Key Takeaways: Best Smart Contract Platforms
- Security is crucial: If your project handles money or sensitive data, choose a blockchain with strong security and decentralization, such as Ethereum or Cardano.
- Speed matters: For applications that need fast execution, like gaming or high-volume DeFi, platforms such as Solana, Avalanche, or Ethereum Layer-2 networks are good options.
- Transaction costs affect adoption: Smart contract platforms with low and predictable fees, like Polygon, BNB Chain, and Layer-2 networks, make apps more affordable and user-friendly.
- Developer tools make building easier: Platforms with strong documentation, testing tools, and popular programming languages like Solidity or Rust help developers create secure and efficient smart contracts.
- Ecosystem and community support: A large ecosystem offers wallets, bridges, data feeds, and ready-made tools. Ethereum leads here, while Solana, Polygon, and BNB Chain are growing rapidly.
- Customization options: Some projects need special governance or compliance features. Avalanche subnets and Cosmos modular chains work well for enterprise and niche use cases.
- Layer-2 networks boost Ethereum: Solutions like Arbitrum and Base provide faster and cheaper transactions while keeping Ethereum’s strong security, making them ideal for scalable dApps.
- Match the platform to your project needs: There is no single best blockchain. Consider speed, security, cost, ecosystem, and flexibility to choose the right smart contract platform for your goals.
Smart contracts are changing the way we use blockchain. They are self-executing programs that run automatically when certain conditions are met. This makes transactions faster, cheaper, and safer by removing the need for middlemen. However, not all blockchains are equally good for smart contracts. Some are faster, some are cheaper, and some are more secure.
Choosing the right platform is important because it affects how well your application works and how many users it can attract. In 2026, there are many strong options, from Ethereum and Solana to Cardano and Avalanche. Each has its own strengths, so developers need to understand their features, speed, cost, and ecosystem before starting a project.
This guide explains what makes a blockchain ideal for smart contracts and highlights the top smart contract platforms to consider in 2026.
What Makes a Blockchain Ideal for Smart Contracts
Not all blockchains are the same for smart contracts. Choosing the right one is important because it affects how safe, fast, and cheap your apps will be. Security comes first. Smart contracts often handle real money or valuable data. A blockchain with many independent validators helps protect against hacks, mistakes, or fraud.
Next is scalability. A scalable blockchain can handle many transactions at the same time. This keeps apps fast and smooth even when lots of people use them. Transaction fees also matter. If fees are too high or change a lot, users may avoid your app. Smart contract platforms with low and stable fees are better.
Developer tools are helpful too. Blockchains with easy programming languages, clear guides, testing tools, and deployment help developers build apps faster and with fewer mistakes.
The ecosystem and community are also important. A strong ecosystem gives wallets, bridges, data feeds, and resources that make it easier to build and connect apps. Language support helps developers start quickly and write safe contracts.
By looking at security, speed, cost, tools, ecosystem, and language support, you can pick a blockchain that is safe, fast, and easy to use for smart contracts in 2026.
Top Smart Contract Platforms to Consider in 2026
In 2026, many blockchain platforms support smart contracts. Smart Contract Platforms let developers build programs that run automatically when certain conditions are met. Each has different strengths, so choosing the right one depends on your project’s needs.
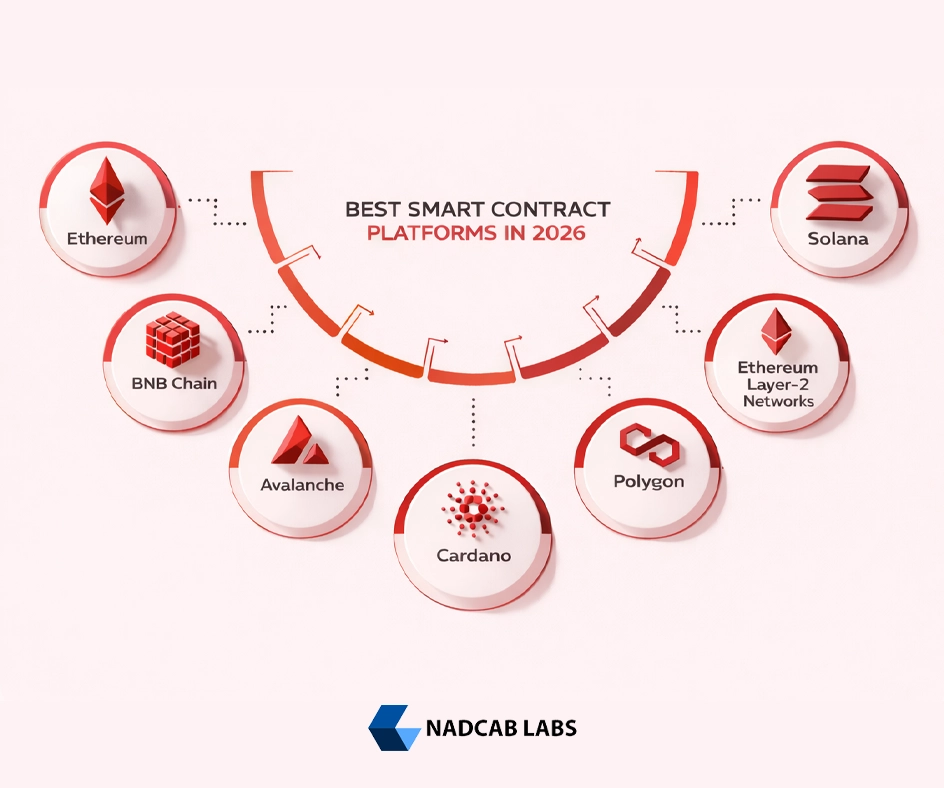
1. Ethereum
Overview
Ethereum is the world’s first and most widely used smart contract platform. According to 101 Blockchains blog, It introduced the idea of decentralized applications (dApps) and remains a key part of the blockchain world. Since 2015, hundreds of thousands of dApps have been built on Ethereum.
