Key Takeaways
- Real-world data oracles act as a bridge that connects blockchain smart contracts to off-chain data like prices, weather, and IoT readings.
- Oracle types include inbound, outbound, consensus-based, human, centralized, and decentralized, each suited for different use cases.
- Decentralized oracles use multiple nodes and consensus to reduce single points of failure and improve data trustworthiness.
- Industries like DeFi, insurance, supply chain, gaming, healthcare, and energy already rely on oracles for automated, data-driven operations.
- Building an oracle system involves defining data needs, selecting oracle architecture, deploying nodes, and integrating with smart contracts.
- Challenges like data accuracy, security risks, and scalability need to be addressed, but AI and cross-chain tech are paving the way for better solutions.
Blockchain technology has changed how we think about trust, ownership, and digital transactions. But here is the thing that most people overlook: blockchains, by design, cannot access data from the outside world on their own. They are closed systems. A smart contract on Ethereum cannot check today’s stock price, pull a weather report, or confirm whether a delivery was completed. It only knows what exists on the chain itself.
This is where real-world data oracles come in. They serve as the connection layer between blockchain networks and external data sources. Without oracles, smart contracts would be limited to processing only on-chain information, making them far less useful for practical applications. When you hear about a DeFi platform liquidating a loan based on a token’s price drop or an insurance contract paying out automatically after a hurricane, oracles are working behind the scenes to make that happen.
Developing a data oracle for blockchain is not a plug-and-play task. It requires planning around data sourcing, validation, node architecture, and security. This article walks through the full picture, from understanding what oracles are to actually building and deploying one. If you are working on blockchain development or exploring how to bring external data into your dApp, this is for you.
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
A blockchain oracle is a service or mechanism that feeds external data into a blockchain network. Think of it as a translator. The blockchain speaks one language, and the outside world speaks another. The oracle sits between the two and passes verified information from external sources into smart contracts.
Oracles do not create or execute smart contracts. They also do not secure transactions. Their job is strictly to deliver data. That data can come from many places: financial markets, weather stations, IoT sensors, sports scoreboards, web APIs, or even human input. Once the oracle delivers this data to the blockchain, the smart contract can use it to trigger specific actions like releasing funds, updating records, or settling bets.
The term “oracle” in this context refers to something that provides knowledge or answers. In blockchain, it describes any tool or protocol that retrieves, verifies, and transmits off-chain data to on-chain systems. According to Wikipedia, blockchain oracles are considered third-party services that provide smart contracts with external information, acting as a bridge between blockchains and the outside world.
One critical thing to understand is the “oracle problem.” Since blockchains are deterministic, every node must arrive at the same result. Introducing external data creates a trust issue because the data itself comes from centralized or semi-centralized sources. The entire point of using blockchain is to remove the need for trust in a single party, so oracle design needs to account for this tension. Game theory plays a big role here. Many oracle systems use staking and penalties to reward accurate data reporting and punish dishonest behavior.
Types of Blockchain Oracles
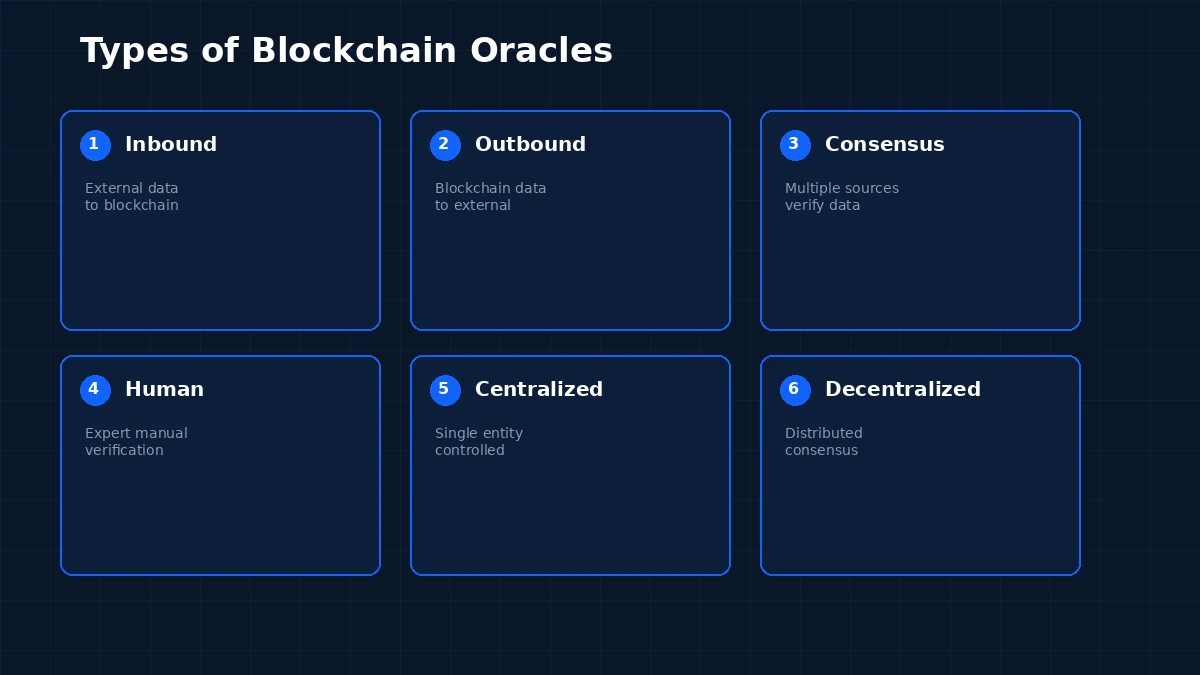
Not all oracles work the same way. The type you choose depends on the data you need, how it flows, and how much trust and decentralization your application requires. Here is a breakdown of the main oracle categories and what each one does.
