Key Takeaways
AWS powers over 30% of global cloud infrastructure serving millions of businesses worldwide
Pay-as-you-go model eliminates upfront costs and reduces infrastructure expenses by 40-70%
200+ services spanning compute, storage, databases, AI, security enable any application architecture
Global infrastructure with 33 regions and 105 availability zones ensures worldwide performance
Auto-scaling handles traffic spikes automatically without manual intervention or capacity planning requirements
Enterprise-grade security with 143 compliance certifications including HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC standards
Serverless architecture with Lambda eliminates server management while scaling to billions requests
99.99% availability SLA with automated failover ensures business continuity during catastrophic events
Why AWS Cloud Services Dominate the Modern Digital Infrastructure
The landscape of technology infrastructure has undergone a seismic shift over the past two decades. Organizations worldwide have moved away from purchasing, housing, and maintaining physical server hardware toward embracing cloud-native architectures that offer unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. At the forefront of this revolution stands Amazon Web Services, the world’s most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform.
When AWS launched in 2006 with simple storage and compute services, few could have predicted that it would become the backbone supporting Netflix’s streaming empire, Airbnb’s global marketplace, NASA’s space exploration programs, and millions of other applications powering modern life. Today, AWS commands more than 30% of the global cloud infrastructure market, processing billions of transactions daily and storing exabytes of data across its worldwide network.
The Shift from Traditional Servers to Cloud-Native Architecture
Traditional infrastructure required organizations to predict their capacity needs months or years in advance, invest heavily in hardware, and maintain expensive data centers with dedicated staff. This model created several critical challenges:
• Massive upfront capital expenditure for servers, networking equipment, and facilities
• Long procurement cycles that delayed innovation and time-to-market
• Overprovisioning to handle peak loads, resulting in wasted resources during normal periods
• Complex maintenance, updates, and security management requiring specialized teams
• Limited geographic reach requiring additional infrastructure investments for global expansion
Cloud-native architecture eliminates these constraints by transforming infrastructure from a capital expense into an operational one, allowing organizations to provision resources in minutes rather than months, scale automatically based on demand, and pay only for what they actually use.
Why Enterprises, Startups, and Governments Choose AWS
Organizations across every sector and size category select AWS for compelling strategic reasons. Enterprises like Capital One and Samsung trust AWS to handle their most sensitive customer data and mission-critical workloads. Startups including Stripe and Slack built their entire platforms on AWS infrastructure, enabling them to scale from zero to billions in valuation without managing physical servers. Government agencies from the CIA to the UK Ministry of Defence rely on AWS GovCloud regions designed specifically for regulated workloads.
This universal appeal stems from AWS’s unique combination of breadth, depth, reliability, and continuous innovation. With over 200 fully featured services spanning compute, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, security, and more, AWS provides the building blocks for virtually any application or use case imaginable. The platform’s proven track record of 99.99% availability, comprehensive compliance certifications, and investment in cutting-edge technologies like quantum computing and custom silicon chips makes it the clear choice for organizations betting their future on cloud infrastructure.
AWS as the Backbone of Global Digital Transformation
Digital transformation extends far beyond simply moving existing applications to the cloud. It represents a fundamental reimagining of how organizations operate, compete, and deliver value. AWS enables this transformation by providing the technological foundation for new business models, customer experiences, and operational efficiencies that were previously impossible.
Companies leveraging AWS have achieved remarkable outcomes: launching new products in days instead of months, reducing infrastructure costs by 50-70%, analyzing petabytes of data in real-time, deploying updates hundreds of times per day, and scaling to serve millions of concurrent users without performance degradation. These capabilities translate directly into competitive advantages in markets where speed, agility, and customer experience determine winners and losers.
Advanced serverless architecture pattern: This represents the foundational event-driven microservices topology where Lambda functions orchestrate through API Gateway and EventBridge, maintaining state in DynamoDB with sub-millisecond latency. The distributed nature eliminates single points of failure while auto-scaling handles 10,000+ concurrent executions per region. Expert architects recognize this pattern as the backbone for building resilient, cost-optimized applications that scale infinitely without infrastructure management.