Why It Still Leads
Ethereum is strong because of its security and large ecosystem. It is highly decentralized, meaning no single person or group controls the network. Many independent validators keep it secure. Ethereum also has the largest collection of tools, libraries, and community support.
The platform uses Solidity, the most widely used language for smart contracts. This makes it easier for developers to learn and build applications with guidance from tutorials, forums, and examples.
Recent Improvements
Ethereum has changed from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). This makes it more energy-efficient and helps the network scale better.
Additionally, Layer-2 networks like Arbitrum and Optimism are built on top of Ethereum. They make transactions faster and cheaper without reducing security, which is great for both developers and users.
Best Use Cases
Ethereum is ideal for:
- DeFi applications like lending, borrowing, and trading
- NFT marketplaces
- DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations)
- Token launches and other blockchain projects
Considerations
Ethereum’s main network can still have high fees when traffic is heavy. However, Layer-2 solutions have made it more affordable for most users and applications, keeping it practical for real-world projects.
2. Solana
Overview
Solana is a high-speed blockchain designed for performance. It can process thousands of transactions per second at very low costs. Its fast finality makes transactions irreversible quickly, giving users a smooth and seamless experience.
Performance and Speed
Speed is Solana’s biggest strength. The network can handle heavy traffic without delays, making it ideal for applications that need fast execution. Transaction fees are very low, which encourages adoption for gaming, NFTs, and real-time financial apps.
Solana uses a unique technology called Proof of History (PoH), which records events in order. This helps the network operate efficiently and process transactions quickly.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts on Solana are written primarily in Rust, a modern programming language known for speed and safety. While Rust is powerful, it may be harder for beginners compared to other languages. Developers who master Rust can create highly efficient and secure applications.
Best Use Cases
Solana is ideal for applications that need speed and low costs, including:
- Gaming platforms and in-game economies
- Real-time DeFi applications
- High-volume NFT marketplaces
- Applications requiring fast, frequent interactions
Considerations
Solana has faced network stability issues in the past, causing temporary outages. However, the team continues to upgrade the network, and community efforts are improving reliability and performance over time.
3. BNB Chain
Overview
BNB Chain is a blockchain developed by Binance, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world. It is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which allows developers to use Ethereum tools and languages with minimal changes.
Why It’s Popular
BNB Chain is known for low transaction fees and fast confirmations, making it a practical choice for projects that want to launch quickly without high costs for users. Its EVM compatibility allows Solidity-based Ethereum contracts to migrate easily, saving time and effort for developers.
Ecosystem and Adoption
BNB Chain has its own ecosystem, including decentralized exchanges, NFT marketplaces, and token projects. It also benefits from Binance’s large user base, which helps attract liquidity and users to new applications. This makes it a strong option for startups and smaller projects.
Best Use Cases
BNB Chain works well for projects that need affordable and fast smart contracts, including:
- Token launches and initial coin offerings
- DeFi applications where cost efficiency is important
- NFT marketplaces and digital collectibles platforms
Considerations
Some critics note that BNB Chain is slightly more centralized than Ethereum. While this may reduce decentralization, many developers still choose it because of its affordability, ease of use, and fast transaction speeds.
4. Avalanche
Overview
Avalanche is a smart contract platform built for speed, scalability, and flexibility. It allows developers to create custom subnets, which are specialized blockchains within the Avalanche network, tailored to specific needs or projects.
Custom Blockchains
Avalanche’s subnet system lets developers control rules, fees, and permissions on their blockchain. This makes it ideal for enterprise applications or projects that need specific governance or compliance requirements. It is also fully EVM-compatible, so Ethereum smart contracts can run without major changes.