Inbound Oracles bring data from the external world into the blockchain. This is the most common type. Examples include feeding cryptocurrency price data into a DeFi lending protocol, sending temperature readings to an insurance smart contract, or pushing sports results into a betting platform. The data always moves in one direction: from outside to inside the chain.
Outbound Oracles work in the opposite direction. They send information from the blockchain to external systems. For instance, a smart contract might trigger a payment through a traditional banking API or update an external database once a condition is met on-chain. These are less common but equally important for real-world integrations.
Consensus-based Oracles query multiple data sources and use a consensus mechanism to agree on a single data point. This reduces the risk of getting bad data from a single source. If five out of seven data providers report the same value, the oracle accepts that as truth. This approach is widely used in decentralized finance.
Human Oracles involve people with specialized knowledge manually verifying and inputting data. While this may seem outdated, it is useful in cases where automated data is unavailable or unreliable, such as verifying the outcome of a legal dispute or confirming a real-world event that sensors cannot capture.
Centralized Oracles are controlled by a single entity. They are simple to set up and can be efficient for private blockchains, like a logistics company tracking its own supply chain. However, they carry a single point of failure. If that entity is compromised, the data integrity of the entire system is at risk.
Decentralized Oracles distribute data sourcing and validation across multiple independent nodes. This removes the need to trust any single party and aligns with blockchain’s core philosophy. Chainlink is the most recognized example. These oracles are often called consensus oracles because they aggregate data from many providers to determine a reliable output. Understanding data availability layers in blockchain is helpful here since oracle data must be accessible and verifiable on-chain.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Oracles: A Comparison
| Parameter | Centralized Oracles | Decentralized Oracles |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Single entity manages data | Distributed across multiple nodes |
| Trust Level | Requires trust in one provider | Trust minimized through consensus |
| Security Risk | Single point of failure | Resistant to individual node failure |
| Cost | Lower operational cost | Higher due to multiple node operators |
| Speed | Faster response time | Slightly slower due to consensus |
| Best Use Case | Private chains, internal tracking | Public chains, DeFi, insurance |
| Example | Proprietary company APIs | Chainlink, Band Protocol |
For applications that handle significant financial transactions or serve a public audience, decentralized oracles are almost always the better option. The added cost and latency are worth it for the improved security and trust guarantees. Centralized oracles still have their place in private and permissioned environments where the organization already controls the entire stack.
How Oracles Gather and Deliver Data
Understanding the data lifecycle of an oracle helps clarify what happens behind the scenes. The process is not just about pulling a number from an API. It involves requesting, fetching, validating, aggregating, and delivering data to the blockchain in a format smart contracts can use.
The cycle begins when a smart contract makes a data request. Let us say a lending protocol needs the current ETH/USD price. The oracle network picks up this request and routes it to its node operators. Each node independently queries one or more external data sources such as exchange APIs or aggregator services. The nodes then validate the data locally. Once enough nodes have reported, the oracle uses a consensus algorithm to determine the accepted value. Only then is the data written on-chain where the smart contract can read and act on it.