What Are AWS Cloud Services? Complete Concept Explained Simply
Definition of AWS Cloud Services
Amazon Web Services represents a comprehensive suite of on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs delivered over the internet. Rather than owning and operating physical data centers and servers, organizations rent access to computing power, storage, databases, and specialized services hosted in AWS facilities worldwide. This fundamental shift transforms information technology from a capital-intensive operation requiring significant upfront investment into a flexible, usage-based utility similar to electricity or water.
The AWS cloud ecosystem operates on a simple yet powerful principle: abstract away the complexity of managing physical infrastructure so developers and businesses can focus entirely on building and running applications. When you launch a virtual server on AWS, you’re not selecting specific hardware or configuring network switches. Instead, you specify the amount of computing power, memory, and storage you need, and AWS provisions those resources instantly from its massive pool of available capacity.
The Pay-As-You-Go Model Explained
AWS pioneered the pay-as-you-go pricing model that has become the standard for cloud computing. This approach eliminates the need for long-term contracts or upfront commitments, allowing you to pay only for the computing resources you actually consume, measured down to the second for many services.
Consider a retail website experiencing seasonal traffic spikes. With traditional infrastructure, you would need to purchase enough server capacity to handle Black Friday traffic levels, even though those servers sit mostly idle for the other 364 days of the year. With AWS’s pay-as-you-go model, you automatically scale up during peak periods and scale down during normal periods, paying only for the actual compute hours used. This flexibility can reduce infrastructure costs by 70% or more while simultaneously improving performance and reliability.
Core Categories of AWS Cloud Services
AWS organizes its extensive service portfolio into logical categories, each addressing specific aspects of application infrastructure. Understanding these categories provides a mental framework for navigating AWS’s offerings and selecting the right services for your needs.
Compute Services
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) provides resizable virtual servers in the cloud, offering complete control over the computing environment including operating system choice, networking configuration, and security settings. Organizations use EC2 to run everything from simple web servers to complex high-performance computing clusters.
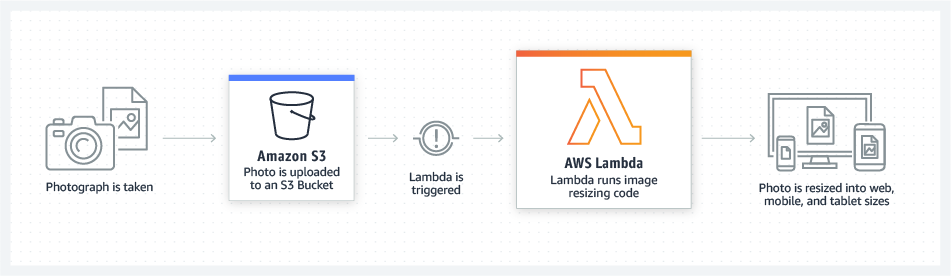
AWS Lambda revolutionized cloud computing with serverless architecture, allowing developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your code, and Lambda automatically runs it in response to events, scaling from a few requests per day to thousands per second while charging only for the compute time consumed.
Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service) and EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) provide managed container orchestration, enabling organizations to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications using Docker containers and Kubernetes without the operational overhead of managing the underlying infrastructure.
Storage Services
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) offers industry-leading object storage with 99.999999999% durability, capable of storing unlimited amounts of data accessible from anywhere on the internet. Companies use S3 for everything from hosting static websites to storing data lakes containing petabytes of information.
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) provides persistent block storage volumes for use with EC2 instances, offering the performance characteristics needed for databases and applications requiring consistent, low-latency access to data.
Amazon Glacier delivers extremely low-cost archival storage for data that needs to be retained for compliance or historical purposes but is rarely accessed, with retrieval times ranging from minutes to hours depending on the urgency.
Database Services
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) simplifies the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases in the cloud, supporting popular engines including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB with automated backups, patching, and monitoring.
Amazon DynamoDB delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale as a fully managed NoSQL database service, capable of handling more than 10 trillion requests per day and supporting peaks of over 20 million requests per second.