Performance
Avalanche provides fast finality, meaning transactions are confirmed quickly and securely. This ensures that applications feel responsive and smooth for users. High throughput and low delays make it suitable for scalable DeFi apps and other high-performance applications.
Best Use Cases
Avalanche is well-suited for:
- Custom enterprise blockchains with specific rules
- Scalable DeFi protocols handling many users
- Applications that require precise governance or permission control
Considerations
While Avalanche offers strong technical features, its ecosystem is smaller than Ethereum or Solana. This means fewer existing applications and tools are available. However, its flexibility and speed make it attractive for niche projects and enterprises looking for tailored solutions.
5. Polygon
Overview
Polygon is a Layer‑2 scaling solution for Ethereum. Instead of competing with Ethereum, it enhances the network by offering lower fees and faster transaction speeds. Polygon helps applications handle more users without sacrificing security, as explained by Blockchain Council.
Why It Matters
Developers who want Ethereum’s security but want to avoid high gas fees often choose Polygon. It is fully EVM-compatible, meaning existing Ethereum smart contracts can be moved easily without major changes.
Polygon has grown into its own ecosystem, including DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, and consumer Web3 applications. This makes it easier for developers to build and integrate new projects.
Best Use Cases
Polygon is ideal for projects that need fast, low-cost, and Ethereum-compatible solutions, including:
- Scalable DeFi and NFT platforms
- Consumer applications with high user numbers
- Projects that need Ethereum’s security but lower fees
Considerations
Polygon relies on Ethereum for security. While this ensures stability, it means that transaction finality is still influenced by Ethereum’s performance. Developers need to consider this dependency when designing critical applications.
6. Cardano
Overview
Cardano is a research-driven blockchain that emphasizes security, sustainability, and formal verification. Formal verification mathematically proves smart contracts work as intended, reducing errors and potential exploits.
Cardano uses Plutus, a programming language inspired by functional programming, which focuses on correctness. This makes it ideal for projects that require high trust and reliability, such as finance or governance applications.
Safety and Verification
Formal verification ensures contracts behave as expected before deployment. This minimizes bugs and security risks, which is crucial for applications managing valuable assets or sensitive data. Cardano also uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus model, making it energy-efficient and eco-friendly compared to older proof-of-work networks.
Best Use Cases
Cardano is best suited for projects needing strong security and reliability, including:
- Institutional applications
- Governance and voting systems
- High-assurance smart contracts
Considerations
Cardano’s ecosystem is smaller than Ethereum or Solana, meaning fewer ready-to-use tools and applications. However, its research-driven approach and long-term focus on security appeal to developers who prioritize stability and trust.
Overall, Cardano provides a secure, sustainable, and reliable environment for smart contracts, making it a strong choice for high-trust applications and projects requiring mathematical verification and long-term reliability.
7. Ethereum Layer‑2 Networks (Arbitrum and Base)
Overview
Layer‑2 networks are built on top of Ethereum to improve scalability and reduce transaction costs. Two of the most popular Layer‑2 solutions in 2026 are Arbitrum and Base. These networks handle transactions off the main Ethereum chain while keeping Ethereum’s security intact.
Why Layer‑2 Matters
Layer‑2 networks are essential for scaling Ethereum. They allow developers to deploy smart contracts with much lower fees and faster transaction speeds. Because they are EVM-compatible, existing Ethereum contracts can be used with minimal changes, saving time and effort.
Layer‑2 solutions also reduce congestion on Ethereum’s main chain, improving user experience for high-traffic applications. This makes Layer‑2 networks ideal for projects that need to scale efficiently.
Best Use Cases
Ethereum Layer‑2 networks are suitable for applications that require speed, affordability, and security, including:
- High-volume Ethereum decentralized applications (dApps)
- Consumer-facing Web3 products with many users
- DeFi applications that need low fees and fast execution
Considerations
Layer‑2 networks depend on Ethereum’s main network. If Ethereum experiences delays or issues, Layer‑2 solutions can also be affected. Despite this dependency, they remain among the most secure and reliable scaling options for developers.
Overall, Ethereum Layer‑2 networks like Arbitrum and Base provide a practical solution for projects that want Ethereum’s security combined with faster, cheaper, and scalable smart contract deployment in 2026.