In decentralized setups, this multi-node validation is what gives the data its credibility. No single node can push false data without being detected and penalized. The entire system relies on economic incentives. Nodes stake tokens as collateral, and they lose that stake if they report inaccurate information. This is similar to how Bitcoin nodes in blockchain operate, where participants are incentivized to follow the rules.
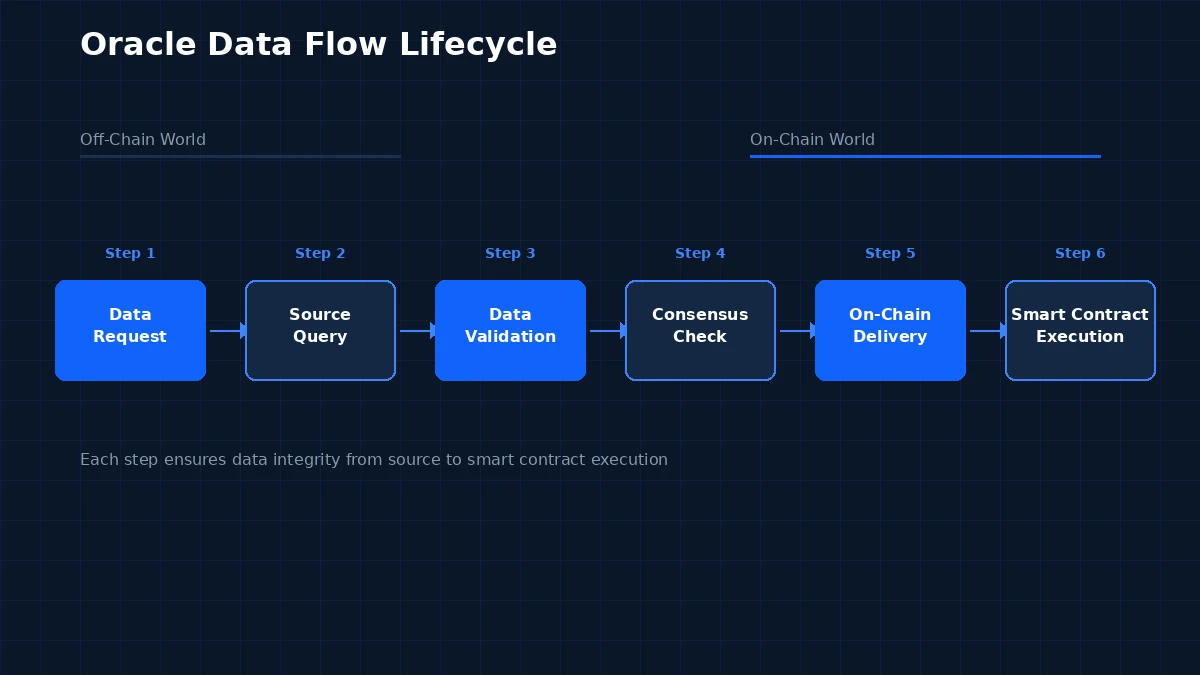
Oracle Data Lifecycle: Step by Step
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Request | A smart contract emits an event requesting specific data |
| 2 | Source Query | Oracle nodes query external APIs, sensors, or databases |
| 3 | Data Validation | Each node independently verifies the data it received |
| 4 | Consensus Check | Aggregated responses are compared and a consensus value is derived |
| 5 | On-Chain Delivery | Validated data is submitted as a transaction to the blockchain |
| 6 | Smart Contract Execution | The smart contract reads the data and triggers its logic |
Hardware oracles add another dimension to this. Physical devices like thermostats, GPS trackers, RFID scanners, and barcode readers can feed data directly into the oracle network. This is especially important for supply chain use cases where you need to prove the physical condition or location of goods.
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain Oracles

Oracles are already in production across several major industries. The applications are practical and solve real problems. Here is how different sectors are using them today.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): This is the largest consumer of oracle services. Platforms like Aave and Compound use Chainlink price feeds to determine collateral values and trigger liquidations. Uniswap relies on oracle-derived pricing for its trading pairs. Without accurate and timely price data, these protocols could not function safely. A wrong price feed could result in millions lost through incorrect liquidations or exploitable arbitrage. For a broader view of how blockchain is reshaping enterprise operations, read this guide on enterprise blockchain applications.