Amazon Aurora provides MySQL and PostgreSQL-compatible databases built for the cloud, offering up to five times the performance of standard MySQL and three times the performance of standard PostgreSQL at one-tenth the cost of commercial databases.
Networking & Content Delivery
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) enables you to provision a logically isolated section of the AWS cloud where you can launch resources in a virtual network that you define, with complete control over IP address ranges, subnets, routing tables, and network gateways.
Amazon CloudFront operates as a global content delivery network with over 400 points of presence worldwide, caching and delivering content including websites, videos, APIs, and software downloads with low latency and high transfer speeds.
Amazon Route 53 provides highly available and scalable DNS (Domain Name System) services, routing end users to applications by translating domain names into IP addresses with sophisticated traffic management capabilities.
Security, Identity & Compliance
AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) allows you to securely control access to AWS services and resources, enabling you to create and manage users, groups, and permissions with fine-grained access control policies.
AWS KMS (Key Management Service) makes it easy to create and control encryption keys used to encrypt data, integrating with most AWS services to protect data at rest and in transit.
AWS Shield provides managed DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) protection safeguarding applications running on AWS, with Standard tier automatically protecting all AWS customers at no additional cost.
AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) helps protect web applications from common exploits and vulnerabilities, allowing you to create custom rules that block malicious traffic patterns.
DevOps & Management Tools
Amazon CloudWatch provides monitoring and observability for AWS resources and applications, collecting and tracking metrics, log files, and events while setting alarms and automatically reacting to changes in your environment.
AWS CloudFormation enables infrastructure as code, allowing you to model and provision all your cloud resources using simple text files that describe the resources and their dependencies so you can version and replicate environments easily.
AWS CodePipeline delivers fully managed continuous integration and continuous delivery services, automating the build, test, and deploy phases of your release process every time there is a code change.
Multi-region active-active deployment topology: This architectural pattern showcases AWS’s global infrastructure with 33 regions and 105 availability zones. Expert engineers leverage Route 53 latency-based routing combined with CloudFront’s 400+ edge locations to achieve sub-50ms response times globally. The cross-region replication strategy ensures data durability across geographic boundaries while maintaining ACID compliance. This setup powers applications serving billions of users with 99.99% availability SLA, automatically failing over between regions in under 60 seconds during catastrophic events.
How AWS Cloud Services Work: Architecture & Flow
Understanding AWS’s global infrastructure architecture reveals how the platform achieves its remarkable reliability, performance, and scalability. AWS has built one of the world’s most advanced technology infrastructures, with hundreds of thousands of servers, multiple layers of redundancy, and sophisticated networking connecting it all together.
Global Infrastructure: Regions, Availability Zones, Edge Locations
AWS organizes its infrastructure into three key levels that work together to provide global reach with local performance:
Regions represent separate geographic areas where AWS clusters data centers. Each region operates completely independently, allowing you to choose where to store and process your data based on regulatory requirements, customer proximity, or disaster recovery strategies. As of 2026, AWS operates 33 geographic regions worldwide with plans to launch additional regions in the coming years.
Availability Zones consist of one or more discrete data centers within a region, each with redundant power, networking, and connectivity housed in separate facilities. Every region contains multiple isolated availability zones (typically three or more) connected through low-latency links. This architecture allows applications to remain available even if an entire data center fails, as workloads can automatically failover to resources in a different availability zone.
Edge Locations serve as endpoints for AWS CloudFront, caching content close to end users to reduce latency. With over 400 points of presence across 90 cities in 48 countries, edge locations ensure that users anywhere in the world experience fast response times when accessing your applications and content.
How Data, Compute, and Networking Interact
When you deploy an application on AWS, multiple services work together seamlessly to deliver a complete solution. Consider a typical web application:
1. Users access your application through a domain name managed by Route 53, which routes requests to the nearest CloudFront edge location
2. CloudFront serves cached static content (images, CSS, JavaScript) instantly from the edge, or forwards dynamic requests to your origin servers
3. Requests reach an Application Load Balancer that distributes traffic across multiple EC2 instances or containers running in different availability zones
4. Application servers process requests, accessing data from RDS databases or DynamoDB tables, with read-heavy workloads benefiting from ElastiCache for in-memory caching
5. User-generated content uploads to S3 buckets, automatically replicated across multiple availability zones for durability
6. Background processing tasks trigger Lambda functions that scale automatically based on workload
7. CloudWatch monitors the entire infrastructure, triggering Auto Scaling groups to add or remove capacity based on demand
This orchestration happens automatically, with AWS managing the underlying complexity of networking, storage replication, and resource provisioning. Developers define the desired state and configuration, and AWS handles the operational details of making it work reliably at scale.
