The journey toward AI powered cybersecurity is not without its challenges, but the rewards far outweigh the obstacles. Organizations must invest in quality data, skilled talent, and trusted technology partners to realize the full potential of AI in their security operations. As the AI arms race between defenders and attackers intensifies, the margin for complacency continues to shrink. Proactive adoption of AI driven security strategies is no longer optional; it is a fundamental requirement for business survival and success.
Nadcab Labs stands at the forefront of this transformation with over 8+ years of expertise in building, deploying, and managing AI Application solutions and AI Platforms for cybersecurity. Having partnered with enterprises across industries including finance, healthcare, e commerce, and technology, Nadcab Labs brings deep domain knowledge, battle tested methodologies, and a commitment to staying ahead of the evolving threat landscape. Our team of certified security professionals and AI engineers work collaboratively with clients to design customized, scalable cybersecurity frameworks that leverage the full power of artificial intelligence. From initial risk assessment and architecture design through deployment, integration, and continuous optimization, Nadcab Labs delivers end to end AI cybersecurity solutions that protect your most valuable digital assets. When it comes to securing your business with the most advanced AI driven security technology available, Nadcab Labs is the partner you can trust to deliver results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, small businesses can access AI powered cybersecurity through cloud based AI Platforms that offer scalable pricing models. Many vendors provide subscription plans tailored for smaller teams. These solutions eliminate the need for costly on premise infrastructure. With the rise of affordable AI Application tools, even startups can deploy intelligent threat monitoring without exceeding their budgets or hiring large security teams.
Deployment timelines vary based on organizational size and complexity. A basic AI Application for endpoint protection can be set up within a few weeks, while enterprise grade AI Platforms with full integration may take two to three months. Proper planning, data migration, and staff training are essential phases. Working with experienced providers like Nadcab Labs can significantly shorten the implementation cycle.
AI does not replace human analysts but significantly enhances their capabilities. AI Platforms handle repetitive tasks like log analysis and alert triaging, freeing analysts to focus on complex investigations. Human judgment remains critical for understanding attacker intent and making strategic decisions. The ideal approach combines AI automation with skilled professionals to build a robust and adaptive security posture.
Industries handling sensitive data benefit the most, including finance, healthcare, government, retail, and telecommunications. These sectors face high volumes of cyber threats and strict regulatory requirements. AI Application tools help them achieve compliance while detecting threats in real time. Energy and manufacturing sectors also increasingly adopt AI Platforms to protect critical infrastructure from sophisticated attacks.
AI cybersecurity solutions are among the best defenses against zero day attacks because they rely on behavioral analysis rather than known signatures. AI Platforms can identify unusual patterns and flag potential zero day exploits before traditional tools detect them. While no solution guarantees complete protection, AI significantly reduces the window of vulnerability by enabling rapid detection and automated containment of unknown threats.
AI cybersecurity systems require network traffic logs, endpoint activity data, user behavior records, threat intelligence feeds, and historical incident reports. The quality and volume of this data directly impact the accuracy of AI Application models. Organizations must ensure data is clean, well structured, and continuously updated. Proper data governance policies are also essential to maintain privacy and regulatory compliance.
Absolutely. Most modern AI Platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing security information and event management (SIEM) systems, firewalls, and endpoint protection tools. This layered approach strengthens overall defense without requiring organizations to discard their current investments. API driven integrations allow AI Application modules to enhance legacy tools by adding intelligent analytics and automation capabilities.
AI reduces false positives by learning from historical data and continuously refining its detection models. Machine learning algorithms on advanced AI Platforms distinguish between genuine threats and benign anomalies with increasing accuracy over time. Feedback loops allow security teams to correct misclassifications, which further trains the AI Application. This results in fewer unnecessary alerts and allows analysts to focus on real incidents.
Reputable vendors should hold certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, and GDPR compliance attestations. For specific industries, look for HIPAA compliance in healthcare or PCI DSS in finance. These certifications demonstrate that the AI Platforms and services meet globally recognized security and privacy standards. Vendors with a proven track record like Nadcab Labs bring additional credibility through years of hands on expertise.
Organizations typically see positive ROI within 12 to 18 months of deploying AI cybersecurity solutions. Savings come from reduced breach costs, lower incident response times, and decreased reliance on manual monitoring. Studies show AI Application tools can cut breach related expenses by up to 30%. Beyond financial returns, businesses gain improved compliance, customer trust, and operational continuity, making the investment highly worthwhile.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