Insurance: Etherisc uses flight data oracles to automatically pay out claims when flights are delayed. There is no need for a person to file a claim or for an adjuster to verify it. The oracle checks the flight status, and if the delay threshold is met, the smart contract sends the payout. Arbol applies the same logic using weather data for agricultural insurance, triggering payments based on rainfall levels.
Supply Chain Management: VeChain uses IoT devices paired with oracles to track products from factory to store shelf. Data about temperature, humidity, and location is fed into the blockchain continuously. This gives buyers and regulators a transparent record of a product’s journey. Account tries in blockchain are also relevant here since they help store and verify state data efficiently.
Gaming and NFTs: Fairness is everything in blockchain gaming. Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) provides provably random numbers for games and NFT drops. This means players can verify that the randomness was not manipulated. Axie Infinity uses oracles to fetch off-chain game asset data and keep in-game economies balanced. If blockchain gaming interests you, explore how blockchain gaming projects are being supported at the development level.
Healthcare: Solve Care uses oracles to verify patient data and automate insurance claims processing. MediLedger applies blockchain and oracles to track pharmaceutical products, helping confirm drug authenticity and fight counterfeits.
Energy and Environment: LO3 Energy manages peer-to-peer energy trading by using oracle-fed data from production and consumption meters. Climate Chain Coalition tracks carbon credit data to bring transparency to carbon offset markets.
Sports and Betting: Augur resolves prediction market bets by fetching verified sports results through oracles. Chiliz powers fan engagement tokens using real-time match and event data.
Industry-Wise Oracle Use Cases Summary
| Industry | Oracle Data Used | Example Platform | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeFi | Asset prices | Chainlink, Aave | Accurate collateral valuation |
| Insurance | Flight, weather data | Etherisc, Arbol | Automated claim payouts |
| Supply Chain | IoT sensor data | VeChain | Real-time product tracking |
| Gaming | Random numbers, game state | Chainlink VRF | Provably fair gameplay |
| Healthcare | Patient, drug records | Solve Care, MediLedger | Fraud prevention, authenticity |
| Energy | Production, consumption | LO3 Energy | Peer-to-peer energy trading |
| Betting | Sports results | Augur, Chiliz | Automated bet resolution |
Build Your Custom Oracle Solution
Need a reliable data oracle for your blockchain project? From architecture design to smart contract integration, get expert help building oracle systems that deliver accurate, real-time data to your dApps.
Benefits of Using Blockchain for Data Oracles
The combination of blockchain infrastructure and oracle technology creates several advantages that centralized data delivery systems cannot match. These benefits are not theoretical. They are already being demonstrated in live production environments across multiple sectors.
Decentralization reduces dependency. Instead of relying on one company to provide accurate data, a decentralized oracle network distributes that responsibility across many independent operators. If one node goes offline or reports bad data, the rest of the network corrects for it. This is fundamental for applications managing significant financial exposure.
Security is built into the architecture. Data delivered through blockchain oracles gets recorded in immutable, tamper-proof ledgers. Cryptographic verification ensures that the data has not been altered during transit. The combination of on-chain recording and off-chain validation creates a two-layer security model. Understanding how blockchain addresses work gives additional context on how data is cryptographically tied to identities and transactions.
Transparency allows anyone to audit. Since oracle data is recorded on a public blockchain, anyone can verify when data was submitted, what the value was, and which nodes contributed. This level of transparency is not possible with traditional centralized data providers.
Reliability comes from redundancy. Consensus mechanisms verify each data point through multiple independent sources. If three out of five nodes agree on a price, the oracle reports that price. This cross-verification significantly reduces the chance of errors reaching the smart contract.
Smart contracts automate execution. Once the oracle delivers data, the smart contract can act on it without human intervention. This removes delays, cuts operational costs, and eliminates manual processing errors. Think about insurance: instead of a weeks-long claims process, the payout happens within minutes of the triggering event being confirmed.
Interoperability bridges different systems. Oracles standardize how external data enters the blockchain, making it easier for different protocols and even different blockchains to work with the same data feeds. This is increasingly important as the ecosystem moves toward multi-chain architectures. If you are exploring how blockchains connect to broader ecosystems, this piece on how Solana is transforming the gig economy shows one example of cross-sector integration.