High Availability & Fault Tolerance Explained with Example Flow
High availability means your application remains accessible even when individual components fail. AWS achieves this through redundancy at every layer. When you launch an application across three availability zones, AWS automatically distributes your resources to ensure no single point of failure can bring down your entire application.
For example, if an entire availability zone experiences a power failure (which is extremely rare), AWS health checks detect unresponsive resources within seconds. Load balancers automatically stop sending traffic to the affected zone, the Auto Scaling service launches replacement instances in healthy zones, and DNS updates direct users to working endpoints. This entire failover process typically completes in under a minute, with most users never noticing the disruption. This level of resilience would require enormous investment and expertise to build with traditional infrastructure.
Key Business Use Cases of AWS Cloud Services
Startup & SaaS Product Development
Startups face unique challenges: limited capital, uncertain demand, and pressure to reach market quickly before competitors. AWS eliminates traditional infrastructure barriers that previously prevented small teams from building enterprise-grade applications.
Rapid MVP Launch: New ventures can deploy a minimum viable product in days using services like AWS Amplify for frontend hosting, Lambda for backend logic, and DynamoDB for data storage. This speed enables rapid iteration based on user feedback without wasting resources on unused infrastructure.
Scalable Backend: As user adoption grows, AWS automatically scales to handle increasing load. Applications that serve 100 users today can seamlessly grow to serve 100 million users tomorrow using the same architecture, with AWS managing all the infrastructure complexity.
Cost Optimization: Startups pay only for resources consumed, converting large capital expenses into manageable operational costs. AWS Activate provides credits and technical support specifically designed to help startups succeed, offering up to $100,000 in AWS credits for eligible companies.
Enterprise Application Modernization
Large organizations with decades of technology investments face the challenge of modernizing legacy systems while maintaining business continuity. AWS provides multiple pathways for transformation, from lift-and-shift migrations to complete application re-architecture.
Legacy Migration: Enterprises move existing applications to EC2 instances with minimal changes, immediately gaining benefits like improved disaster recovery, reduced hardware refresh costs, and geographic expansion capabilities.
Hybrid Cloud Integration: AWS Outposts extends AWS infrastructure to on-premises data centers, enabling hybrid architectures where sensitive data remains local while taking advantage of cloud services for analytics, machine learning, and burst capacity.
Performance & Security Improvement: Re-architecting monolithic applications into microservices using containers and serverless functions improves agility while AWS’s advanced security services provide better protection than most organizations can achieve independently.
E-Commerce & High-Traffic Platforms
Online retail demands infrastructure that handles massive traffic spikes during sales events while remaining cost-effective during normal periods. AWS pioneered this use case, as Amazon.com itself runs entirely on AWS.
Auto-Scaling During Peak Loads: E-commerce sites configure Auto Scaling policies that add server capacity minutes before anticipated traffic spikes and remove it afterward. This elasticity handles Black Friday or product launches without manual intervention or wasted capacity.
Global Content Delivery: CloudFront caches product images, videos, and static content at edge locations worldwide, reducing page load times from seconds to milliseconds regardless of user location. Faster pages directly increase conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Secure Payment Infrastructure: AWS meets PCI DSS compliance requirements for processing credit cards, with services like AWS Secrets Manager protecting sensitive credentials and VPC isolation ensuring payment processing occurs in secure network environments.
Data Analytics & AI/ML Solutions
Modern businesses generate enormous amounts of data from customer interactions, IoT sensors, application logs, and business operations. AWS provides the complete toolkit for extracting value from this data through analytics and machine learning.