Summary Table – Best Smart Contract Blockchains in 2026
The table below shows the top smart contract blockchains in 2026, comparing their security, speed, cost, and ecosystem. It helps developers quickly see which platform fits their project needs.
| Platform | Security | Speed | Cost | Ecosystem | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | Very High | Medium | High | Massive | DeFi, DAOs |
| Layer-2s | Very High | High | Low | Growing | Scalable dApps |
| Solana | Medium | Very High | Very Low | Strong | Gaming, Trading |
| Polygon | High | High | Low | Strong | Enterprise |
| BNB Chain | Medium | High | Very Low | Large | Retail DeFi |
| Avalanche | High | High | Low | Growing | Custom chains |
| Cardano | Very High | Medium | Low | Moderate | Secure finance |
| Polkadot | High | Medium | Low | Growing | Interoperability |
| Cosmos | High | High | Low | Modular | App-chains |
How to Choose the Right Smart Contract Platform
Choosing the right smart contract platform is essential for building successful decentralized applications. The platform you pick affects security, cost, speed, and long-term growth. Here are key factors to consider when making your decision.
-
Security vs. Speed
If your project manages high-value assets or sensitive data, security should be your top priority. Smart contract platforms like Ethereum and Cardano offer strong decentralization and verified smart contracts. If speed is more important, Solana or Avalanche may be better choices.
-
Cost and Transaction Fees
Transaction fees can impact user adoption. If your application expects many users or frequent interactions, look for platforms with low and predictable fees such as Polygon, BNB Chain, or Layer-2 Ethereum networks.
-
Developer Tools and Language Support
Consider smart contract platforms that offer good documentation, testing frameworks, and programming language support. EVM-compatible networks like Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, and Polygon allow developers to use Solidity, saving time and effort.
-
Ecosystem and Community
A strong ecosystem provides wallets, oracles, bridges, and integrations. Platforms with large communities offer support, pre-built tools, and partnerships, which reduce development challenges and accelerate adoption.
-
Customization Needs
Some projects may require specific rules or governance models. Platforms like Avalanche with custom subnets provide flexibility for enterprises or regulated applications.
By balancing security, speed, cost, developer support, ecosystem, and customization, you can choose the best smart contract platform for your project. Evaluating your project’s needs first will guide you to the blockchain that aligns with your goals.
Choosing the Right Smart Contract Platform in 2026?
From platform selection to smart contract design and deployment, Nadcab Labs helps businesses and developers identify the best blockchain for their performance, security, and scalability needs.
Final Words
Choosing the right smart contract platform can make or break your blockchain project. Security, speed, cost, developer tools, ecosystem, and customization are all important factors to consider. Ethereum remains the most popular, but alternatives like Solana, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, Cardano, and Ethereum Layer-2 networks each offer unique advantages.
Your choice should depend on your project’s needs, whether it’s fast transactions, low fees, strong security, or specific governance rules. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each platform, you can build smart contracts that are safe, efficient, and scalable.
In 2026, the blockchain landscape offers many opportunities for developers, and picking the right platform is the first step toward creating successful, user-friendly decentralized applications.
Frequently Asked Question: Best Smart Contract Platforms
There is no single blockchain that is best for every smart contract project. Ethereum is the most trusted and widely used platform because it offers strong security and a large developer ecosystem. However, blockchains like Solana, Polygon, and Avalanche are often preferred for faster transactions and lower fees, depending on application needs.
Ethereum is the largest blockchain-based platform for smart contracts in 2026. It has the highest number of developers, decentralized applications, NFTs, and DeFi projects. Most other smart contract blockchains are either compatible with Ethereum or inspired by its technology, showing Ethereum’s long-term dominance in the blockchain ecosystem.
The top smart contract platforms on blockchain in 2026 include Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Cardano, Polkadot, Cosmos, Ethereum Layer-2 networks like Arbitrum and Optimism, and NEAR Protocol. Each platform offers different benefits such as security, scalability, low transaction costs, or cross-chain support.
Solana is considered the fastest smart contract blockchain. It can process thousands of transactions per second while keeping fees extremely low. This high speed makes Solana suitable for real-time use cases like blockchain games, NFT marketplaces, and high-frequency trading platforms where fast execution is very important.
Yes, Solana fully supports smart contracts, which are called programs on its network. These programs are mostly written in the Rust programming language. Solana smart contracts are designed for high performance and low cost, making them popular for DeFi applications, NFTs, and blockchain gaming platforms.
No, all blockchains do not use the same programming languages. Ethereum, Polygon, BNB Chain, and Avalanche mainly use Solidity. Solana uses Rust, while Cardano uses Plutus, which is based on Haskell. Because of this, developers often choose blockchains based on language familiarity.
Yes, smart contracts are the core technology behind NFTs and DeFi. In NFTs, smart contracts control minting, ownership, transfers, and royalty payments. In DeFi, they manage lending, borrowing, trading, staking, and rewards. Without smart contracts, decentralized finance and NFT ecosystems cannot function.
Beginners can build on both Solana and Cardano, but the learning curve is different. Solana is easier for those who know Rust but has a complex structure. Cardano is more difficult because it uses Plutus and advanced logic. Beginners usually find Ethereum or Polygon easier to start with.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.