Step-by-Step: Developing a Blockchain Oracle
Building an oracle is not just about writing code. It is a system design challenge that requires careful consideration of data requirements, trust models, node architecture, and security. Below is a practical walkthrough of the development process.
Step 1: Define Your Data Requirements. Start by identifying exactly what data your smart contract needs. Is it price data? Weather conditions? Delivery confirmations? Define the data type, update frequency, acceptable latency, and the level of accuracy required. A DeFi price feed that updates every 10 seconds has very different requirements from a crop insurance oracle that checks weather once a day.
Step 2: Choose Your Oracle Architecture. Decide whether you need a centralized or decentralized oracle. For private use cases, a centralized approach may be sufficient. For public-facing applications, a decentralized architecture with multiple node operators is strongly recommended. You can build from scratch or integrate with existing oracle networks like Chainlink or Band Protocol. For those working with DAOs or governance-driven projects, understanding how DAOs operate in blockchain can inform how oracle governance is structured.
Step 3: Identify and Vet Data Sources. This is critical. The oracle is only as good as its data sources. Use reputable APIs from established providers. Cross-reference data from multiple sources. For financial data, consider sources like exchanges, aggregators, and market data platforms. For IoT data, make sure your hardware devices are calibrated and tamper-resistant. Getting initial funds to test your system on testnets is simple. Learn about blockchain faucets to get started without spending real tokens.
Step 4: Design and Deploy Oracle Nodes. Each oracle node is responsible for fetching data from sources, validating it locally, and reporting it to the network. In a decentralized setup, you need multiple nodes run by independent operators. These nodes should be geographically distributed and have redundant internet connections. Each node stakes tokens to participate, creating an economic incentive to report accurately.
Step 5: Implement Data Aggregation and Consensus. Once nodes report their data, the aggregation layer combines the inputs. Common aggregation methods include median calculation, weighted averages, or outlier removal. The consensus mechanism determines which reported value is accepted. This is the layer that protects against individual node manipulation.
Step 6: Write and Integrate Smart Contracts. The on-chain component is a smart contract that receives data from the oracle and makes it available to other contracts. This contract needs to handle data formatting, timestamping, and access control. It should also include mechanisms for dispute resolution and data staleness checks.
Step 7: Test, Audit, and Launch. Before going live, test the entire system on a testnet. Simulate scenarios like node failures, data source outages, and adversarial attacks. Get a third-party security audit for both the oracle contracts and node software. After launch, implement continuous monitoring and community governance for ongoing maintenance.
Oracle Development Phases Overview
| Phase | Key Activities | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Define data needs, choose architecture, select data sources | Requirements document |
| Development | Build node software, write smart contracts, set up aggregation | Working oracle prototype |
| Testing | Testnet deployment, adversarial testing, load testing | Test results and bug fixes |
| Audit | Third-party security review, code audit, penetration testing | Audit report with fixes |
| Launch and Monitoring | Mainnet deployment, real-time monitoring, governance setup | Live oracle network |
Challenges in Building Oracle Systems
Building a reliable oracle system is not straightforward. There are several practical and technical hurdles that developers need to plan for early in the process.