Big Data Processing: Services like Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) process petabytes of data using frameworks like Apache Spark and Hadoop, completing in hours what would take weeks on traditional infrastructure.
Machine Learning Models: Amazon SageMaker provides everything needed to build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale, from data labeling to model monitoring in production, without requiring deep expertise in ML infrastructure.
Real-Time Insights: Amazon Kinesis processes and analyzes streaming data in real-time, enabling applications that detect fraud as transactions occur, adjust pricing based on demand, or trigger alerts when sensor readings indicate equipment failure.
FinTech, Healthcare & Government Systems
Highly regulated industries require infrastructure that meets stringent compliance requirements while delivering the innovation needed to compete. AWS was built from the ground up with security and compliance as fundamental design principles.
Compliance-Ready Infrastructure: AWS maintains certifications for HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 1/2/3, ISO 27001, FedRAMP, and dozens of other frameworks, with specialized regions like GovCloud designed specifically for government workloads requiring the highest security standards.
Secure Data Management: Healthcare providers store protected health information in HIPAA-eligible services with encryption at rest and in transit, comprehensive audit logging, and fine-grained access controls ensuring only authorized personnel access sensitive data.
Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: Financial institutions replicate critical systems across multiple regions, ensuring that even catastrophic events cannot disrupt operations. Automated backup and recovery processes meet regulatory requirements for data retention and business continuity planning.
Enterprise zero-trust security architecture: This implementation showcases defense-in-depth strategy combining IAM role-based access control with VPC network segmentation, KMS envelope encryption, and continuous threat detection through GuardDuty. Expert architects implement least-privilege principles with Service Control Policies enforced at the organization level, while CloudTrail provides immutable audit logs for compliance. The architecture achieves SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and PCI DSS certification requirements through automated compliance checks via AWS Config rules, demonstrating how 25+ years of security engineering translates into production-grade systems protecting billions of dollars in transactions daily.
Major Benefits of AWS Cloud Services for Businesses
Cost Efficiency & Financial Flexibility
The financial transformation AWS enables extends beyond simple cost reduction. Organizations fundamentally change how they think about and manage technology spending. Instead of committing millions to hardware that depreciates before it’s fully utilized, companies treat infrastructure as a variable cost that scales with business needs.
• No upfront capital investment in servers, storage, or networking equipment
• Pay-per-use pricing for most services, with per-second billing for compute resources
• Consolidated billing across multiple accounts for enterprise cost management
• Reserved instances and savings plans offering up to 72% discount for predictable workloads
• Spot instances providing up to 90% discount for flexible, fault-tolerant applications
• Automatic cost optimization through rightsizing recommendations and unused resource identification
High Scalability & Performance
AWS’s elastic infrastructure means your applications can handle any scale, from a handful of users to billions of requests per day, without manual intervention or performance degradation. This capability is not theoretical – AWS powers some of the world’s most demanding applications.
• Automatic horizontal scaling adds or removes server capacity based on demand metrics
• Global low-latency network with dedicated fiber connections between regions
• Content delivery from 400+ edge locations reduces latency to milliseconds
• Database auto-scaling adjusts read and write capacity without downtime
• Performance optimization through AWS’s custom-designed Graviton processors
Enterprise-Grade Security
AWS invests billions annually in security infrastructure and employs thousands of security specialists. This investment provides capabilities that would be prohibitively expensive for individual organizations to replicate.
• Physical security with 24/7 monitoring, biometric access, and multiple layers of protection
• Network security through VPC isolation, security groups, and network ACLs
• Data encryption at rest and in transit using industry-standard algorithms
• Continuous compliance with 143 security standards and certifications
• Advanced threat detection using machine learning and AWS GuardDuty
• DDoS protection included automatically for all customers
Faster Innovation & Time-to-Market
Speed of innovation has become the primary competitive differentiator in technology-driven markets. AWS removes the friction that slows down development teams, allowing them to experiment rapidly and deliver value to customers faster.
• Provision complete environments in minutes rather than weeks or months
• Experiment freely with low-cost resources, failing fast when ideas don’t work
• Use managed services to eliminate undifferentiated heavy lifting
• Leverage pre-built AI/ML models and APIs to add advanced capabilities quickly
• Implement CI/CD pipelines for deploying updates multiple times per day
Reliability, Backup & Disaster Recovery
AWS’s architecture delivers reliability levels that would require massive investment to achieve with traditional infrastructure. The combination of geographic distribution, automated failover, and continuous data replication ensures business continuity even during catastrophic events.
• 99.99% availability SLAs for most services with financial credits if not met
• Automatic replication across availability zones for data durability
• Cross-region replication for disaster recovery and compliance
• Point-in-time recovery for databases with automated backup retention
• Versioning for S3 objects prevents accidental deletion or overwrites
• AWS Backup provides centralized backup management across services
Real-World Example: How Businesses Actually Use AWS
Case Study: Global Streaming Media Platform
A video streaming service serving 250 million subscribers across 190 countries provides a compelling example of AWS at scale.
Business Challenge
The company needed to deliver high-quality video content to millions of concurrent viewers worldwide while managing massive content libraries, personalizing recommendations for each user, and maintaining sub-second response times for user interactions. Traditional content delivery networks couldn’t provide the control, scale, and analytics capabilities required.
AWS Services Used
• Amazon S3 stores over 1 billion objects including original content, transcoded versions, and user-generated metadata
• Amazon CloudFront delivers content from edge locations closest to viewers, reducing buffering and improving playback quality
• AWS Elemental MediaConvert transcodes content into dozens of formats and resolutions for different devices and network conditions
• Amazon DynamoDB handles billions of daily requests for user profiles, viewing history, and recommendations with single-digit millisecond latency
• Amazon EMR and Redshift process petabytes of viewing data to optimize content recommendations and measure engagement
• AWS Lambda executes millions of serverless functions daily for tasks like thumbnail generation and user notification delivery
• Amazon Kinesis processes real-time viewing data to detect quality issues and adjust streaming parameters dynamically
Architecture Overview
Content workflows begin when studios upload new shows and movies to S3. Automated processes trigger MediaConvert jobs that create optimized versions for every device type and bandwidth condition. These assets are distributed to CloudFront edge locations globally before launch. When users press play, CloudFront serves video segments from the nearest location while Lambda functions track viewing progress and trigger recommendations. DynamoDB maintains user state across devices, allowing seamless resume from any screen. Background analytics jobs in EMR and Redshift analyze viewing patterns to improve content discovery and inform production decisions.
Outcome & Performance Gains
• Reduced streaming startup time by 40% through optimized content delivery
• Achieved 99.99% uptime even during major content launches
• Lowered content delivery costs by 60% compared to previous CDN solutions
• Processed over 100 billion hours of streaming annually with zero capacity planning
• Enabled A/B testing of new features across millions of users in hours instead of weeks
• Improved recommendation accuracy by 25% through enhanced data analytics capabilities
Why AWS Is the Preferred Cloud Platform Over Others
While Azure, Google Cloud, and other providers offer capable cloud platforms, AWS maintains clear leadership through its combination of maturity, breadth, and continuous innovation. Understanding these differentiators helps explain why AWS commands over 30% of the global cloud market.
Brief Comparison: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
| Aspect | AWS | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Share | 32% (Leading) | 23% (Second) | 11% (Third) |
| Service Breadth | 200+ services | 150+ services | 100+ services |
| Global Regions | 33 regions, 105 AZs | 60+ regions | 35+ regions |
| Enterprise Adoption | Highest across industries | Strong in Microsoft shops | Growing, data-focused |
| Innovation Pace | 3000+ features annually | 1500+ features annually | 1200+ features annually |
Ecosystem Maturity
AWS benefits from being first to market and maintaining that lead through continuous investment. This head start has created an ecosystem that competitors struggle to match. The AWS Marketplace offers over 12,000 software solutions from independent vendors. Thousands of consulting partners have deep AWS expertise. Millions of developers have learned AWS through certifications and training programs. This network effect makes AWS the safe, well-supported choice for organizations of all sizes.