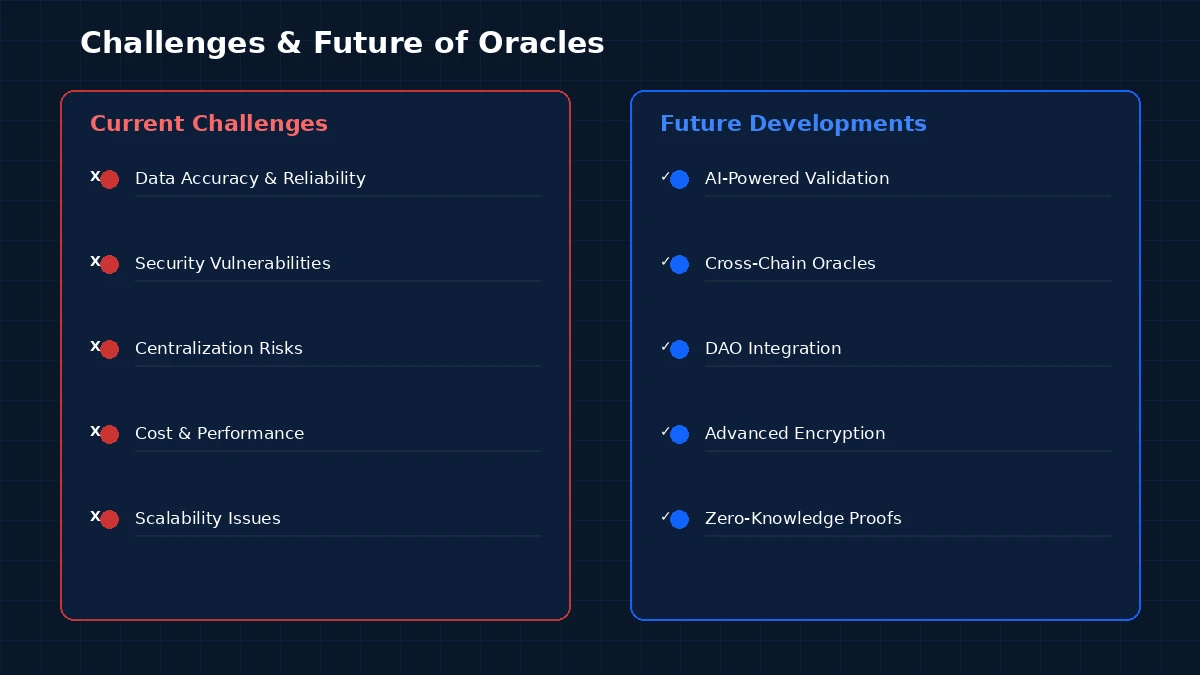
Data accuracy is the first concern. An oracle is only as trustworthy as the data it brings in. If the underlying sources report wrong or outdated information, the oracle will pass that bad data to the smart contract. In DeFi, a price feed error of even a few percentage points can trigger millions in incorrect liquidations. Developers need to plan for source failures, stale data, and outlier detection.
Security vulnerabilities are real. Oracles introduce new attack surfaces into blockchain systems. Flash loan attacks have exploited oracle weaknesses in the past, manipulating prices on low-liquidity exchanges to trick price feeds. Node operators can be bribed or compromised. Data sources can be spoofed. A solid security model includes encryption during data transit, node reputation systems, and slashing mechanisms for dishonest behavior.
The centralization vs. decentralization tradeoff. More decentralized oracle networks are harder and more expensive to run. Fewer nodes mean faster responses but less security. Finding the right balance depends on your application’s risk profile. A gaming app might tolerate a simpler oracle setup, while a lending protocol handling hundreds of millions in collateral needs maximum decentralization.
Cost is a factor. Running oracle nodes costs money. Data source APIs often charge fees. Every on-chain data update requires a blockchain transaction, which means gas fees. For high-frequency data feeds, these costs add up quickly. Developers need to design update strategies that balance freshness with cost, such as heartbeat updates (regular intervals) combined with deviation-based updates (triggered by significant price changes).
Scalability remains an open problem. As blockchain adoption grows, oracles need to serve more contracts, deliver more data types, and support more chains. Current oracle networks are working on cross-chain solutions and off-chain computation layers to handle this growth without compromising speed or reliability.
The Future of Blockchain Oracles
Oracle technology is evolving quickly, driven by the expanding needs of blockchain applications and the broader push toward decentralized infrastructure.
AI-powered data validation is one of the most promising developments. Machine learning models can detect anomalies in data feeds faster and more accurately than rule-based systems. An AI layer sitting between data sources and oracle nodes could flag suspicious data before it ever reaches the blockchain, reducing the window for manipulation.
Cross-chain oracle networks are becoming essential as the blockchain ecosystem fragments across multiple chains. Oracles that can serve data to Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, and other networks from a single infrastructure layer will reduce redundancy and improve consistency. This aligns with the growing demand for interoperability across chains.
Integration with DAOs will change how oracle networks are governed. Instead of a central team deciding on data source selection and node operator requirements, DAOs can allow token holders to vote on these decisions. This creates a more transparent and community-driven governance model.
Zero-knowledge proofs could allow oracles to prove the correctness of data without revealing the raw data itself. This is particularly relevant for privacy-sensitive use cases in healthcare, financial services, and government applications.
NFT and real-world asset tokenization will increase oracle demand significantly. As more physical assets get tokenized on blockchains, oracles will need to continuously feed data about asset conditions, valuations, and ownership status. This creates a massive growth opportunity for oracle providers.
Oracle Security Best Practices
Security needs to be baked into every layer of oracle development. Here are the practices that matter most based on lessons learned from real-world deployments and exploits.