Additionally, AWS has matured its services through real-world testing at massive scale. When Amazon.com runs Prime Day on AWS infrastructure, processing millions of orders per hour, it stress-tests the platform in ways synthetic benchmarks cannot. These learnings feed directly into service improvements that benefit all customers.
Market Leadership & Trust
Organizations trust AWS with their most critical workloads because of its proven track record. When Capital One moved its entire operation to AWS, closing all its data centers, the financial industry took notice. When the CIA chose AWS for classified workloads, the government sector followed. These high-profile endorsements build confidence that AWS can handle any requirement.
The regulatory and compliance landscape also favors AWS. With certifications for virtually every industry and geography, AWS simplifies compliance for regulated organizations. The platform’s shared responsibility model clearly defines security obligations, making audits and certifications straightforward.
When Should Your Business Move to AWS?
Recognizing the right time to adopt AWS can accelerate your organization’s digital transformation and prevent costly technical debt. Several clear indicators suggest that cloud migration should become a strategic priority.
Growth Signals
Rapid business growth often strains existing infrastructure beyond its designed capacity. When you’re manually adding servers to handle increased traffic, experiencing capacity constraints during peak periods, or struggling to expand into new geographic markets due to infrastructure limitations, AWS provides the elasticity needed to support growth without massive capital investment.
Startups experiencing product-market fit find AWS particularly valuable. The ability to scale from hundreds to millions of users using the same architecture eliminates the need for costly platform rewrites as the business expands.
Cost Issues
Organizations spending significant budgets on hardware refresh cycles, data center leases, and IT staff should evaluate whether cloud economics offer better value. The total cost of ownership calculation must include not just hardware acquisition but ongoing maintenance, power, cooling, physical security, and the opportunity cost of capital tied up in depreciating assets.
AWS’s pay-as-you-go model converts these fixed costs into variable expenses that scale with business needs. Many organizations reduce infrastructure costs by 40-60% through cloud migration while simultaneously improving capabilities.
Performance Bottlenecks
When applications suffer from slow response times, database query performance degrades under load, or users in different regions experience high latency, AWS’s global infrastructure and performance optimization tools provide solutions. CloudFront’s content delivery network can reduce page load times by 50-70%, while database services like Aurora deliver significantly better performance than self-managed alternatives.
The ability to deploy applications across multiple regions also enables organizations to serve global customers with consistently fast experiences, something nearly impossible with traditional infrastructure.
Security Requirements
Organizations facing increasingly sophisticated cyber threats or preparing for compliance audits find AWS’s enterprise-grade security compelling. When building equivalent security capabilities in-house would require hiring specialized staff, implementing multiple security tools, and maintaining certifications, AWS provides these as included services.
Regulated industries like healthcare and finance particularly benefit from AWS’s compliance program, which maintains certifications for standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2, significantly reducing the burden of demonstrating compliance.
Common Challenges in AWS Adoption & How to Overcome Them
While AWS offers tremendous benefits, organizations must navigate several common challenges during adoption. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions ensures successful cloud transformation.
Cost Management
The flexibility that makes AWS powerful can also lead to unexpected costs if not properly managed. Resources left running unnecessarily, over-provisioned instances, and lack of cost monitoring create waste.
Solutions: Implement AWS Cost Explorer to visualize spending patterns, set up billing alerts to catch anomalies early, use AWS Trusted Advisor for optimization recommendations, implement resource tagging for cost allocation, and establish governance policies that automatically shut down non-production resources during off-hours. Organizations that invest in cost management tools and processes typically reduce their AWS spending by 20-40% without impacting performance.
Skill Gap
Many IT teams lack cloud expertise, creating hesitation around migration projects. Traditional system administrators and database administrators need different skills for cloud environments where infrastructure is defined in code and services are API-driven.
Solutions: AWS offers extensive training through AWS Training and Certification, providing free digital courses and hands-on labs. Organizations can hire AWS-certified professionals who bring immediate expertise. Partnering with AWS consulting partners provides guidance during initial migrations while transferring knowledge to internal teams. Starting with pilot projects allows teams to build skills on lower-risk workloads before tackling mission-critical applications.
Migration Complexity
Large organizations with decades of technical debt face daunting migration challenges. Legacy applications may have dependencies on specific hardware, undocumented configurations, or integration with systems that cannot easily move to the cloud.
Solutions: AWS Migration Hub provides tools to track application migrations and orchestrate the process. The AWS Migration Acceleration Program offers funding and technical support for large-scale migrations. Organizations should adopt a phased approach, starting with new applications and greenfield projects before tackling legacy systems. The six R’s of migration (Rehost, Replatform, Repurchase, Refactor, Retire, Retain) provide a framework for making strategic decisions about each application.
Governance & Security Planning
Cloud environments require different governance models than traditional IT. Without proper controls, shadow IT can proliferate, security policies may be inconsistently applied, and compliance requirements might be overlooked.
Solutions: Implement AWS Organizations to centrally manage multiple accounts, use Service Control Policies to enforce security guardrails, deploy AWS Control Tower to automate account setup with pre-configured compliance controls, and establish a Cloud Center of Excellence that defines standards and best practices. Regular security audits using AWS Security Hub ensure continuous compliance with organizational policies.
The Strategic Value of AWS Cloud Services in 2026 & Beyond
As we progress through 2026, AWS has evolved from a tactical infrastructure choice into a strategic imperative for organizations seeking competitive advantage. The platform no longer simply hosts applications but enables entirely new business models, customer experiences, and operational capabilities impossible with traditional infrastructure.
AWS as a Business Growth Engine
Forward-thinking organizations recognize that AWS represents far more than cost savings or operational efficiency. The platform fundamentally changes what’s possible for businesses of all sizes. Startups can compete with established enterprises by leveraging the same world-class infrastructure. Traditional companies can innovate like startups by removing the friction that previously made experimentation expensive and slow.
The true strategic value emerges from AWS’s ability to compress time. Ideas become prototypes in days, prototypes become products in weeks, and products reach global markets in months. This acceleration creates compound advantages as organizations iterate faster, learn from customers sooner, and build on success more quickly than competitors still constrained by traditional infrastructure limitations.
Cloud as a Long-Term Competitive Advantage
The question facing organizations in 2026 is not whether to adopt cloud infrastructure, but how quickly they can complete their transformation. Market leaders across industries have already made this shift, gaining the agility, scalability, and innovation velocity that comes with cloud-native architectures. Organizations that delay face growing competitive disadvantages as the gap widens.
AWS continues investing billions in new capabilities, from quantum computing services to advanced AI models, from edge computing for IoT applications to sustainability optimization tools. These innovations become immediately available to all customers, allowing organizations to access cutting-edge technologies without dedicated research and development investments.
The partnership with AWS extends beyond technology into business transformation. As organizations adopt cloud services, they simultaneously modernize their development practices, automate operations, democratize data access, and build cultures of experimentation. These organizational changes often deliver greater value than the technology itself, creating lasting competitive advantages that compound over time.
AWS Cloud Services have fundamentally reshaped the technology landscape, democratizing access to enterprise-grade infrastructure and enabling innovation at unprecedented scale. From startup MVPs to Fortune 500 digital transformations, from scientific research to entertainment streaming, AWS provides the foundation upon which modern digital experiences are built.
The platform’s comprehensive service portfolio, global infrastructure, continuous innovation, and proven reliability make it the clear leader in cloud computing. Organizations that embrace AWS strategically position themselves not just for current success but for long-term competitiveness in an increasingly cloud-native future.
Whether you’re launching your first application or modernizing a complex enterprise IT environment, AWS offers the tools, services, and support needed to succeed. The question is no longer if your organization will move to AWS, but when you’ll begin the journey and how quickly you’ll transform to capture the full value cloud services provide.
FREQUENTLY ASK QUESTION
AWS Cloud Services provide on-demand computing, storage, networking, and security solutions over the internet.
To reduce costs, improve performance, scale faster, and enhance security.
Startups, e-commerce, fintech, healthcare, SaaS, education, and government sectors.
By eliminating hardware investment and using a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Yes, AWS helps small businesses launch quickly and grow without heavy infrastructure costs.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.