First, always use multiple data sources. Never rely on a single API or exchange for price data. Aggregate from at least three to five independent providers and implement outlier detection to catch anomalies before they reach your smart contract.
Second, implement time-weighted average pricing (TWAP). Instead of using spot prices that can be manipulated in a single block, TWAP smooths the data over a window of time, making it much harder for attackers to influence. This approach was specifically developed as a response to oracle manipulation attacks in DeFi.
Third, set up data freshness checks. Your smart contract should verify that the data it receives is recent enough to be useful. If the last oracle update is more than a defined threshold old, the contract should pause or use fallback logic rather than act on stale data.
Fourth, run regular security audits. Oracle contracts and node software should be audited by reputable third-party firms before launch and periodically after. New attack vectors emerge constantly, and yesterday’s secure design may have today’s vulnerability.
Fifth, build in circuit breakers. If the oracle reports a value that differs dramatically from the previous value, the system should flag it and potentially halt operations until a manual review confirms the data. This prevents flash crash scenarios from cascading through your application.
Need Expert Oracle Development?
From oracle architecture design to full deployment, get the technical expertise your blockchain project needs. Secure, scalable, and built for real-world performance.
Final Thoughts
Real-world data oracles are not optional for blockchain applications that want to interact with the outside world. They are a fundamental piece of infrastructure. Without them, smart contracts remain isolated programs that can only process what is already on-chain. With them, blockchain becomes a platform that can respond to real events, automate real decisions, and manage real assets.
Building a good oracle system takes planning. You need to think about what data you need, where it comes from, how it gets validated, and how it reaches the blockchain securely. The choices you make in architecture, from centralized vs. decentralized to data aggregation methods, directly impact the reliability and security of every smart contract that depends on that oracle.
The space is maturing fast. AI is improving data validation. Cross-chain solutions are making oracles more versatile. DAO governance is making them more transparent. And the growing tokenization of real-world assets is creating demand for oracle services that will only increase over time. For developers and businesses looking to build on blockchain, understanding and investing in solid oracle infrastructure is one of the most important decisions you can make.
Frequently Asked Questions
A real-world data oracle is a service that connects blockchain networks to external information sources. Since blockchains cannot access off-chain data directly, oracles act as intermediaries that retrieve, validate, and deliver data from APIs, IoT devices, websites, and other sources into smart contracts. This enables automated on-chain actions based on real events like price changes, weather conditions, or delivery confirmations. Oracles are essential for any blockchain application that depends on external data.
Centralized oracles are managed by a single entity that controls data sourcing and delivery. This creates a single point of failure. If that entity is compromised, the entire data feed is at risk. Decentralized oracles distribute data collection and validation across multiple independent nodes. They use consensus mechanisms to agree on the correct data value, which reduces manipulation risk and increases trustworthiness. Decentralized oracles are preferred for public blockchains and financial applications.
The main security risks include data manipulation attacks where bad actors influence source data, oracle node compromise through bribery or hacking, and flash loan exploits that manipulate low-liquidity price feeds. Stale data is another risk, where outdated information triggers incorrect smart contract actions. Developers can mitigate these risks by using multiple independent data sources, implementing time-weighted pricing, adding circuit breakers, and conducting regular third-party security audits.
Decentralized finance is the largest user of blockchain oracles, relying on them for accurate price feeds that drive lending, borrowing, and trading. Insurance companies use oracles to automate claim payouts based on verifiable events like flight delays or weather conditions. Supply chain management, healthcare, gaming, energy trading, and sports betting all benefit significantly. Any industry that needs to trigger blockchain-based actions using external, verifiable real-world data can gain from oracle integration.
Oracle development costs vary based on complexity. Building on top of existing networks like Chainlink reduces development time but involves ongoing node operation and data fees. Custom oracle development requires investment in node infrastructure, smart contract development, security audits, and data source API subscriptions. Every on-chain data update requires a blockchain transaction fee. High-frequency price feeds on Ethereum, for example, can accumulate significant gas costs over time.
The oracle problem refers to the fundamental challenge of getting trustworthy external data into a trustless blockchain system. Since blockchains are deterministic and decentralized, introducing data from centralized external sources creates a potential trust bottleneck. Solutions include decentralized oracle networks that use multiple independent nodes and consensus, staking mechanisms that penalize dishonest data reporting, and cryptographic proofs that verify data authenticity without exposing raw data.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







